Custodial violence primarily refers to violence in police custody and judicial custody. Custodial violence, which includes torture, death and other excesses in police custody or prison.
Police Reforms against Custodial Violence in India is always a point of debate whenever any issue concerning the same makes the headlines or otherwise too. Read about Police Reforms in India in the linked article.
In 2020, the Supreme Court asked the Government’s response pertaining to the implementation of Section 176(1A) of the CrPc, which calls for mandatory judicial inquiry related to incidents of deaths, disappearance, rape, etc. in judicial custody.
Discussed further below in this article are the causes, cases and laws for custodial violence in India. IAS Exam aspirants must refer to the information given further below as questions based on the same may be asked in the upcoming Civil Services Exam under the General Studies-2 paper or is related to GS 4 case studies.
Custodial Violence [UPSC Notes]:-Download PDF Here
| Preparing for the upcoming IAS Exam?? Test how prepared you are with the UPSC Previous Year Question Papers! Also, complement your preparation with the links given below: |
Custodial Violence – Key Points
- Custodial violence is the violence that takes place in judicial and police custody where an individual who has done a crime is tortured mentally or physically
- Most of the custodial deaths were attributed to reasons other than custodial torture, which included suicide and death in hospitals during treatment
- One of the biggest issues with custodial violence is that it has put human rights at stake. This crime is an outburst against humanity and is one of the many root obstacles in a Democratic country
- Although, overcrowding, malnutrition, unhygienic conditions and lack of medical care are some of the factors of death in police and judicial custody, but custodial violence remains the common cause of deaths in prisons and lock-ups
- Many human rights activists and social workers have found that the worst violations of human rights take place during the course of an investigation when the police, with a view to securing evidence or confessions, often resort to third-degree methods including torture and techniques of arrests by either not recording them or describing the deprivation of liberty merely as “prolonged interrogations”
Any case of custodial violence is reported to the National Human Rights Commission in India. To know more about the objectives, significance and roles of NHRC, candidates can visit the linked article.
Types of Custodial Violence
There are different types of custodial violence. Discussed below are the same:
- Physical Violence
- Through physical force or bashing which may lead to the exhaustion and fear of death
- Psychological Violence
- Not providing correct information and mentally torturing them. This may also be done through humiliation and threats
- Sexual Violence
- This may include verbal sexual abuse and humiliation of one’s dignity. This may leave a long-lasting psychological impact on the victim
Custodial Violence in India
Custodial Violence in India has been a major human rights issue for decades now. It is one of the root obstacles to democracy and the development of human well being. According to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, between 2001 and 2018, only 26 policemen were convicted of custodial violence despite 1,727 such deaths being recorded in India.
Given below is the data released by the National Human Resources Commission for the month of April 2021 in regard to the complaints registered for custodial violence:
| Nature of Incidents | No. of cases Registered | Disposed | Pending |
| CUSTODIAL DEATH (POLICE) (Inc. Code 807) | 13 | 8 | 301 |
| CUSTODIAL DEATH (JUDICIAL) (Inc. Code 301) | 178 | 151 | 3029 |
The International Human Rights Day on 10th December annually marks the occasion of the signing of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948. Candidates can read in detail about the significance of this day at the linked article.
Statistics on Custodial and Judicial Violence in India
- Between 2015-2019, 36% of deaths by suicide in police custody have been reported
- 2014 onwards, physical assault by police has been recorded in only 6% of the cases
- In the last 10 years, 403 of 1,004 deaths (40%) in police custody are listed as due to “Hospitalisation/ Illness/ Natural deaths” – a majority of such deaths
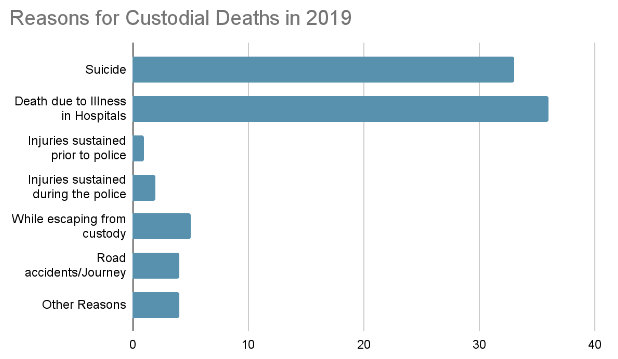
- As per the Crime in Indian Report 2019 released by the National Crime Records Bureau, the following have been the major reasons for custodial deaths in 2019:
Legal Provisions for Custodial Violence in India
The following provisions were enacted to curb the tendency of policemen to resort to torture to extract confessions, etc.:
- Sections 330, 331 & 348 of Indian Penal Code (IPC)
- Sections 25 & 26 of the Indian Evidence Act
- Section 76 of Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) and Section 29 of the Police Act, 1861
Other important constitutional provisions are as follows:
- Protection from torture is a fundamental right enshrined under Article 21 (Right to Life) of the Indian constitution
- Section 41 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) was amended in 2009 to include safeguards under 41A, 41B, 41C and 41D, so that arrests and detentions for interrogation have reasonable grounds and documented procedures, arrests are made transparent to family, friends and public, and there is protection through legal representation
- Article 21 of the Indian Constitution provides that no person shall be deprived of life or personal liberty except according to the procedure established by the law
To know more about the other Important Articles of the Indian Constitution, candidates can visit the linked article.
Causes of Custodial Violence in India
There are multiple reasons which have led to the increased cases of custodial and judicial violence in the country. A few of the most common causes have been discussed below:
- Absence of Strict Laws – It is important that strict and mandatory laws are passed in order to stop custodial violence. In India, custodial violence is yet to be criminalised and an unfair benefit of which has been taken by those in power over the past many decades
- No Solid Prison Reforms – The entire prison system is inherently opaque giving less room for transparency. Prisons in India continue to be affected by poor conditions, overcrowding, acute manpower shortages and minimal safety against harm in prisons
- Work Pressure – The police work under extreme pressure and in cases of a quick solution to complex cases, they choose violence to get evidence and confessions
- Social Factor – Considering the approach of “an eye for an eye”, the people in power choose to use violence to get out information from the ones accused of a crime
- Not following International Standards – India had signed the United Nations Convention against Torture in 1997 but its implications are yet to be mandatorily followed in the country
Limited time for interrogation, pressure from higher authorities and long working hours are few other reasons for custodial violence in the country.

Prohibition of Custodial Violence – The Way Forward
- Proper reforms must be implemented to completely prohibit custodial and judicial violence.
- India should ratify the UN Convention Against Torture as it will mandate a systematic review of the colonial, methods, practices and arrangements for the custody and treatment of persons subjected to arrest, detention or imprisonment
- The police officials must be trained under special guidelines so that any kind of violence can be prevented
- Separate rooms with CCTV cameras installed must be set up in police stations for the purpose of interrogation
- Prison conditions must be in line with human rights requirement
- Implementation of Law Commission of India’s 273rd Report that suggests that those accused of committing custodial torture – be it, policemen, military and paramilitary personnel – should be criminally prosecuted instead of facing mere administrative action establishing an effective deterrent
Custodial Violence [UPSC Notes]:-Download PDF Here
Frequently Asked Questions about Custodial Violence
What is custodial violence?
What is the reason behind custodial violence in India?
Reason behind custodial violence is as follows:
- Absence of Strong Legislation: India does not have an anti-torture legislation and is yet to criminalise custodial violence, while action against culpable officials remains illusory.
- The Indian state either denies the existence of torture in the country or defends its resistance to enact a law by claiming there are sufficient provisions in the domestic legal framework to prohibit and penalise torture.
- These claims however remain superficial and without any such protections.
IAS Exam aspirants can get updated with the latest UPSC Syllabus for the prelims and mains examination at the linked article and start their preparation accordingly.
For the latest exam updates and study material, turn to BYJU’S for assistance.

Comments