Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “Electrochemistry”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams, during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S, for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for Electrochemistry
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
Electrochemistry |
NEET Exams |
|
Electrochemistry |
|
|
Galvanic Cell |
Converts the chemical energy released during redox reaction into electrical energy E.g. Daniell cell Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) |
|
Cell Electromotive Force (emf) |
The potential difference between the two electrodes of a galvanic cell, i.e. of the cathode and anode. Cathode – reduction (right) Anode – oxidation (left) Ecell = Eright – Eleft |
|
Nernst Equation |
For the electrode reaction: Mn+(aq) + ne– → M(s) E(Mn+/M) = E⊖(Mn+/M) – RT/nF ln 1/[Mn+] |
|
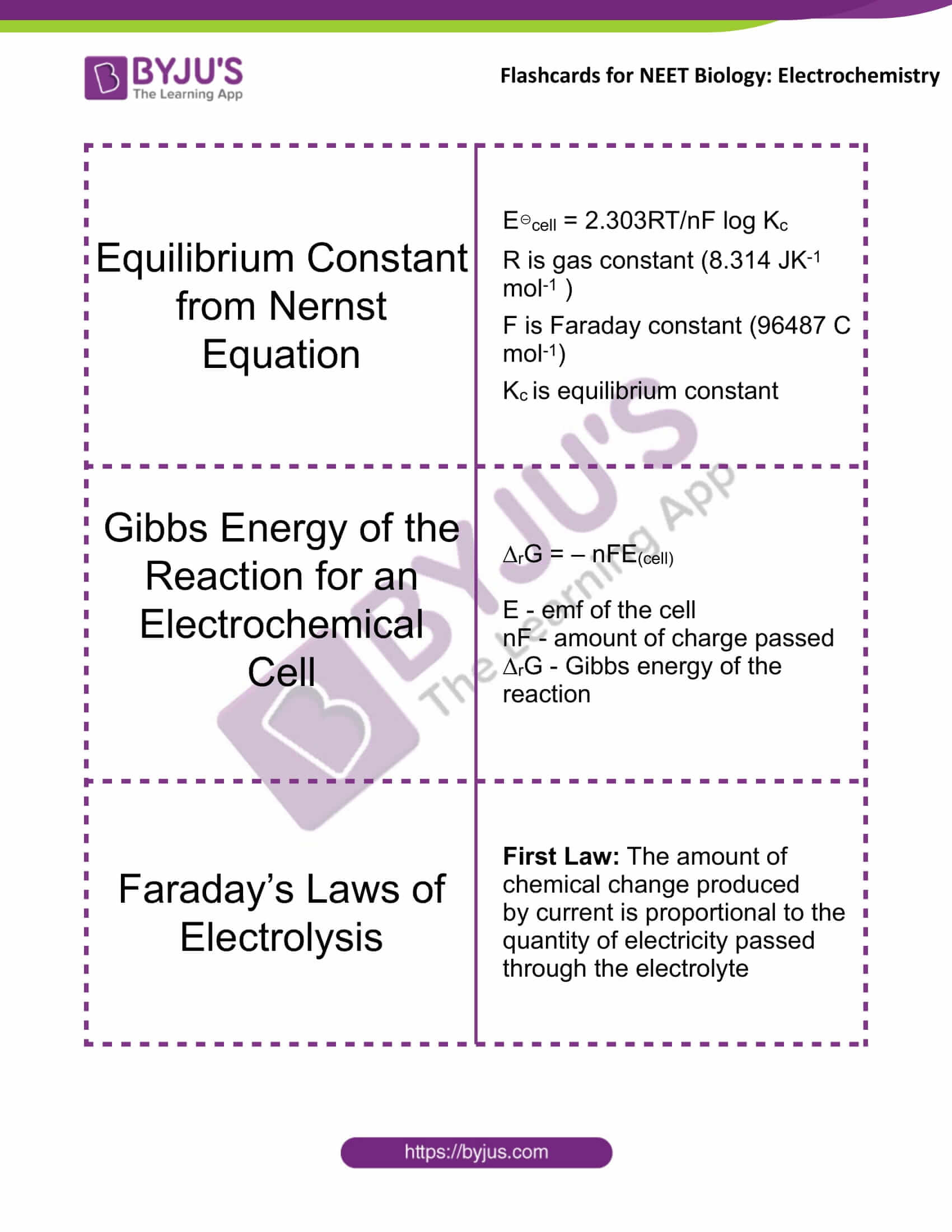
Equilibrium Constant from Nernst Equation |
E⊖cell = 2.303RT/nF log Kc R is gas constant (8.314 JK-1 mol-1 ) F is Faraday constant (96487 C mol-1) Kc is equilibrium constant |
|
Gibbs Energy of the Reaction for an Electrochemical Cell |
∆rG = – nFE(cell) E(cell) – emf of the cell nF – the amount of charge passed ∆rG – Gibbs energy of the reaction |
|
Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis |
First Law: The amount of chemical change produced by the current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte |
|
Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis |
Second Law: The amounts of chemical changes produced by the same quantity of electricity in different substances are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights |
|
Primary Batteries |
It cannot be reused. E.g. Dry cell or Leclanche cell Anode: Zn(s) → Zn2+ + 2e– Cathode: MnO + NH4+ + e– → MnO(OH) + NH3 |
|
Mercury Cell |
Primary battery Anode: zinc – mercury amalgam Cathode: a paste of HgO and carbon |
|
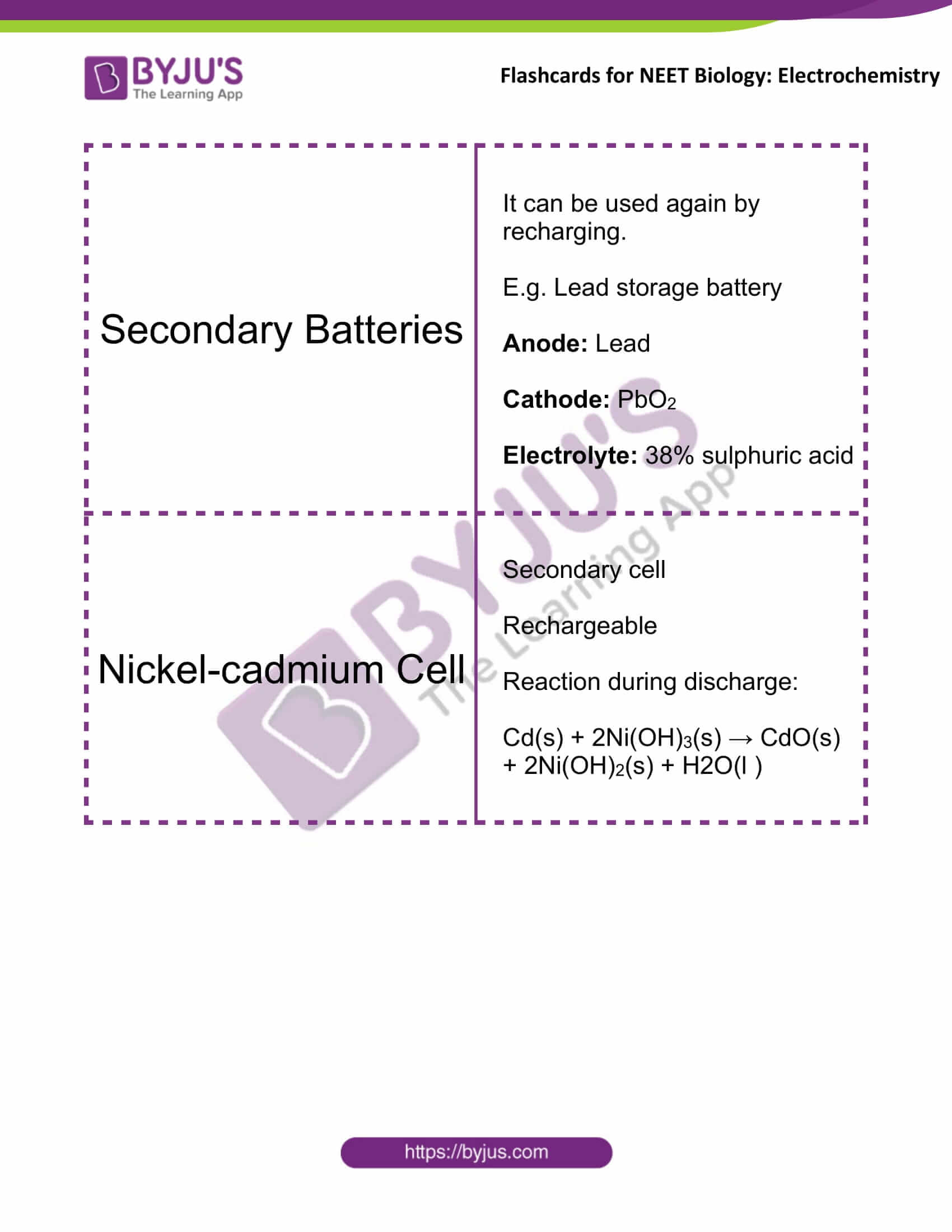
Secondary Batteries |
It can be used again by recharging. E.g. Lead storage battery Anode: lead Cathode: PbO2 Electrolyte: 38% sulphuric acid |
|
Nickel-cadmium Cell |
Secondary cell Rechargeable Reaction during discharge: Cd(s) + 2Ni(OH)3(s) → CdO(s) + 2Ni(OH)2(s) + H2O(l ) |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Videos:


|
Also check: |


Comments