What Is Catalase Enzyme?
As the name suggests, catalase is an enzyme bringing about the catalysis of a reaction through which hydrogen peroxide is decomposed into oxygen and water. Catalase is responsible for preventing the accumulation of cellular organelles and safeguards these organelles and tissues from any destruction by the peroxide as peroxide is continuously synthesized by a number of metabolic reactions. Catalase is mainly found in the liver of mammals.
Commonly found in almost all living entities enabled with oxygen exposure, catalase is pivotal in preventing cells from oxidative damage by the ROS (reactive oxygen species). This antioxidant enzyme is found in all aerobic entities and catalyzes in an energy-efficient manner in the cells uncovered to environmental stress.
In higher plants, they are situated in all the major sites of hydrogen peroxide production in the cellular components such as chloroplast, mitochondria, cytosol and peroxisomes. A factor which indicates its versatility in the plant system is the existence of catalase isozymes in multiple molecular forms. Structural genes Cat1, Cat2 and Cat3 encode for catalase isozymes CAT-1, CAT-2, CAT-3 respectively, whose expression indicates species, time and stress specificity.
Chemical Nature of Catalase Enzyme
The enzyme is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains wherein every chain possesses more than 500 amino acids. It contains 4 iron-containing heme groups which are key, enabling it to react with the hydrogen peroxide. The optimal pH level for human catalase is nearly 7. The optimal pH for other catalases fluctuates between 4-11 varying from species to species, same goes with the temperature parameter, it varies.
Catalase Enzyme Function
For the sustenance of life on earth, oxygen is pivotal. When the body uses oxygen, it constantly generates free radicals. These free radicals are atoms or molecules that are known to be chemically unstable. In addition to this, they also lead to the instability of other atoms or molecules present in the body which subsequently causes damage to cell membranes, proteins and even the DNA structure. The phenomena can also result in permanent cellular and tissue damage causing joint and heart diseases, infections, depressed immunity systems, mental decline and so on.
This is where catalase pitches in, it has a role to play in fighting against the threat that free radicals pose to the body. It converts toxic superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxides which later decomposes it into oxygen and water.
Catalase Enzyme Reaction
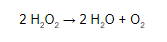
When catalase is found in a tissue or microbial sample, it can be illustrated by the addition of hydrogen peroxide and then the reaction can be noted. Oxygen release is indicated through bubble formation. It is a simple and easy demonstration, visible to naked eyes as catalase is known to have a very high specific activity generating an evident response. In addition to this, one of the products is a gas, hence making the test easier.
This was some information on catalase enzyme, hope this was insightful. BYJU’S enlightens students with other related articles important for NEET as well, visit BYJU’S NEET for more.
See More:
| What is Deuterostomes? |
| What is Bioprocessing? |

Comments