Cell division could either be mitosis type or meiosis type. The process of meiosis is conserved, in one or the other form, across all the entities reproducing sexually. It seems to drive the reproductive abilities in different entities, focusing on common evolutionary routes for sexually reproducing entities.
There is a significant difference in the process of meiosis occurring in males and females with regard to its timing and follow-up of events. The vital difference lies in the gametes produced. The process of meiosis in males begins after hitting puberty and continues throughout one’s lifetime. In females, on the other hand, the process starts approximately at the 12th week of fetal development. Until one hits puberty, it does not resume.
Where does meiosis occur in males and females?
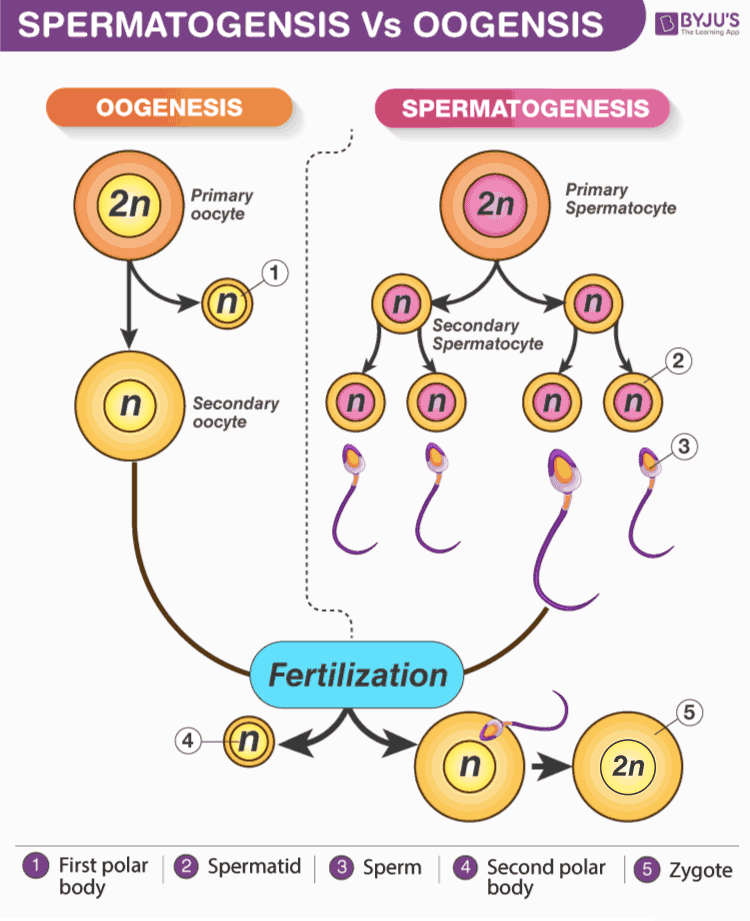
Meiosis in males occurs during spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles after puberty. The diploid cells present in the testes experience meiosis to produce haploid sperm cells having 23 chromosomes. One diploid cell gives 4 haploid sperm cells through the process of meiosis.
Meiosis in females starts at the time of the fetal stage with the entrance of a series of diploid cells into meiosis I. In females, the process of oogonia occurs in the ovaries.
Key Differences between Meiosis in Males and Females
The table below depicts the differences between meiosis in males and females.
|
Meiosis in Males |
Meiosis in Females |
| What does it mean? | |
| A continuous process commencing from the time one hits puberty and stays throughout one’s life. It yields the production of several lakhs of spermatozoa daily. | The process can span over forty years from the initiation to the finish. Merely some oocytes reach the final phases. This is because, before birth, a significant amount of them are lost. |
| Where does it occur? | |
| Testicles (seminiferous tubules) | Ovary |
| Time Duration | |
| Takes days or even weeks | It takes upto months or even years |
| Size of Gametes | |
| Sperms smaller than spermatocytes | Ova larger than oocytes |
| Type of Cell Division | |
| Symmetrical | Asymmetrical |
| When does it commence? | |
| At the time of puberty | Starts before birth |
| Production of Gametes | |
| Continued production of spermatocytes | A finite number of eggs produced, the number declines with age – menopause |
| Result of Meiosis | |
| Spermatogenesis – all 4 daughter cells formed become sperms | Oogenesis – a single daughter cell becomes ovum, other 3 daughter cells formed are small and non-functional polar bodies |
You read about some differences between meiosis in males and females. Learn and find more such articles by visiting us at BYJU’S NEET.
Recommended Video:
NEET Preparation | Biology Concepts Explained | Spermatogenesis

More here:
Comments