Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “The d- and f-Block Elements”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams, during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for The d- and f-Block Elements
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
The d- and f-Block Elements |
NEET Exams |
|
The d- and f-Block Elements |
|
|
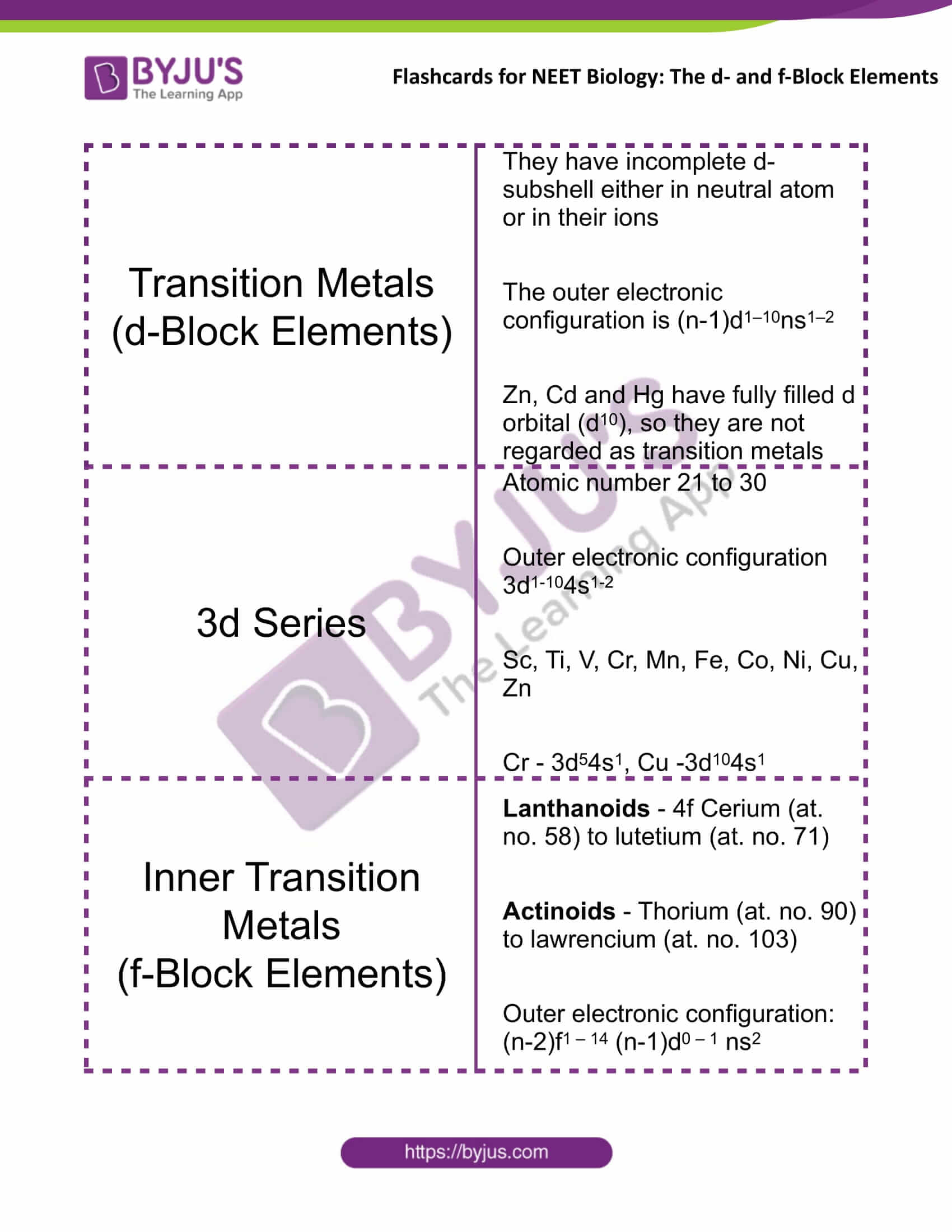
Transition Metals (d-Block Elements) |
They have incomplete d-subshell either in neutral atom or in their ions The outer electronic configuration is (n-1)d1–10ns1–2 Zn, Cd and Hg have fully filled d orbital (d10), so they are not regarded as transition metals |
|
3d Series |
Atomic number 21 to 30 Outer electronic configuration 3d1-104s1-2 Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn Cr – 3d54s1, Cu – 3d104s1 |
|
Inner Transition Metals (f-Block Elements) |
Lanthanoids – 4f Cerium (at. no. 58) to lutetium (at. no. 71) Actinoids – Thorium (at. no. 90) to lawrencium (at. no. 103) Outer electronic configuration: (n-2)f1–14 (n-1)d0 – 1 ns2 |
|
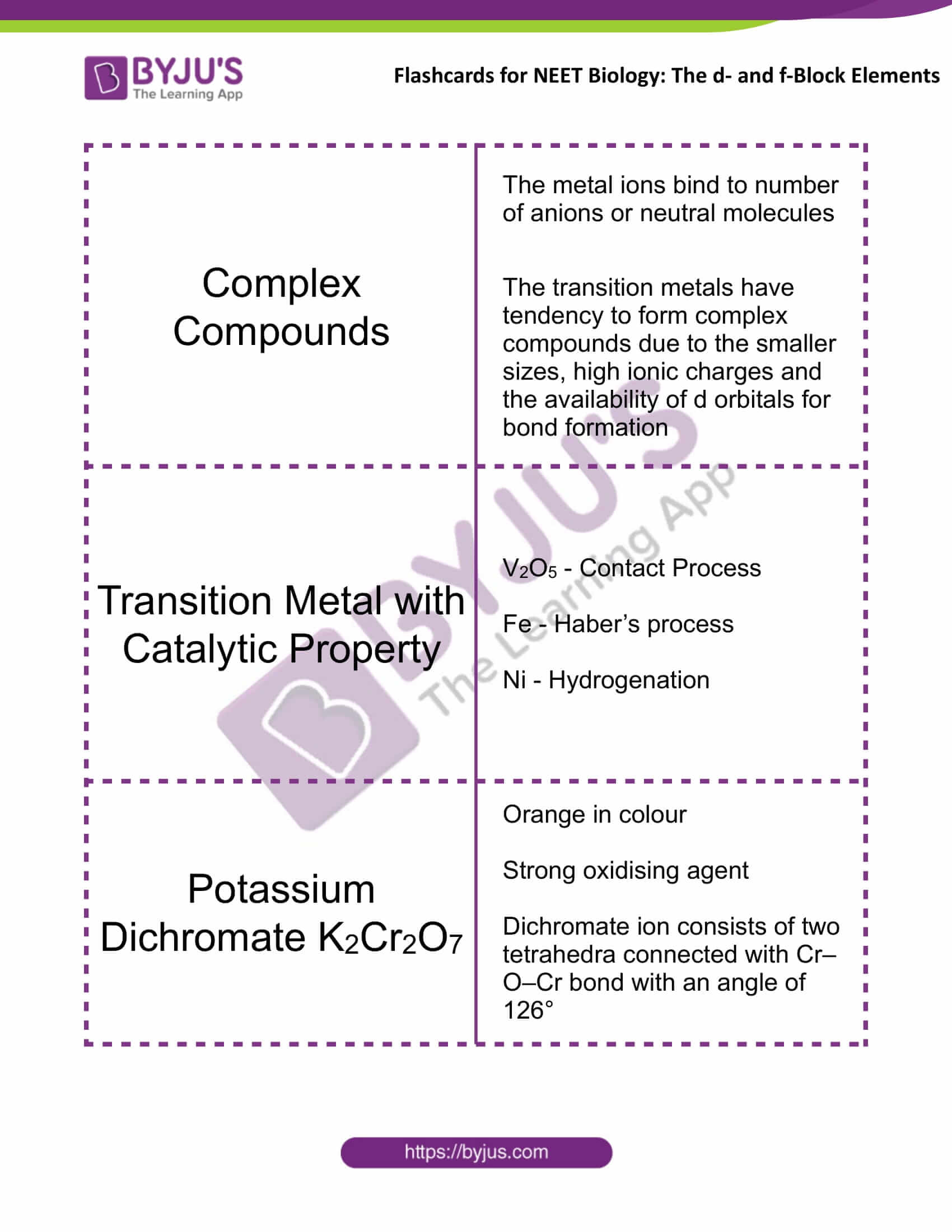
Complex Compounds |
The metal ions bind to number of anions or neutral molecules The transition metals have tendency to form complex compounds due to the smaller sizes, high ionic charges and the availability of d orbitals for bond formation |
|
Transition Metal with Catalytic Property |
V2O5 – Contact Process Fe – Haber’s process Ni – Hydrogenation |
|
Potassium Dichromate K2Cr2O7 |
Orange in colour Strong oxidising agent Dichromate ion consists of two tetrahedra connected with Cr–O–Cr bond with an angle of 126° |
|
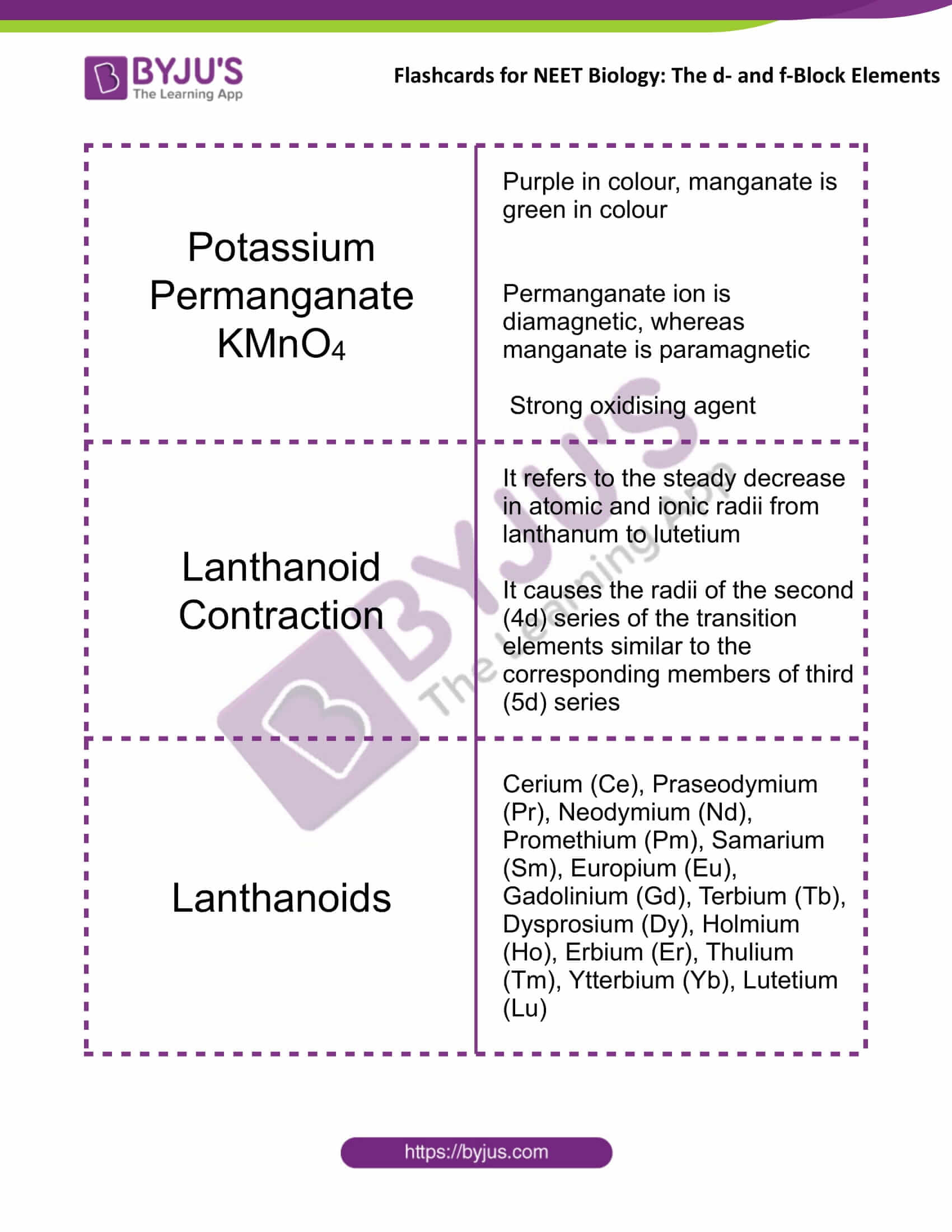
Potassium Permanganate KMnO4 |
Purple in colour, manganate is green in colour Permanganate ion is diamagnetic, whereas manganate is paramagnetic Strong oxidising agent |
|
Lanthanoid Contraction |
It refers to the steady decrease in atomic and ionic radii from lanthanum to lutetium It causes the radii of the second (4d) series of the transition elements similar to the corresponding members of third (5d) series |
|
Lanthanoids |
Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), Samarium (Sm), Europium (Eu), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), Holmium (Ho), Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb), Lutetium (Lu) |
|
Actinoids |
Thorium (Th), Protactinium (Pa), Uranium (U), Neptunium (Np), Plutonium (Pu), Americium (Am), Curium (Cm), Berkelium (Bk), Californium (Cf), Einsteinium (Es), Fermium (Fm), Mendelevium (Md), Nobelium (No), Lawrencium (Lr) |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
|
Also check: |

Comments