Alternating current is a current that changes its magnitude and polarity at regular interval of time. If the current maintains its direction constant it is called direct current.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Alternating Current
Download Now

AC voltage, v = V0sinωt
AC current, i = I0sinωt
Capacitive Reactance V0/I0 = 1/ωC = Xc
RMS voltage, Vrms = V0/√2
RMS current, Irms = I0/√2
Inductive Reactance V0/I0 = ωL = XL
Phase angle of an RLC series circuit Φ = tan-1 (XL – XC)/R
AC version of Ohm’s law, I0 = V0/Z
RLC series circuit Impedance ,
Average power associated with circuit element, Pavc = (1/2)I0V0cos Φ
Resonant angular frequency of the circuit, ω0 = √1/LC
Root Mean Square: The Root mean square of a function from T1 to T2 is given by

Power Consumed or Supplied in AC circuit
The average power consumed in a cycle
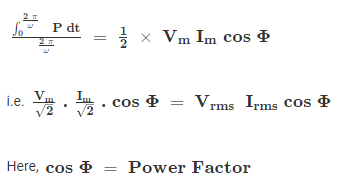
Purely Resistive Circuit: In a purely resistive circuit, the power is dissipated by the resistance and phase of both voltage and current remains the same.

P = VrmsIrms cosΦ = Vrms2/R
Pure Inductive Circuit: In a purely inductive circuit current lags the voltage by 900

i = im sin(ωt- π/2)
Purely Conductive Circuit: In a purely inductive circuit, the current flowing through the capacitor leads the voltage by 900.

I = {Vm/(1/ωC)}cosωt
I = (Vm/Xc)cosωt
I = Imcosωt
I = Imsin(ωt + π/2)
Recommended Video:
Electric Current and Electrical Networks | Ohm’s Law in Scalar form | NEET 2021/2022/2023 | Physics

You might like:
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- How to Score 170 Plus in NEET Physics
- Last Minute Preparation Tips for NEET Physics
- NEET Physics Weightage
- Physics Formulae For NEET
- NEET Physics Important Topics
- NEET Physics MCQs
Comments