Interphase is the resting stage of the cell cycle, where cells prepare themselves to divide. It is important for a cell to grow and duplicate the cellular contents to divide. There are three stages in the interphase, the cell grows in the G1 phase, DNA synthesis takes place in S phase and synthesis of proteins and growth continues in G2. At the end of the interphase, the cell is fully prepared for the division and enters the M phase of the cell cycle.
Interphase
In 1953, Howard and Pelc proposed the four stages of the cell cycle, i.e. G1, S, G2 and M. Interphase comprises G1, S, and G2 phases. Interphase accounts for more than 95% of the cell cycle duration.
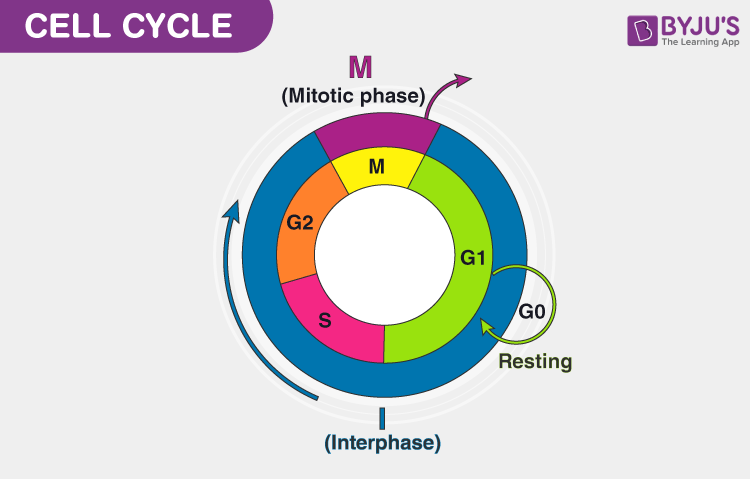
1. G1 (Gap 1)
It is also known as the first gap or growth phase. The cell becomes fully active metabolically and starts to grow. Synthesis of RNA and proteins takes place. All the three types of RNAs (mRNA, tRNA and rRNA) are transcribed. Nucleolus appears big and it indicates the synthesis of rRNA.
Regulatory proteins, which regulate mitosis are synthesized in this phase. The other proteins, which are synthesized during this phase are enzymes required for DNA synthesis, e.g. DNA polymerases, proteins required for the formation of mitotic apparatus, e.g. tubulin, etc.
The duration of the G1 phase varies depending on the cell types. Rapidly dividing cells, e.g. blastomeres of mammals lack this phase. The cell division gets arrested at the G1 stage and known as G0 phase or quiescent stage in the cells, which are fully differentiated and do not divide unless they need to repair due to damage or cell death, e.g. neurons, striated muscles of heart, etc.
2. S (Synthesis)
As the name implies, the DNA synthesis or replication takes place in this stage. DNA content of chromosomes gets doubled. Histone proteins are also synthesised to form nucleosomes. It is important to note that the number of chromosomes in a cell remains the same. In the animal cells, duplication of centriole takes place in the cytoplasm.
3. G2 (Gap 2)
This stage is marked by the continued synthesis of proteins and cell growth. The cell is now fully prepared for division and enters the M or mitosis phase.
So the main characteristics of the interphase cell are the following:
- Chromosomes remain diffused and extended, long and coiled.
- The nuclear membrane remains intact.
- DNA replication takes place so the amount of DNA and genes gets doubled.
- Due to rRNA synthesis and accumulation, the size of the nucleolus increases.
- Duplication of centrioles in animal cells.
- Cell synthesizes, proteins, lipids, membranes and other cellular components.
This was in brief about Interphase. Get access to all the NEET Questions with explanations, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
Cell Cycle and Cell Division- MCQs | Class 11 Biology | Rapid Fire Tuesday Quiz-1 | NEET 2022 & 2023


Related Articles:

Comments