Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Environmental Issues. These flashcards on Environmental Issues are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Environmental Issues, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Environmental Issues
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Environmental Issues | NEET exams |
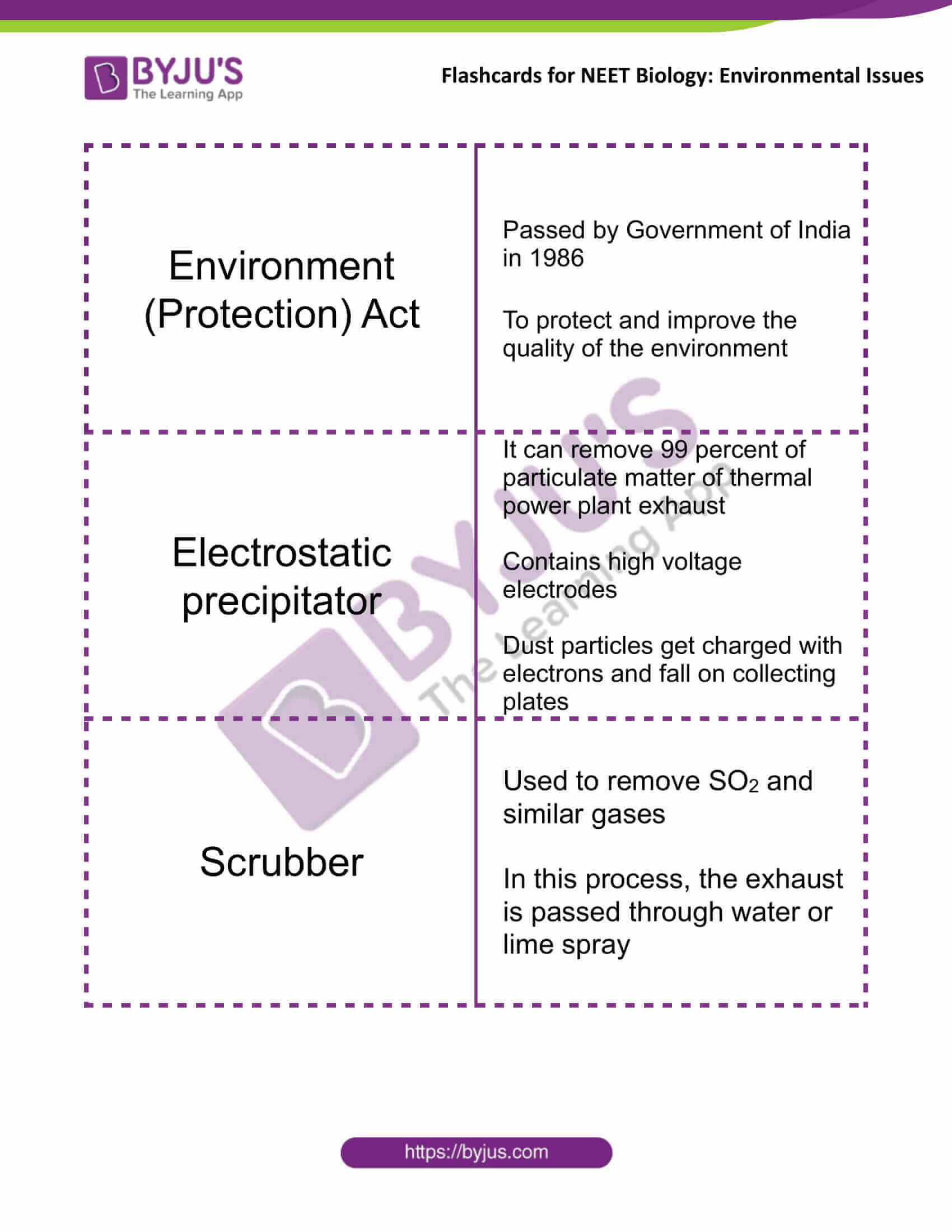
| Environment (Protection) Act | Passed by Government of India in 1986
To protect and improve the quality of the environment |
| Electrostatic precipitator | It can remove 99 percent of particulate matter of thermal power plant exhaust
Contains high voltage electrodes Dust particles get charged with electrons and fall on collecting plates |
| Scrubber | Used to remove SO2 and similar gases
In this process, the exhaust is passed through water or lime spray |
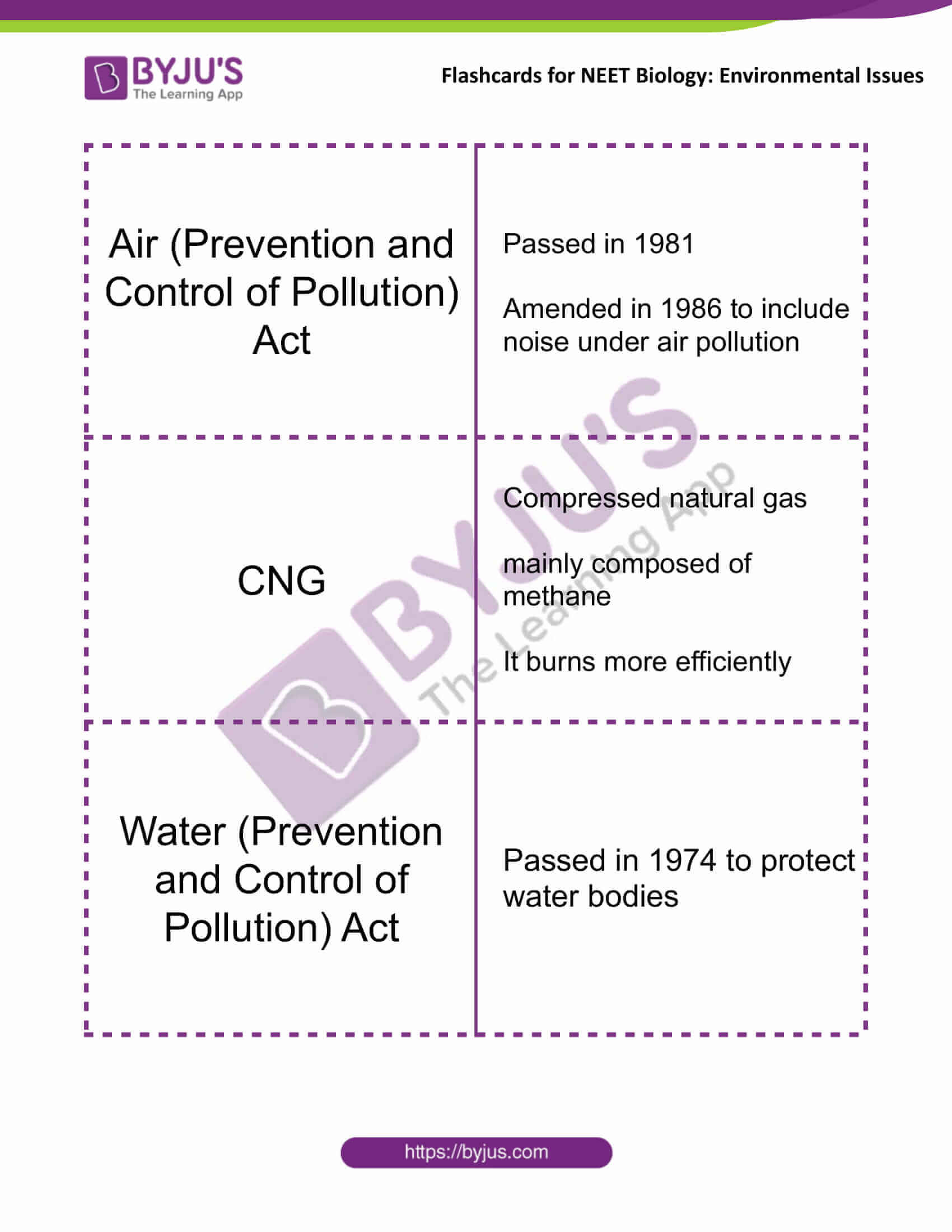
| Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act | Passed in 1981
Amended in 1986 to include noise under air pollution |
| CNG | Compressed natural gas
mainly composed of methane It burns more efficiently |
| Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act | Passed in 1974 to protect water bodies |
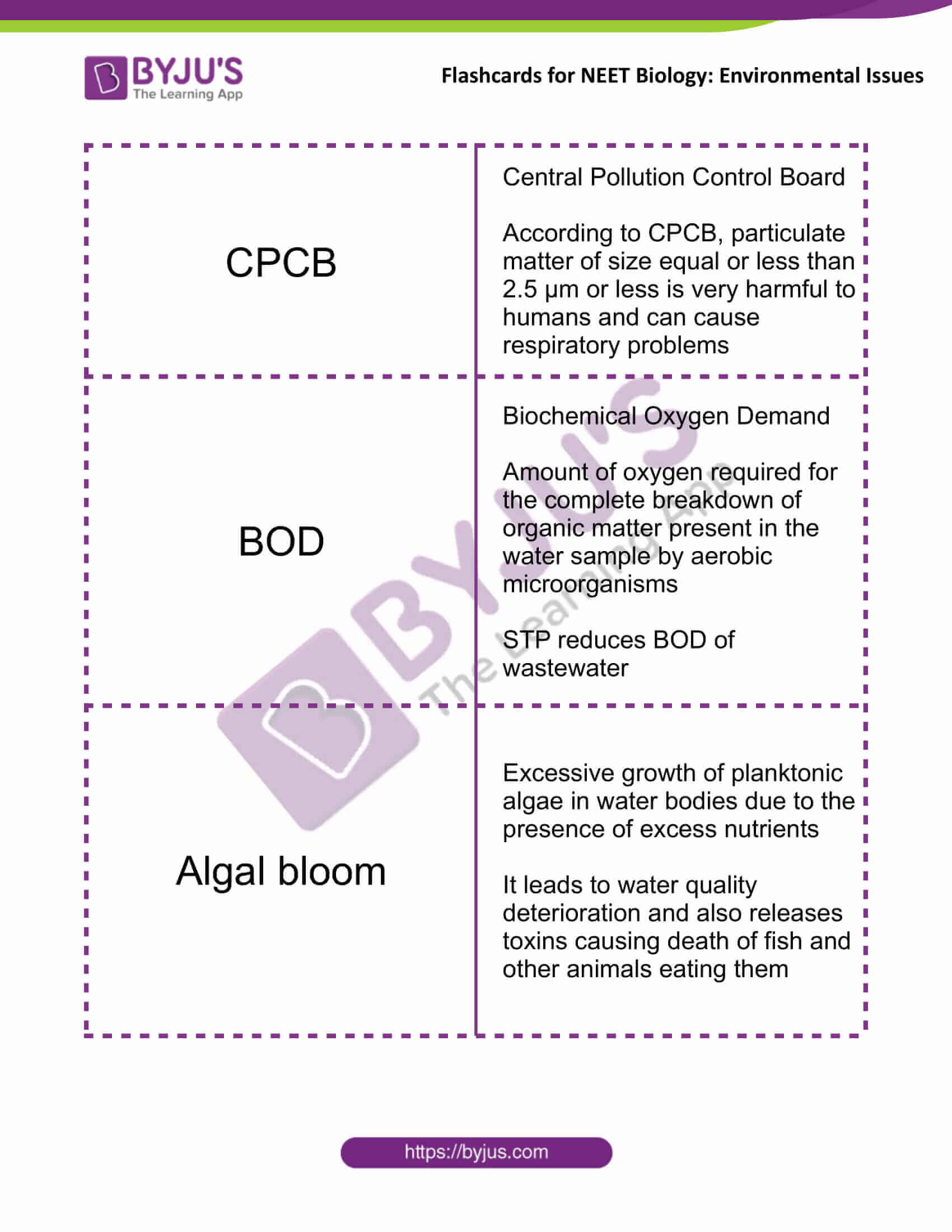
| CPCB | Central Pollution Control Board
According to CPCB, particulate matter of size equal or less than 2.5 µm or less is very harmful to humans and can cause respiratory problems |
| BOD | Biochemical Oxygen Demand
Amount of oxygen required for the complete breakdown of organic matter present in the water sample by aerobic microorganisms STP reduces BOD of wastewater |
| Algal bloom | Excessive growth of planktonic algae in water bodies due to the presence of excess nutrients
It leads to water quality deterioration and also releases toxins causing the death of fish and other animals eating them |
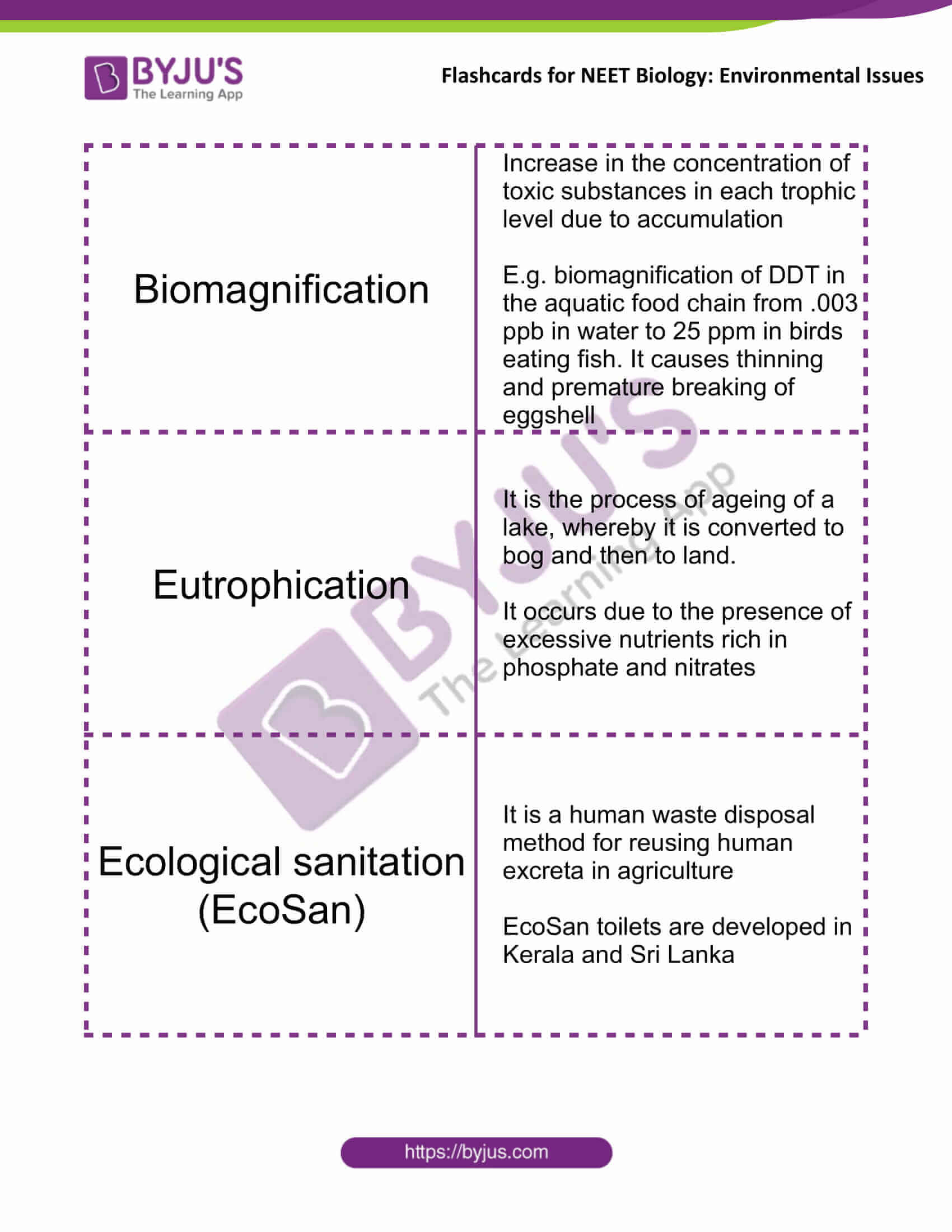
| Biomagnification | Increase in the concentration of toxic substances in each trophic level due to accumulation
E.g. biomagnification of DDT in the aquatic food chain from .003 ppb in water to 25 ppm in birds eating fish. It causes thinning and premature breaking of eggshell |
| Eutrophication | It is the process of ageing of a lake, whereby it is converted to bog and then to land
It occurs due to the presence of excessive nutrients rich in phosphate and nitrates |
| Ecological sanitation (EcoSan) | It is a human waste disposal method for reusing human excreta in agriculture
EcoSan toilets are developed in Kerala and Sri Lanka |
| Polyblend | Recycled and modified fine powder of plastic
Made by Ahmed Khan in Bangalore Polyblend increases water repellent property of bitumen and when this mixture is laid on a road, it increased the durability of the road three times |
| Integrated organic farming | It includes maximum utilisation of resources with zero waste and no chemical fertilisers
E.g. Ramesh Chandra Dagar in Sonipat utilises waste products of one process in another simultaneously such as bee-keeping, dairy, composting, agriculture, etc. |
| Greenhouse effect | The phenomenon responsible for heating the Earth’s surface
Greenhouse gases CO2, CH4 absorb a part of solar radiation and do not allow to escape |
| Global warming | Increase in the temperature of Earth’s atmosphere due to an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases
Contribution of gases in global warming- CO2– 60%, CH4– 20%, CFCs- 14%, N2O- 6% |
| Montreal protocol | Signed in 1987 and came into effect from 1989
To protect the ozone layer by controlling the use of ozone-depleting substances such as CFCs |
| Joint Forest Management (JFM) | Conceptualised in 1980 by Government of India
It involves a joint partnership of local communities and forest department in the protection and management of forests |
| Chipko movement | In 1974, Garhwal Himalayas |
| Jhum cultivation | A cause of deforestation
Slash and burn agriculture Commonly practised in North-East states of India |
| National Forest Policy | Came into force in 1988
According to it, plains should have 33% forest cover and hills 67% forest cover |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
Environmental Issues | NEET Botany Exam | NEET 2022

Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Biotechnology And Its Applications
NEET Flashcards: Organisms And Populations



Comments