Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. These flashcards on Photosynthesis in Higher Plants are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Photosynthesis in Higher Plants, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Recommended Videos:

Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
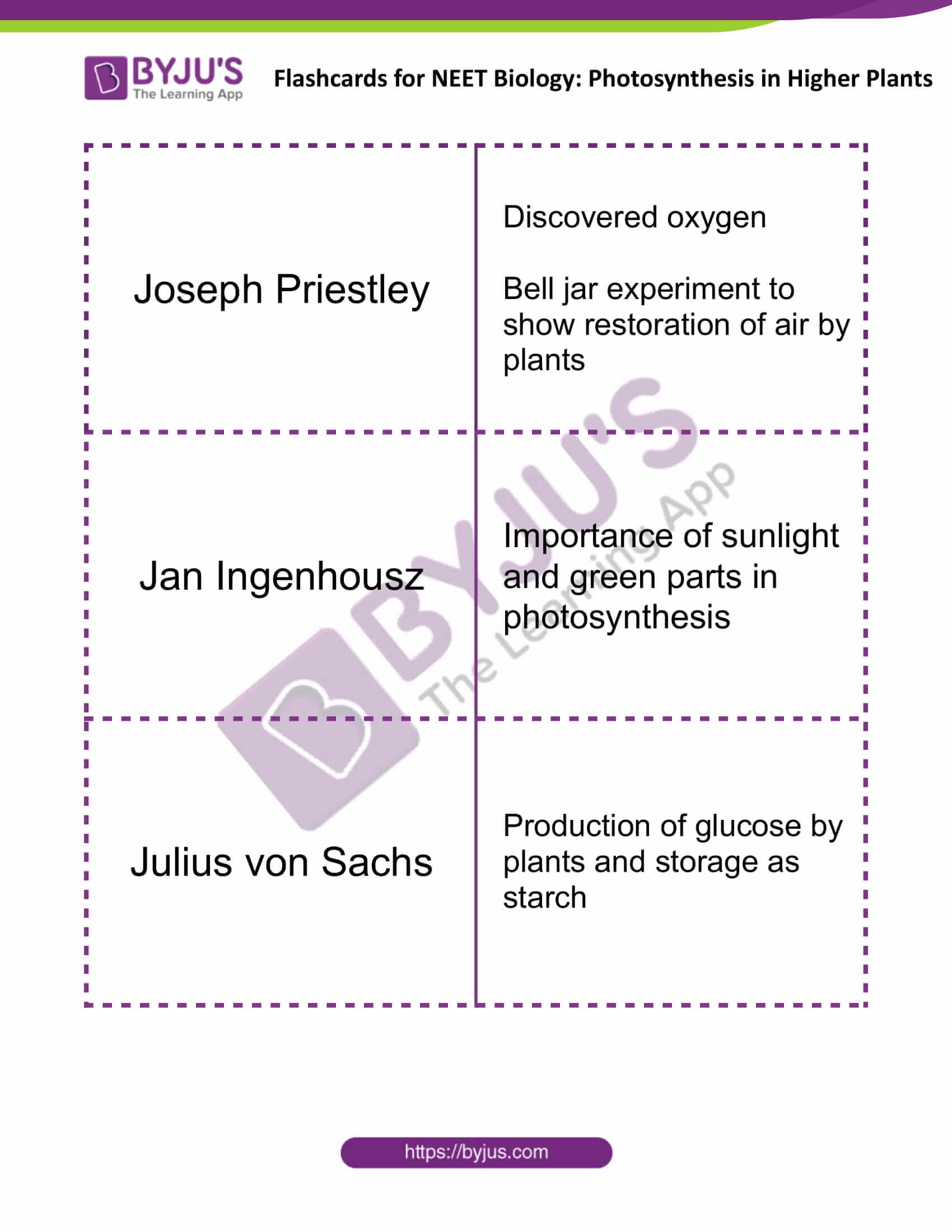
| Joseph Priestley | Discovered oxygen
Bell jar experiment to show restoration of air by plants |
| Jan Ingenhousz | Importance of sunlight and green parts in photosynthesis |
| Julius von Sachs | Production of glucose by plants and storage as starch |
| T.W Engelmann | Action spectrum of photosynthesis and showed that maximum absorption occurs in blue and red light
Experimented on green alga Cladophora |
| Cornelius van Niel | Proved that oxygen is evolved from splitting of water and not from CO2
Experimented on purple and green sulphur bacteria |
| Light reaction | Occurs in the membrane system of chloroplasts, i.e. grana thylakoids and stroma lamellae
light energy is trapped, photolysis of water to liberate oxygen and ATP and NADPH are produced |
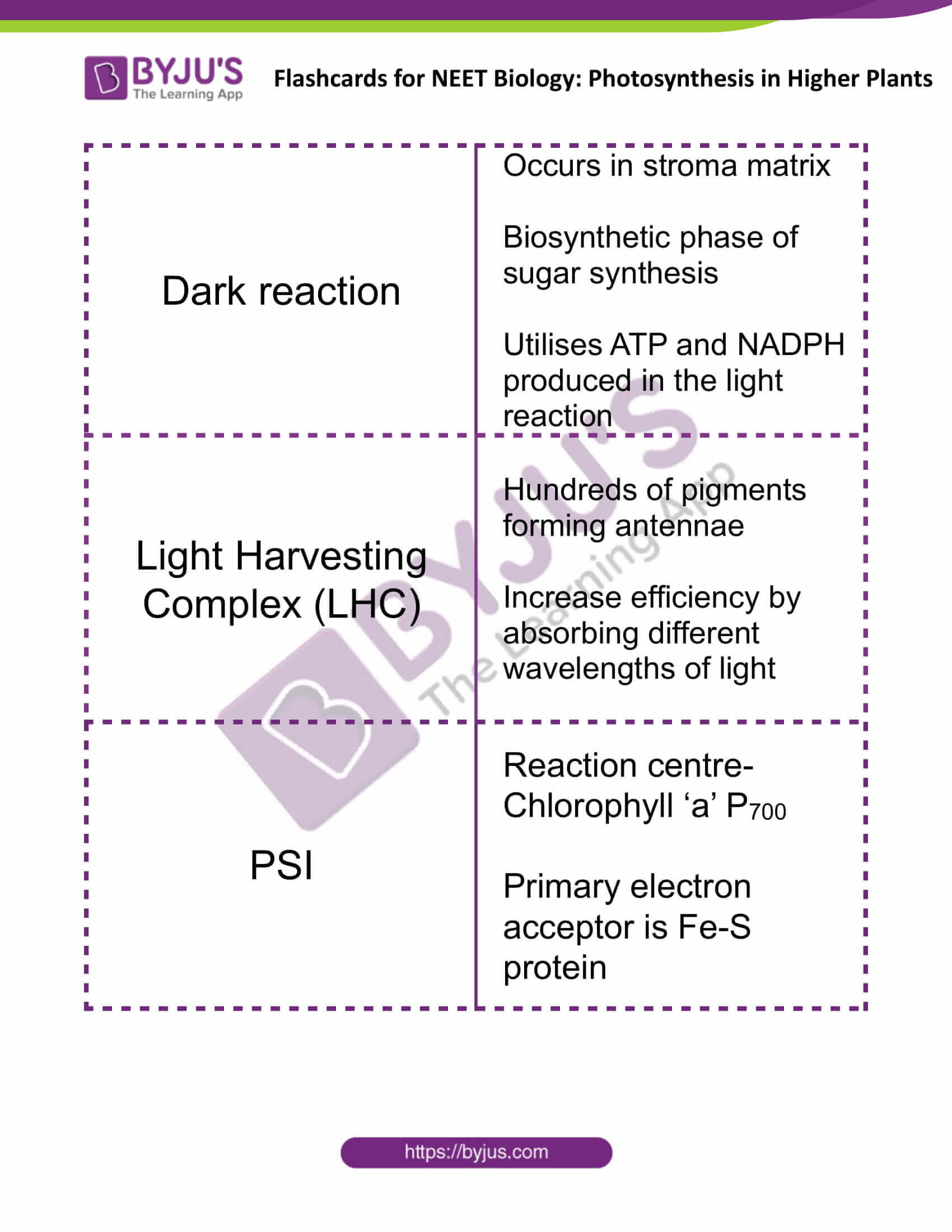
| Dark reaction | Occurs in stroma matrix
Biosynthetic phase of sugar synthesis Utilises ATP and NADPH produced in the light reaction |
| Light Harvesting Complex (LHC) | Hundreds of pigments forming antennae
Increase efficiency by absorbing different wavelengths of light |
| PSI | Reaction centre- Chlorophyll ‘a’ P700
Primary electron acceptor is Fe-S protein |
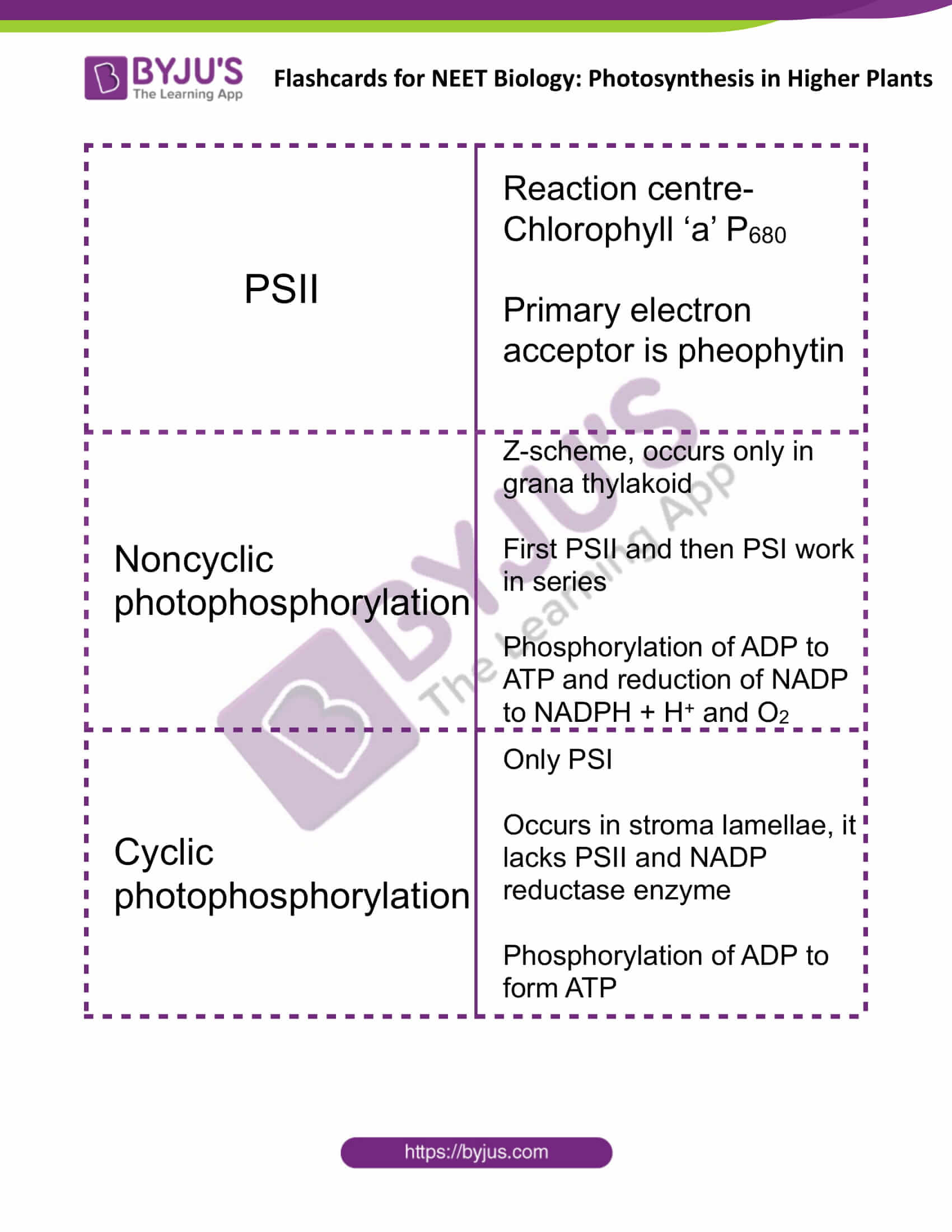
| PSII | Reaction centre- Chlorophyll ‘a’ P680
Primary electron acceptor is pheophytin |
| Noncyclic photophosphorylation | Z-scheme, occurs only in grana thylakoid
First PSII and then PSI work in series Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP and reduction of NADP to NADPH + H+ and O2 |
| Cyclic photophosphorylation | Only PSI
Occurs in stroma lamellae, it lacks PSII and NADP reductase enzyme Phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP |
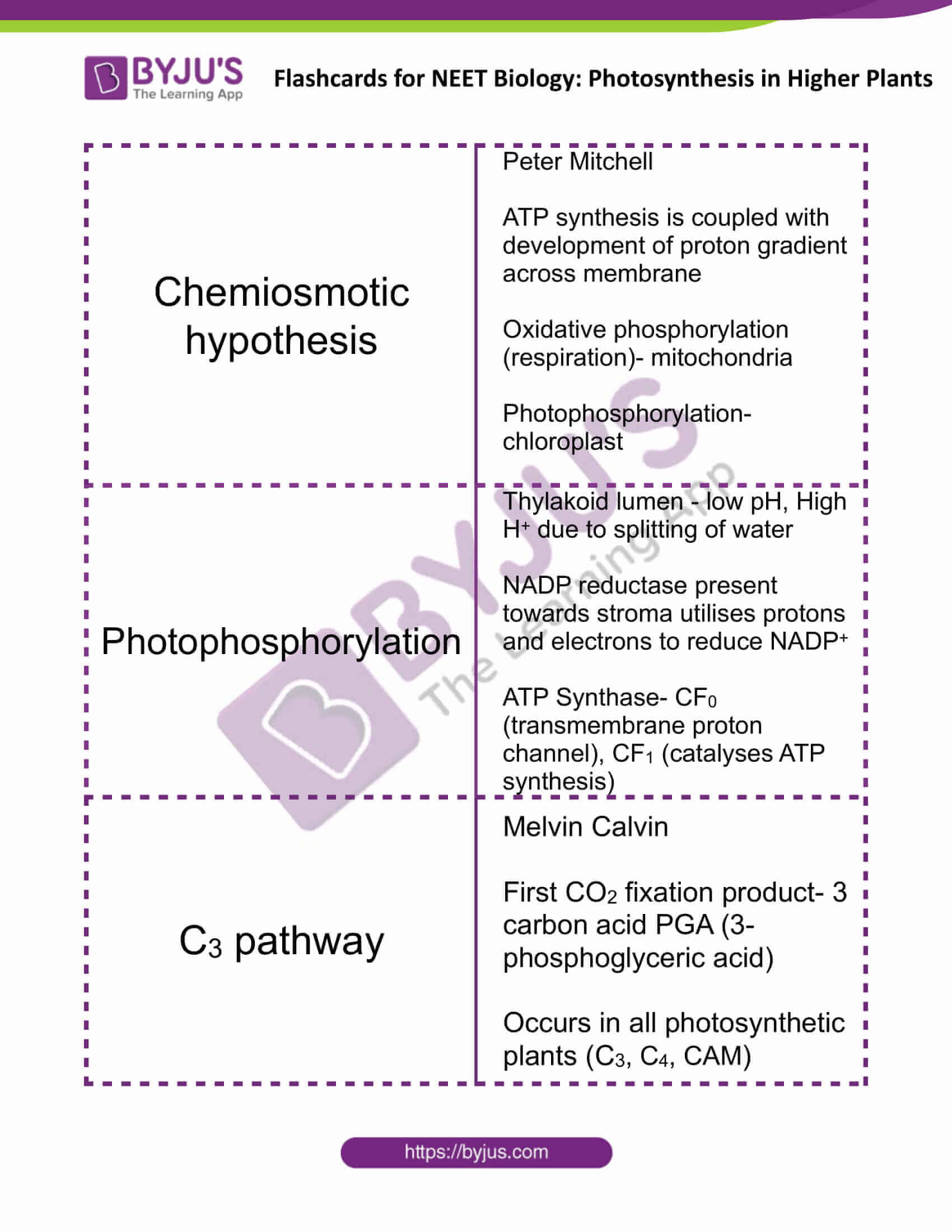
| Chemiosmotic hypothesis | Peter Mitchell
ATP synthesis is coupled with the development of proton gradient across the membrane Oxidative phosphorylation (respiration)- mitochondria Photophosphorylation- chloroplast |
| Photophosphorylation | Thylakoid lumen – low pH, High H+ due to splitting of water
NADP reductase present towards stroma utilises protons and electrons to reduce NADP+ ATP Synthase- CF0 (transmembrane proton channel), CF1 (catalyses ATP synthesis) |
| C3 pathway | Melvin Calvin
First CO2 fixation product- 3 carbon acid PGA (3-phosphoglyceric acid) Occurs in all photosynthetic plants (C3, C4, CAM) |
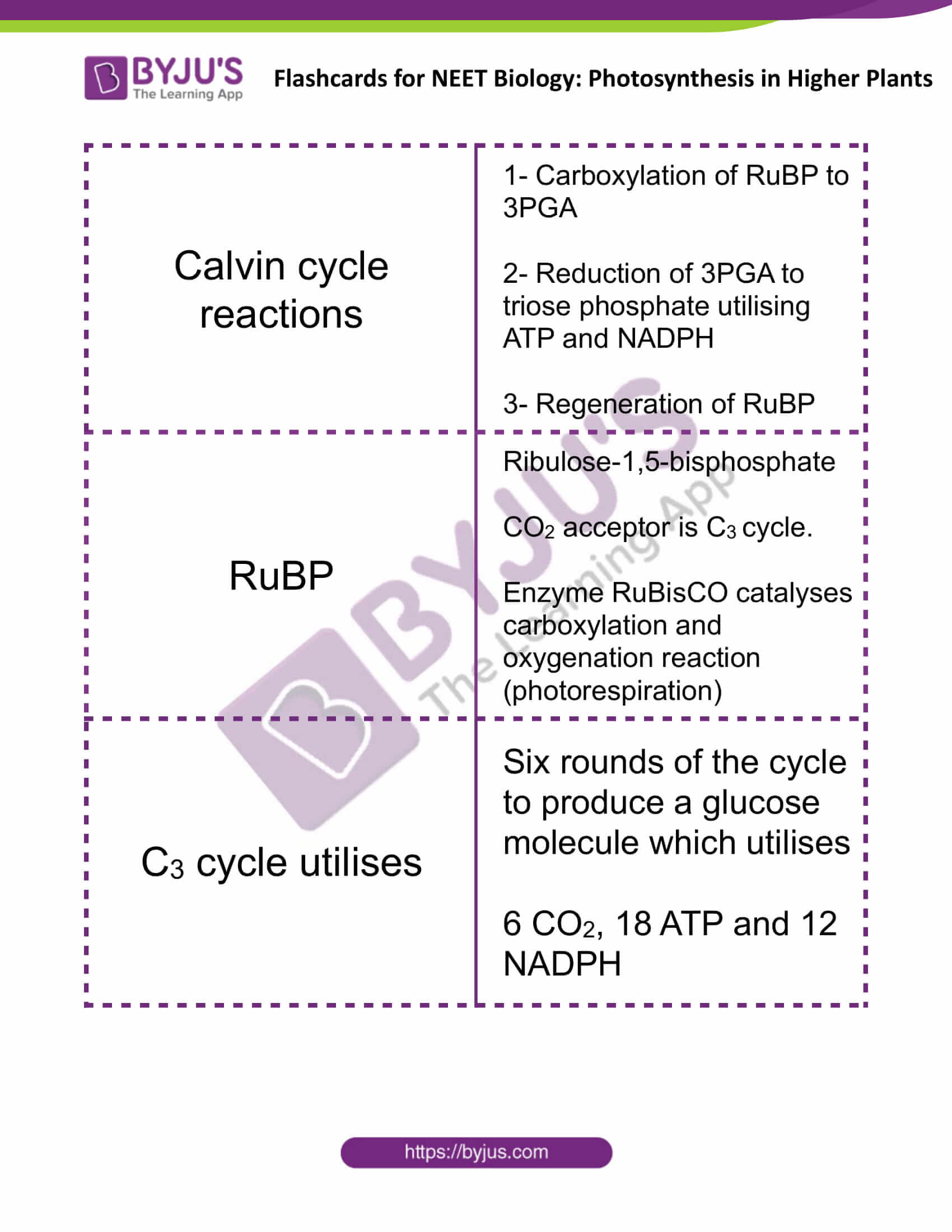
| Calvin cycle reactions | 1- Carboxylation of RuBP to 3PGA
2- Reduction of 3PGA to triose phosphate utilising ATP and NADPH 3- Regeneration of RuBP |
| RuBP | Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
CO2 acceptor is C3 cycle. Enzyme RuBisCO catalyses carboxylation and oxygenation reaction (photorespiration) |
| C3 cycle utilises | Six rounds of the cycle to produce a glucose molecule which utilises
6 CO2, 18 ATP and 12 NADPH |
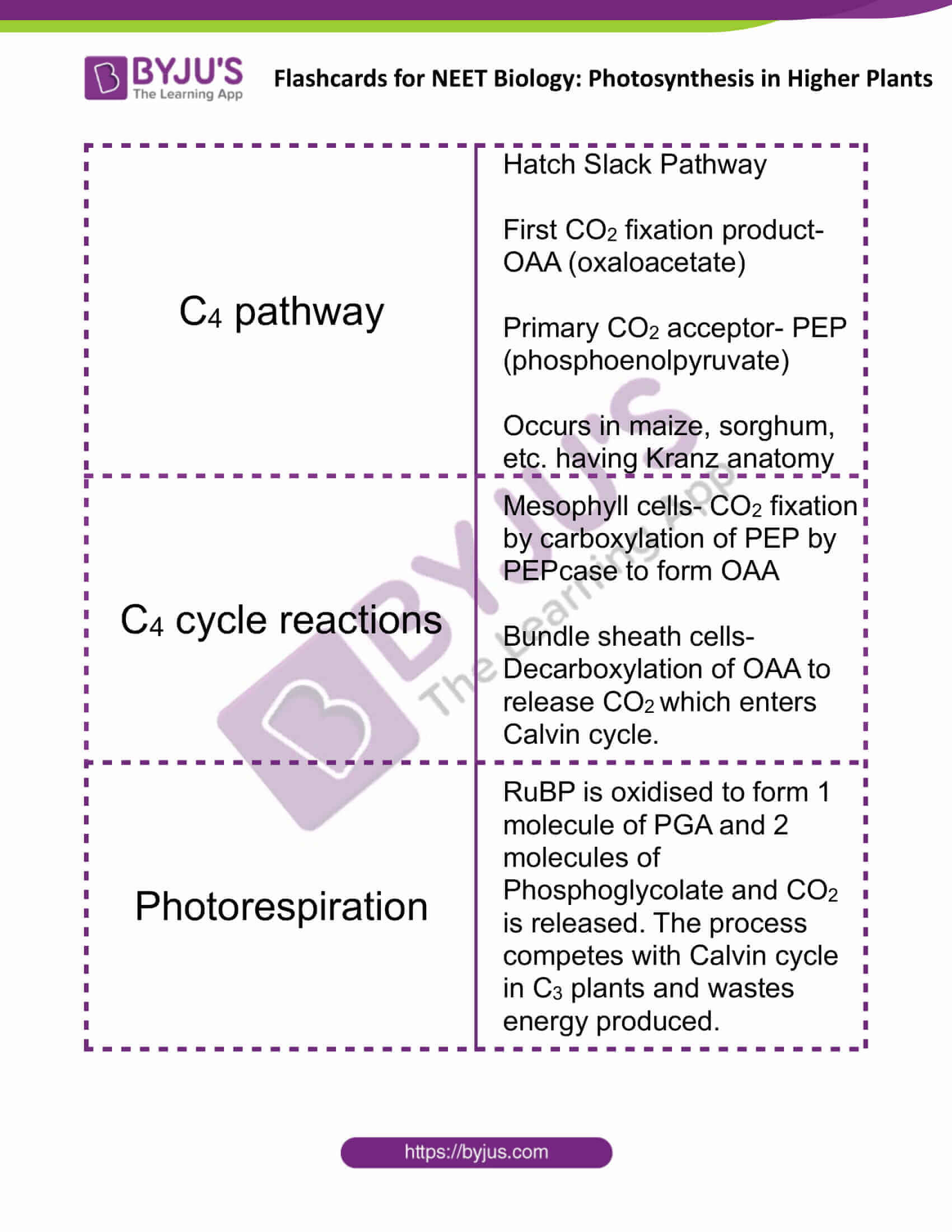
| C4 pathway | Hatch Slack Pathway
First CO2 fixation product- OAA (oxaloacetate) Primary CO2 acceptor- PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) Occurs in maize, sorghum, etc. having Kranz anatomy |
| C4 cycle reactions | Mesophyll cells- CO2 fixation by carboxylation of PEP by PEPcase to form OAA
Bundle sheath cells- Decarboxylation of OAA to release CO2 which enters Calvin cycle. |
| Photorespiration | RuBP is oxidised to form 1 molecule of PGA and 2 molecules of Phosphoglycolate and CO2 is released. The process competes with Calvin cycle in C3 plants and wastes energy produced. |
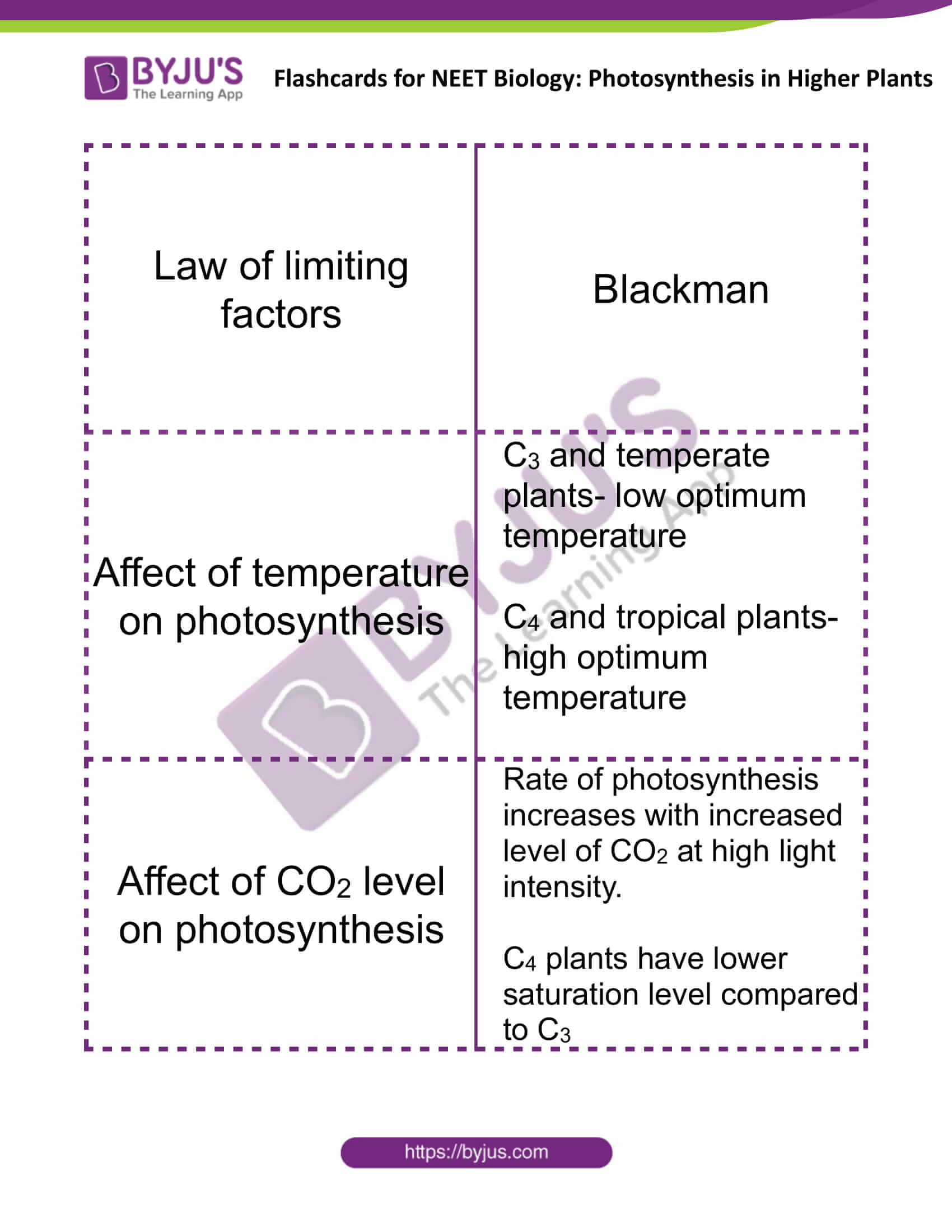
| Law of limiting factors | Blackman |
| Affect of temperature on photosynthesis | C3 and temperate plants- low optimum temperature
C4 and tropical plants- high optimum temperature |
| Affect of CO2 level on photosynthesis | Rate of photosynthesis increases with an increased level of CO2 at a high light intensity.
C4 plants have a lower saturation level compared to C3 |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Videos:

Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Cell Cycle And Cell Division
NEET Flashcards: Transport In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Mineral Nutrition

Comments