Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants. These flashcards on Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Recommended Videos:


Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants | NEET exams |
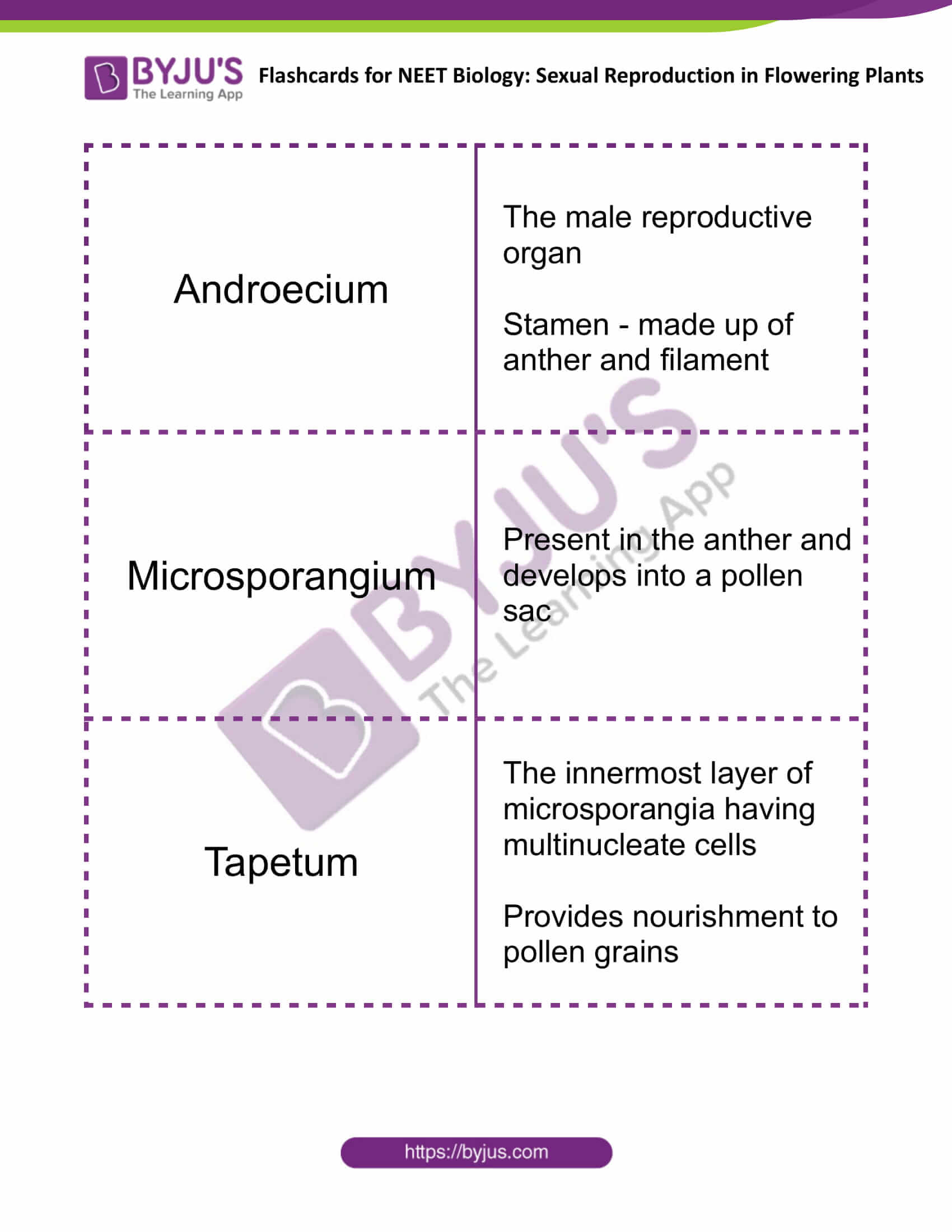
| Androecium | The male reproductive organ
Stamen – made up of anther and filament |
| Microsporangium | Present in the anther and develops into a pollen sac |
| Tapetum | The innermost layer of microsporangia having multinucleate cells
Provides nourishment to pollen grains |
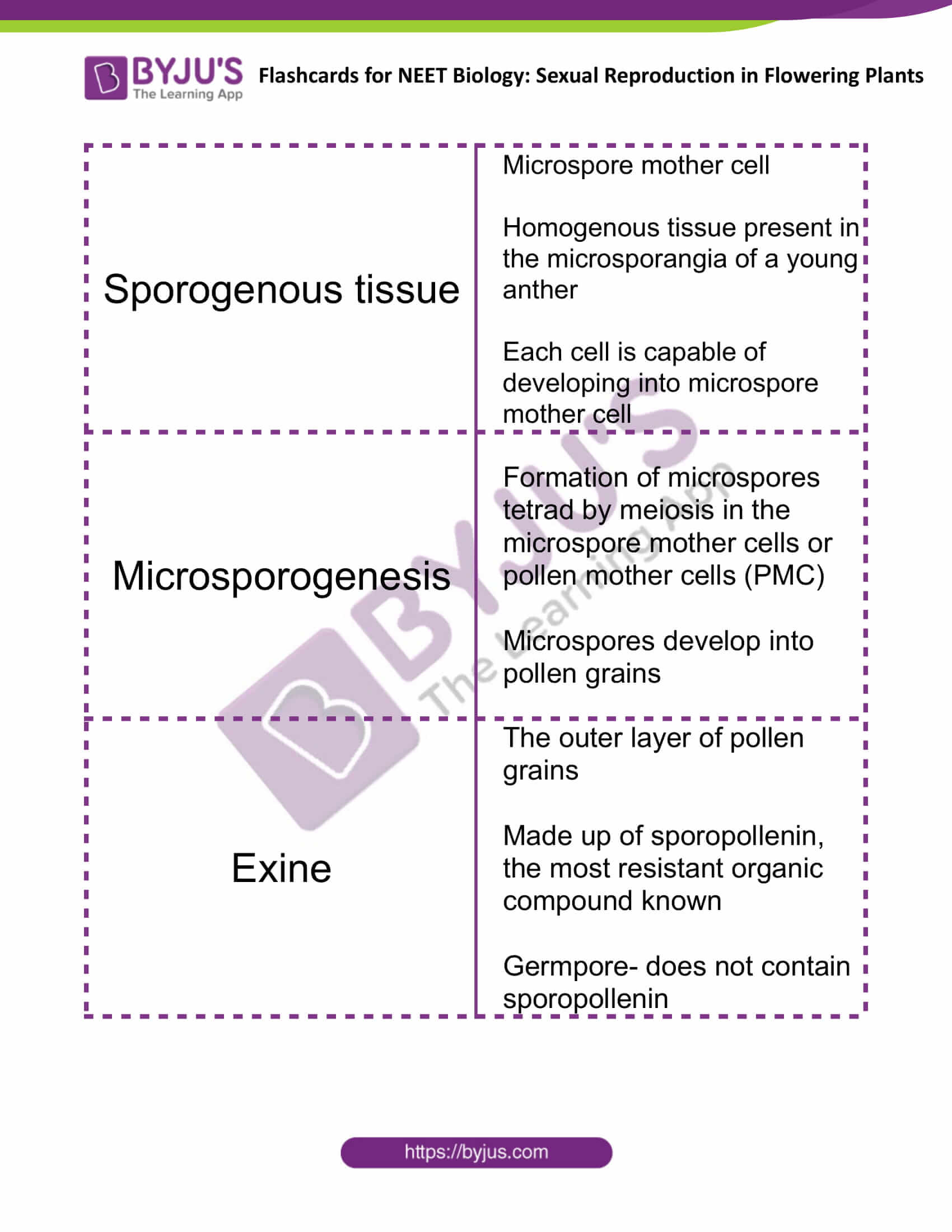
| Sporogenous tissue | Microspore mother cell
Homogenous tissue present in the microsporangia of a young anther Each cell is capable of developing into microspore mother cell |
| Microsporogenesis | Formation of microspores tetrad by meiosis in the microspore mother cells or pollen mother cells (PMC)
Microspores develop into pollen grains |
| Exine | The outer layer of pollen grains
Made up of sporopollenin, the most resistant organic compound known Germpore- does not contain sporopollenin |
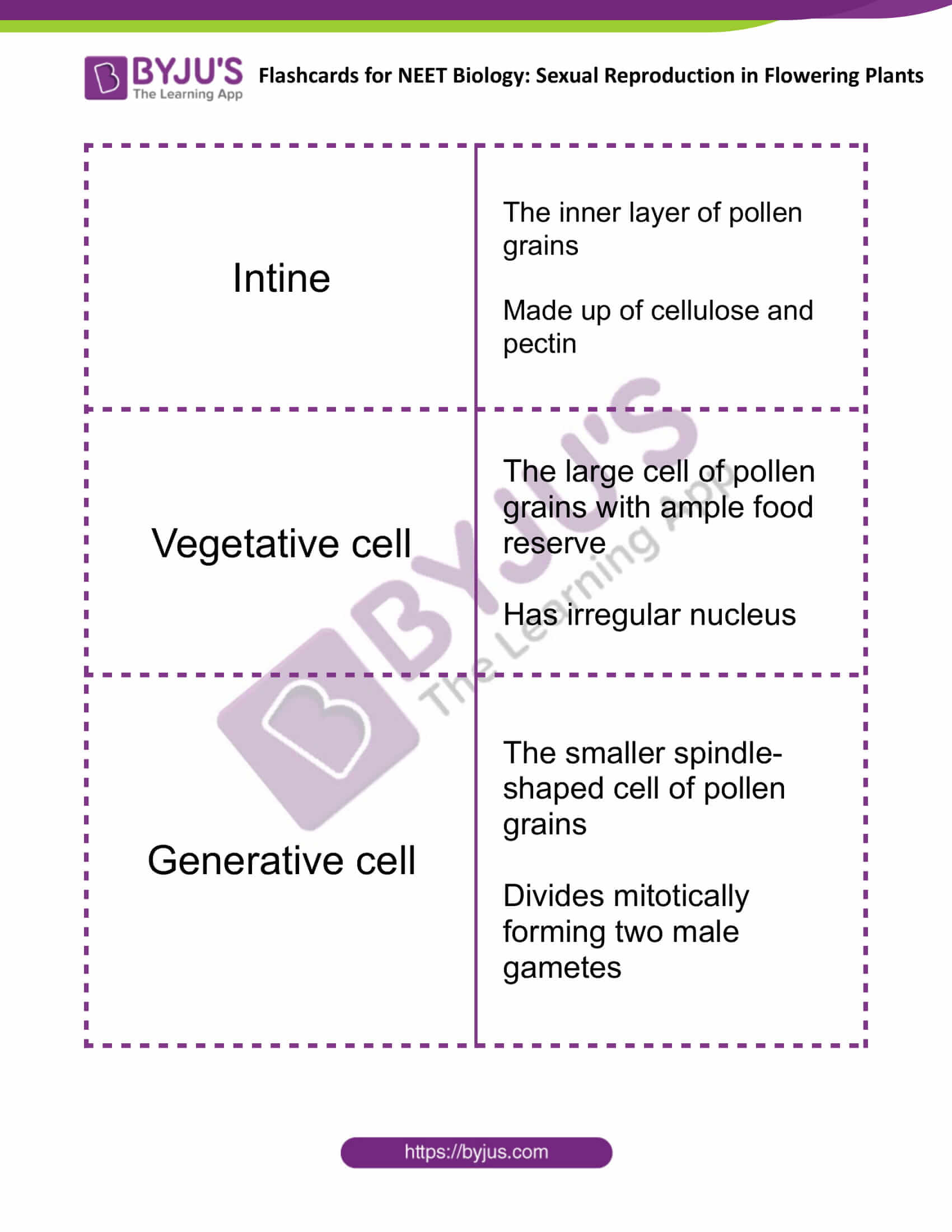
| Intine | The inner layer of pollen grains
Made up of cellulose and pectin |
| Vegetative cell | The large cell of pollen grains with ample food reserve
Has irregular nucleus |
| Generative cell | The smaller spindle-shaped cell of pollen grains
Divides mitotically forming two male gametes |
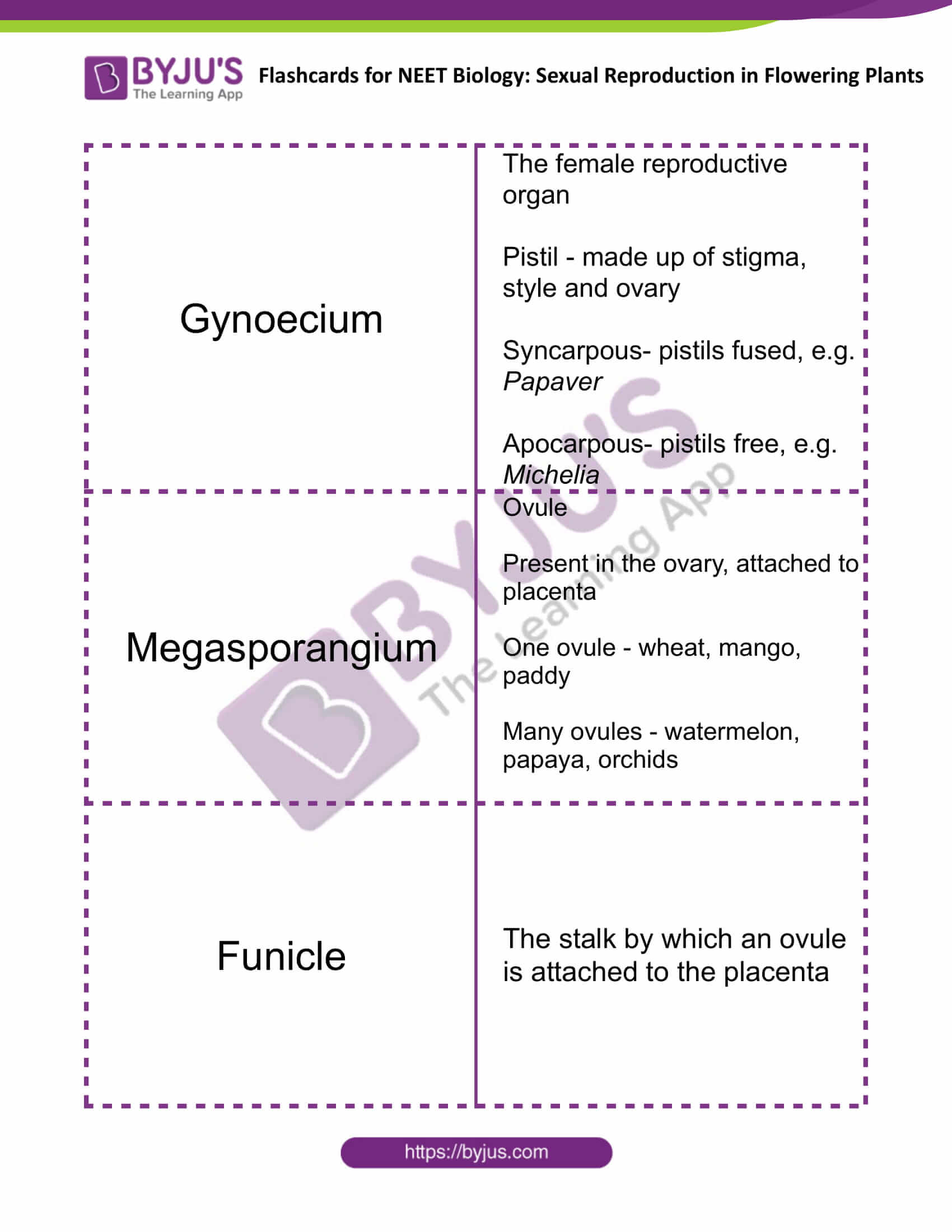
| Gynoecium | The female reproductive organ
Pistil – made up of stigma, style and ovary Syncarpous- pistils fused, e.g. Papaver Apocarpous- pistils free, e.g. Michelia |
| Megasporangium | Ovule
Present in the ovary, attached to placenta One ovule – wheat, mango, paddy Many ovules – watermelon, papaya, orchids |
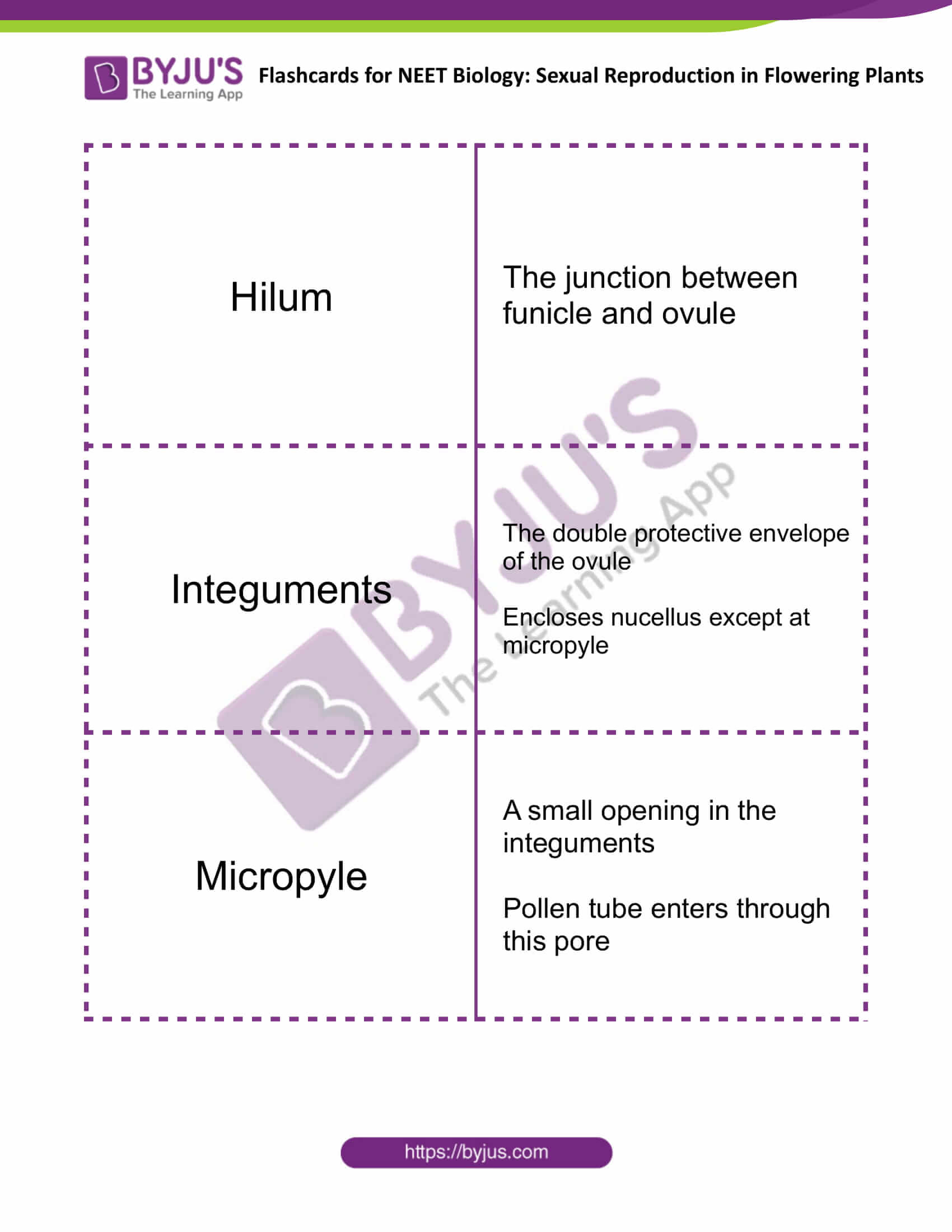
| Funicle | The stalk by which an ovule is attached to the placenta |
| Hilum | The junction between funicle and ovule |
| Integuments | The double protective envelope of the ovule
Encloses nucellus except at micropyle |
| Micropyle | A small opening in the integuments
Pollen tube enters through this pore |
| Chalaza | The basal part of the ovule opposite to the micropylar end
Antipodal cells are present at the chalazal end |
| Megasporogenesis | Formation of megaspores by meiosis in the megaspore mother cell (MMC)
Only one cell at the micropylar end differentiates into the megaspore mother cell |
| Female gametophyte | Embryo sac
Only one of the four megaspores develop into female gametophyte, rest three degenerate |
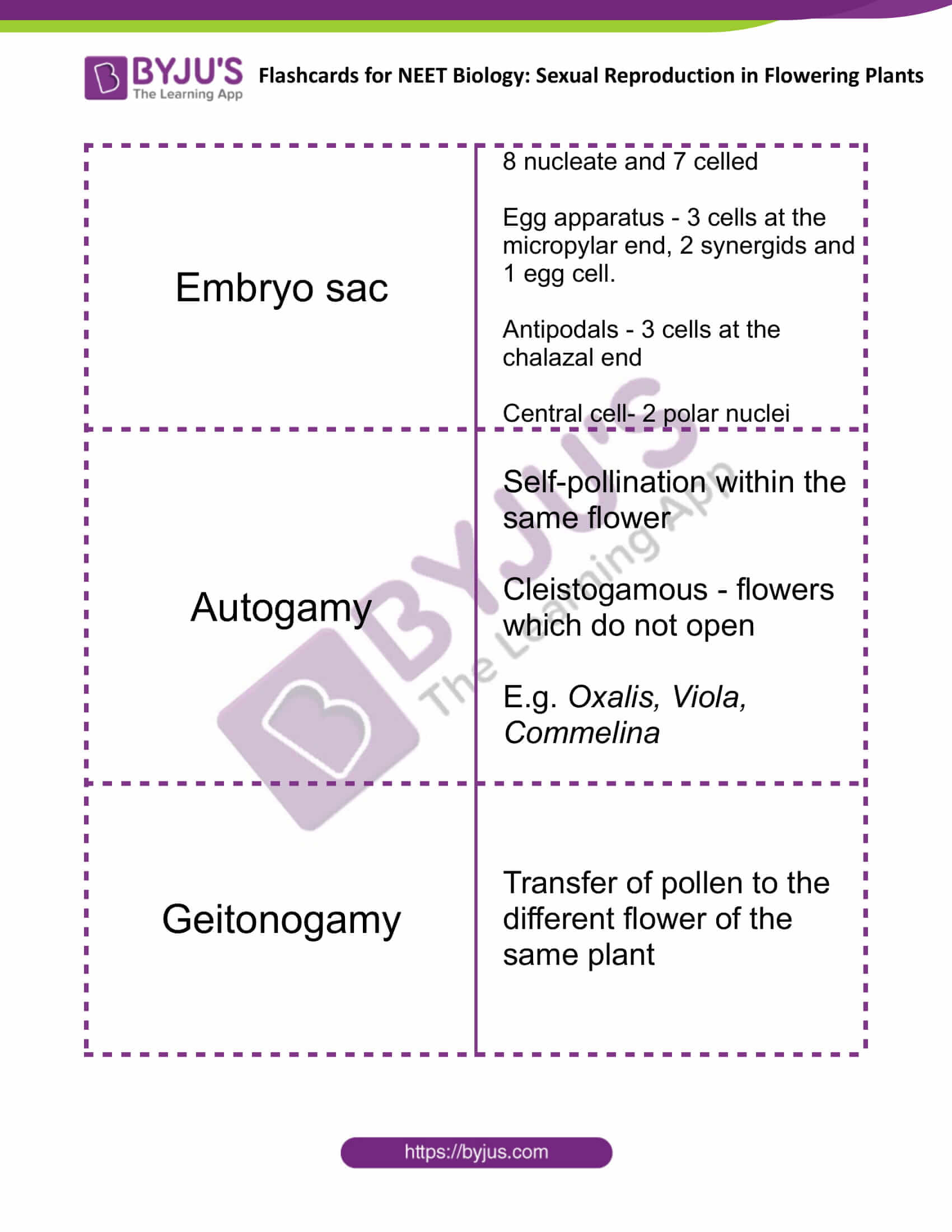
| Embryo sac | 8 nucleate and 7 celled
Egg apparatus – 3 cells at the micropylar end, 2 synergids and 1 egg cell. Antipodals – 3 cells at the chalazal end Central cell- 2 polar nuclei |
| Autogamy | Self-pollination within the same flower
Cleistogamous – flowers which do not open E.g. Oxalis, Viola, Commelina |
| Geitonogamy | Transfer of pollen to the different flower of the same plant |
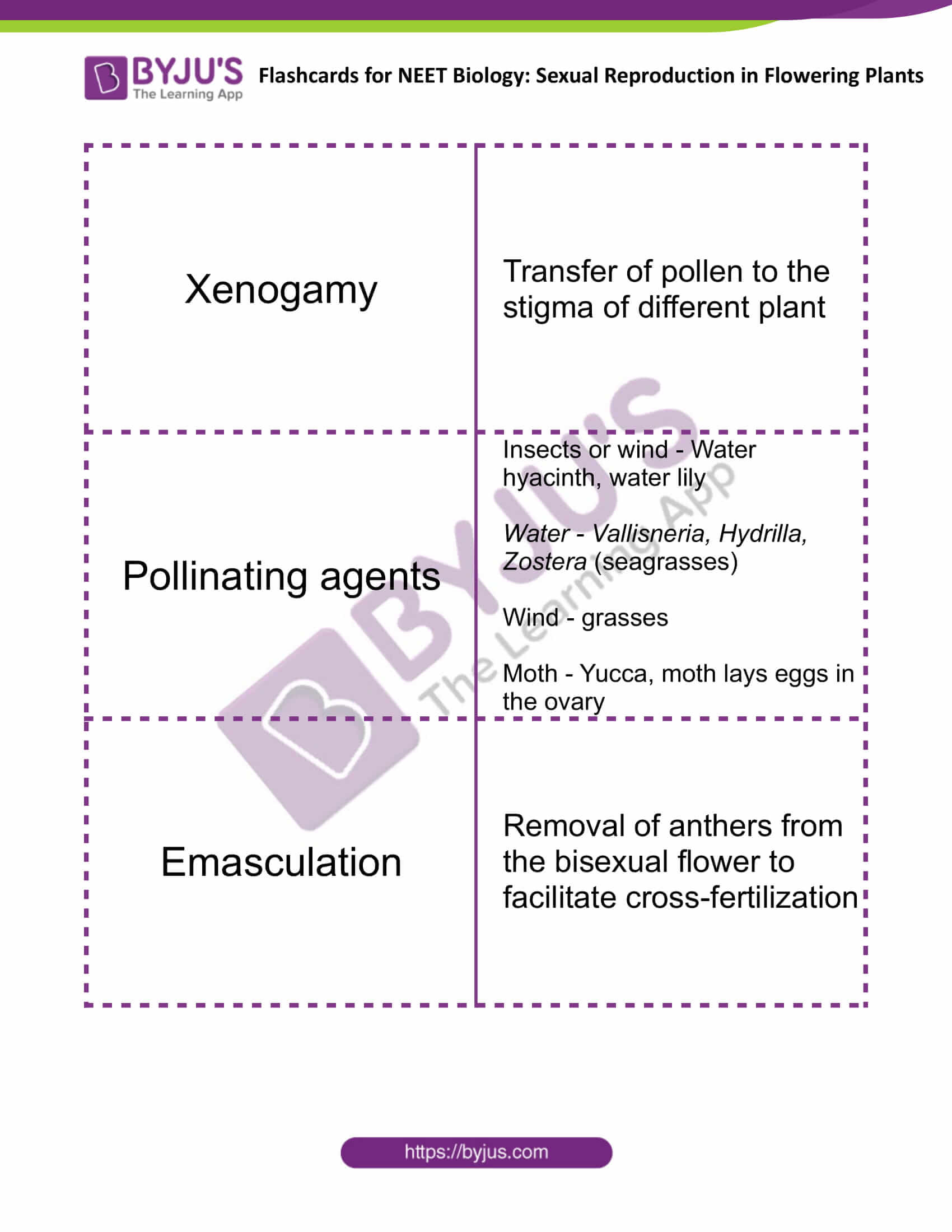
| Xenogamy | Transfer of pollen to the stigma of different plant |
| Pollinating agents | Insects or wind – Water hyacinth, water lily
Water – Vallisneria, Hydrilla, Zostera (seagrasses) Wind – grasses Moth – Yucca, moth lays eggs in the ovary |
| Emasculation | Removal of anthers from the bisexual flower to facilitate cross-fertilization |
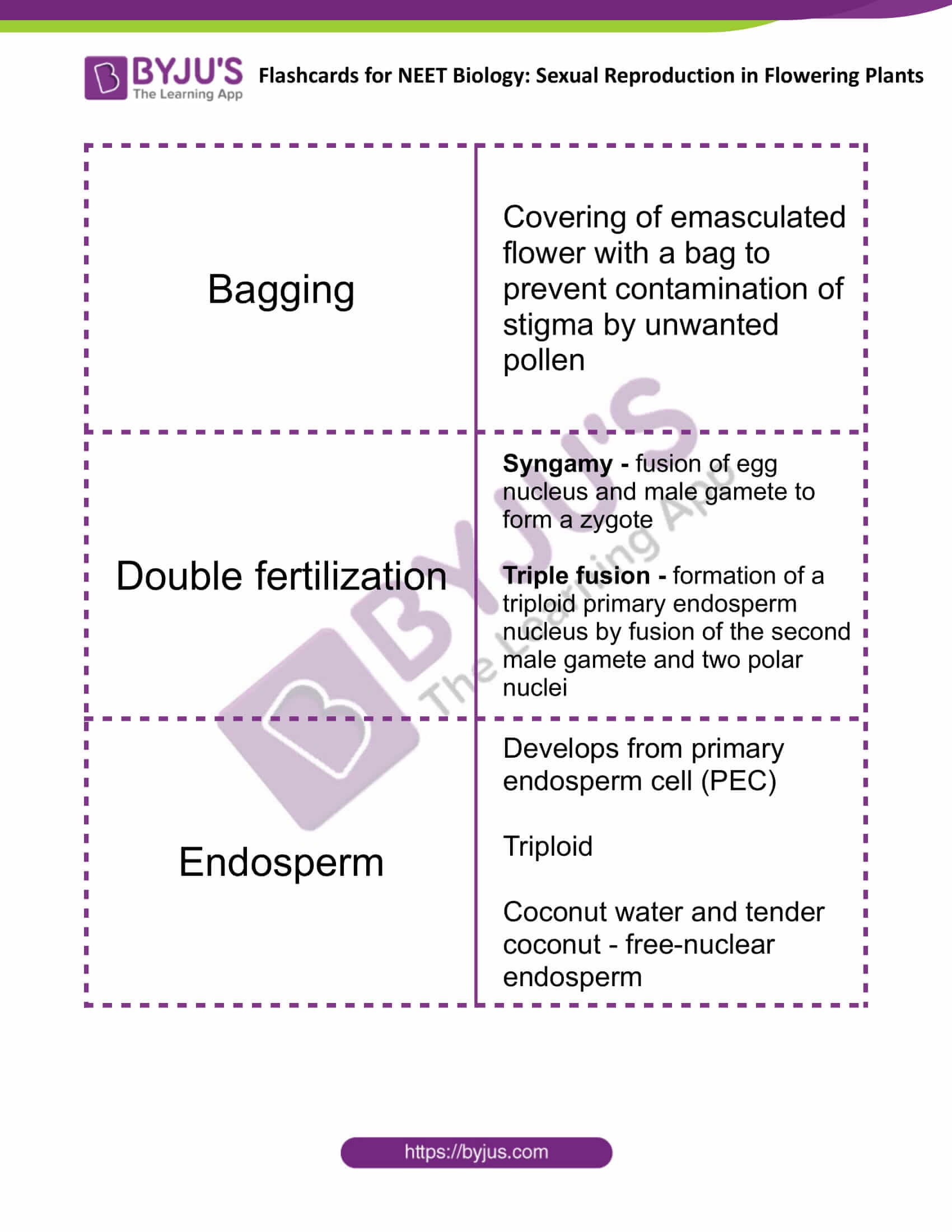
| Bagging | Covering of emasculated flower with a bag to prevent contamination of stigma by unwanted pollen |
| Double fertilization | Syngamy – fusion of egg nucleus and male gamete to form a zygote
Triple fusion – formation of a triploid primary endosperm nucleus by fusion of the second male gamete and two polar nuclei |
| Endosperm | Develops from primary endosperm cell (PEC)
Triploid Coconut water and tender coconut – free-nuclear endosperm |
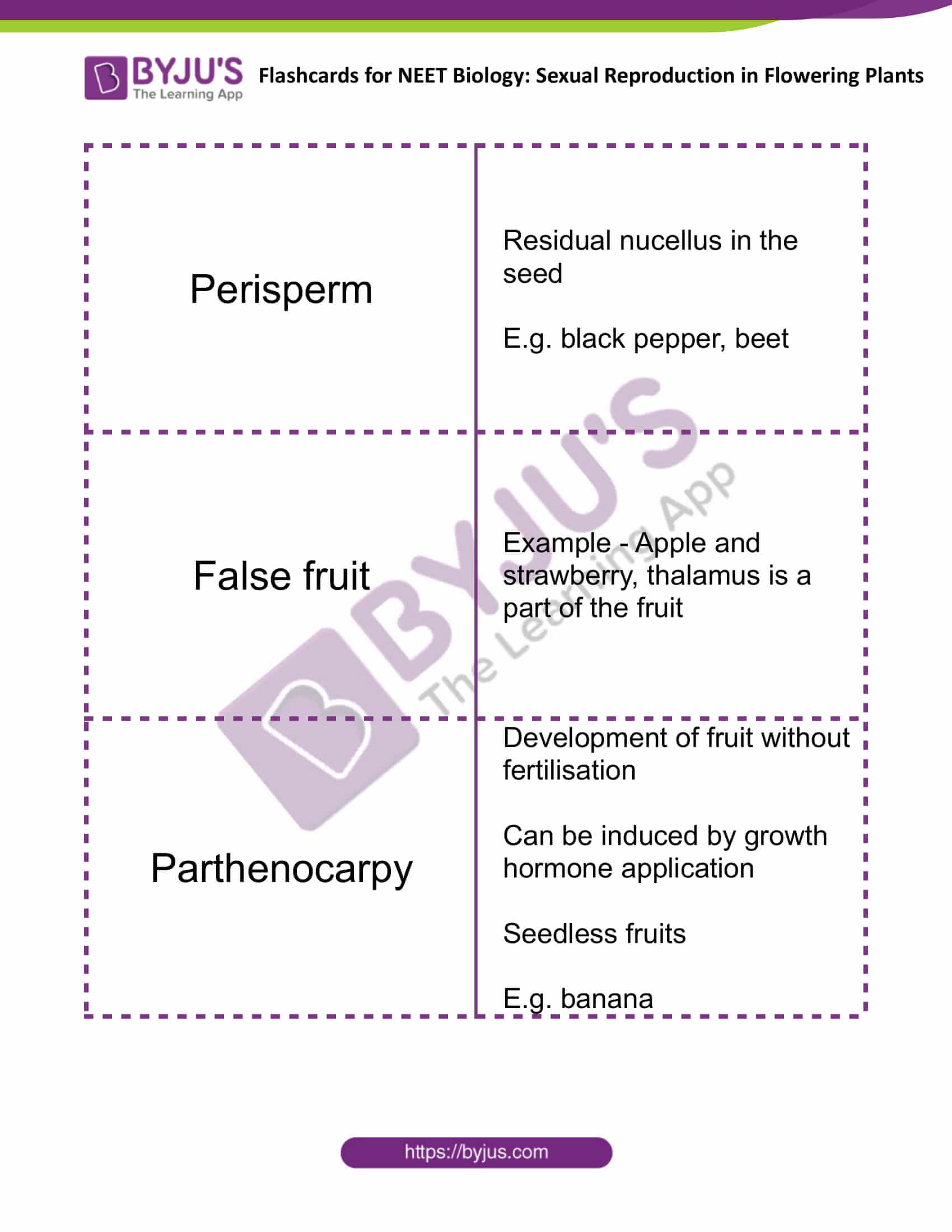
| Perisperm | Residual nucellus in the seed
E.g. black pepper, beet |
| False fruit | Example – Apple and strawberry, thalamus is a part of the fruit |
| Parthenocarpy | Development of fruit without fertilisation
Can be induced by growth hormone application Seedless fruits E.g. banana |
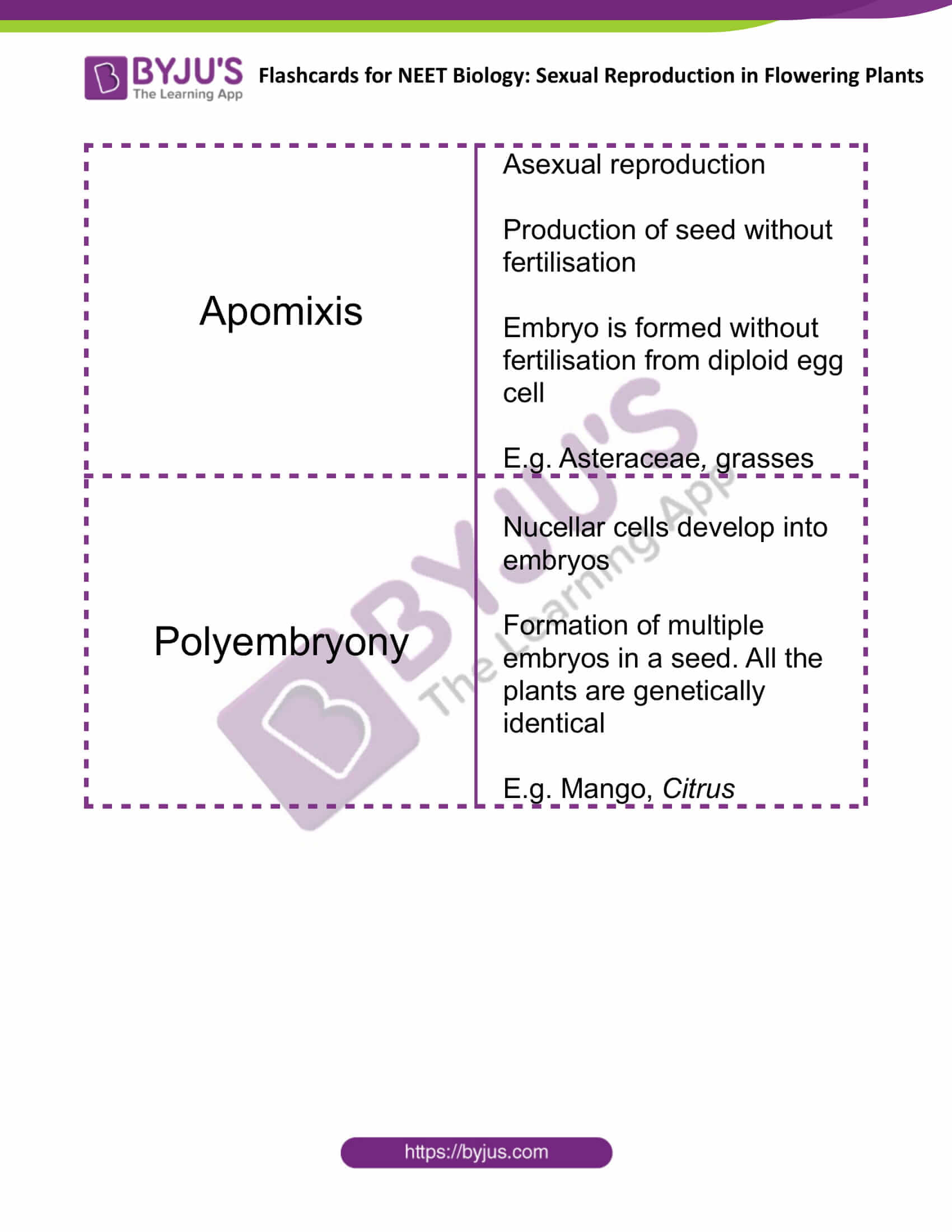
| Apomixis | Asexual reproduction
Production of seed without fertilisation Embryo is formed without fertilisation from diploid egg cell E.g. Asteraceae, grasses |
| Polyembryony | Nucellar cells develop into embryos
Formation of multiple embryos in a seed. All the plants are genetically identical E.g. Mango, Citrus |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Transport In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Mineral Nutrition
NEET Flashcards: Photosynthesis In Higher Plants
NEET Flashcards: Respiration In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Plant Growth And Development
Recommended Videos:





Comments