Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Biodiversity and Conservation. These flashcards on Biodiversity and Conservation are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Biodiversity and Conservation, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Biodiversity and Conservation
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Biodiversity and Conservation | NEET exams |
| Genetic diversity | Genetic variability existing within a species
E.g. 50,000 varieties of rice and 1000 varieties of mango exist in India, the concentration of reserpine differs in the different strains of Rauwolfia vomitoria |
| Species diversity | Different types of species and their relative abundance in an ecosystem
David Tilman experimentally showed that higher species diversity leads to less year-to-year variation and higher productivity in an ecosystem |
| Species richness | Number of different species present in an ecosystem
Species richness contributes to more stable communities |
| Species evenness | It refers to the abundance of all the species in an ecosystem
High evenness contributes to greater species diversity |
| Ecological diversity | It refers to different types of ecosystems pertaining to a geographical area |
| Global biodiversity | Robert May estimated that ~7 million species of plants and animals exist globally, ~1.5 million have already been described
70% are animals, out of which 70% are insects 22% are plants including algae, fungi, bryophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms Amazon rain forest in South America has the greatest biodiversity |
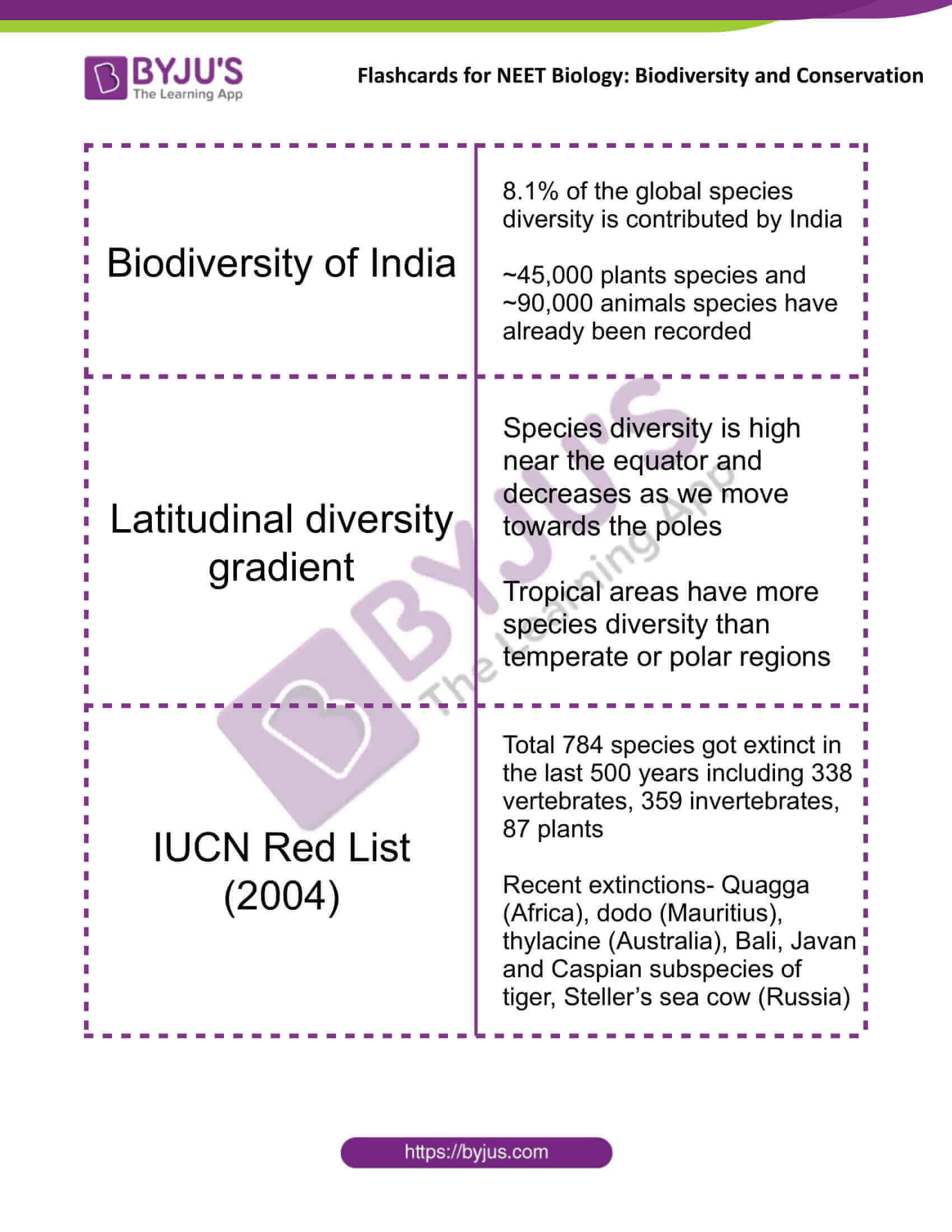
| Biodiversity of India | 8.1% of the global species diversity is contributed by India
~45,000 plants species and ~90,000 animals species have already been recorded |
| Latitudinal diversity gradient | Species diversity is high near the equator and decreases as we move towards the poles
Tropical areas have more species diversity than temperate or polar regions |
| IUCN Red List (2004) | Total 784 species got extinct in the last 500 years including 338 vertebrates, 359 invertebrates, 87 plants
Recent extinctions- Quagga (Africa), dodo (Mauritius), thylacine (Australia), Bali, Javan and Caspian subspecies of tiger, Steller’s sea cow (Russia) |
| The Evil Quartet | Refers to the four major causes of biodiversity loss
Loss of habitat, over-exploitation, alien species invasions, co-extinctions |
| “Lungs of the planet” | Amazon rain forest
They contribute to 20% of the total oxygen present in the earth’s atmosphere through photosynthesis |
| Alien species | Non-native invasive species introduced in an area. They may lead to modification of an ecosystem and indigenous species
E.g. The Nile perch caused the extinction of 200 species of cichlid fish in Lake Victoria, invasive weed species such as Parthenium, Lantana, Eicchornia, etc. |
| Keystone species | Conceptualised by Robert T. Paine
Species that have a large effect on its ecosystem and play a critical role to maintain its structure E.g. large predator species such as sharks, sea otter in kelp forest, Gray wolves in greater Yellowstone, etc. |
| Endemic species | Species that are native to a particular area and not found anywhere else
E.g. Asiatic lion, Nilgiri Tahr, Pygmy Hog, Glacier bear, Nepenthes khasiana, etc. |
| Stratification | Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels
E.g. tree at the top, followed by shrubs and then herbs and grasses |
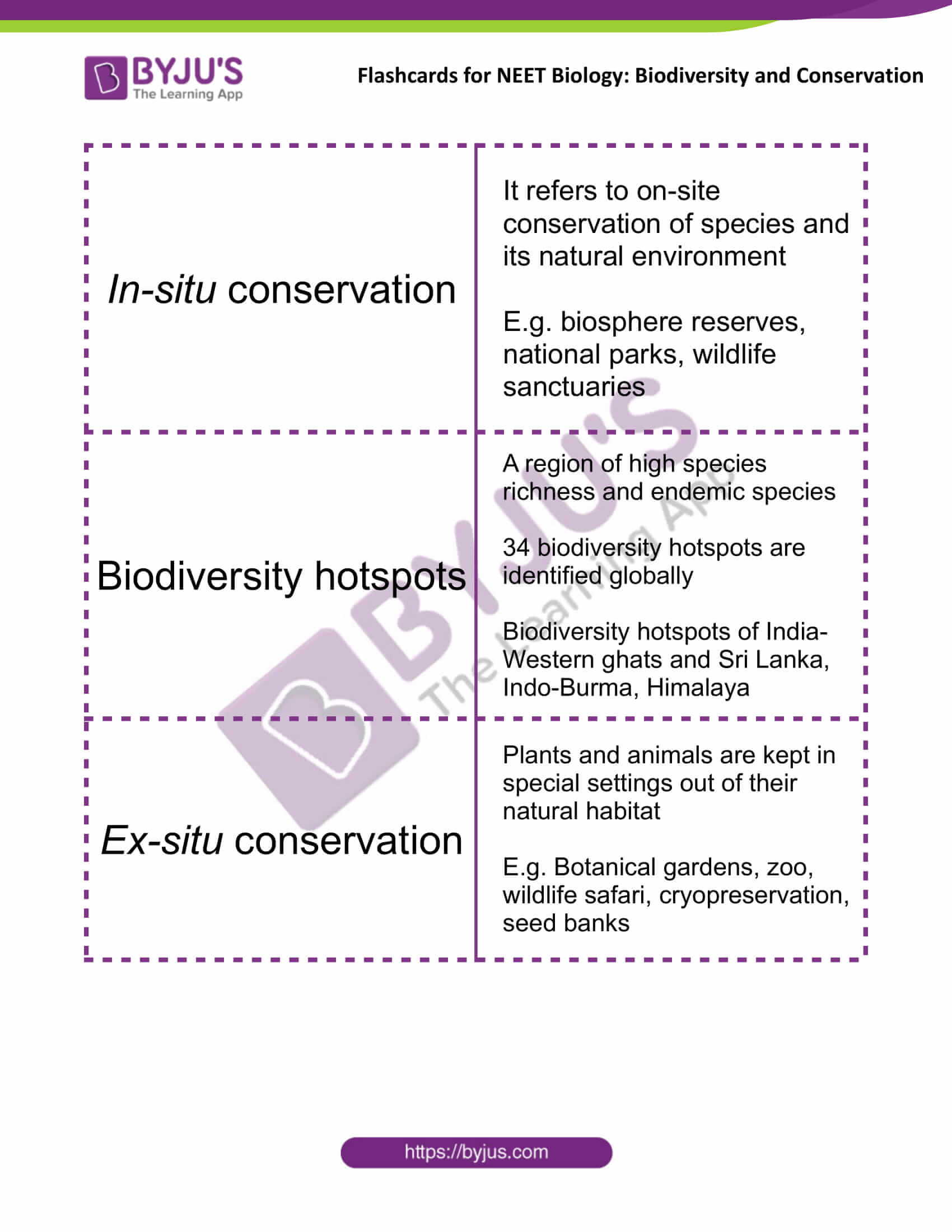
| In-situ conservation | It refers to on-site conservation of species and its natural environment
E.g. biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries |
| Biodiversity hotspots | A region of high species richness and endemic species
34 biodiversity hotspots are identified globally Biodiversity hotspots of India- Western ghats and Sri Lanka, Indo-Burma, Himalaya |
| Ex-situ conservation | Plants and animals are kept in special settings out of their natural habitat
E.g. Botanical gardens, zoo, wildlife safari, cryopreservation, seed banks |
| The Earth Summit | United Nations Conference on Environment and Development
Held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 |
| World Summit on Sustainable Development | Held in Johannesburg in 2002
190 countries took part and pledged to reduce biodiversity loss significantly by 2010 |
| Sacred Groves | Short forest fragments, which are protected by rural communities and have religious significance
It is a method of biodiversity conservation as commercial activities are prohibited in that area |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:

Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Organisms And Populations
NEET Flashcards: Environmental Issues
NEET Flashcards: Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production





Comments