Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Human Reproduction. These flashcards on Human Reproduction are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Human Reproduction, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Human Reproduction
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Human Reproduction | NEET exams |
| Human Reproduction | |
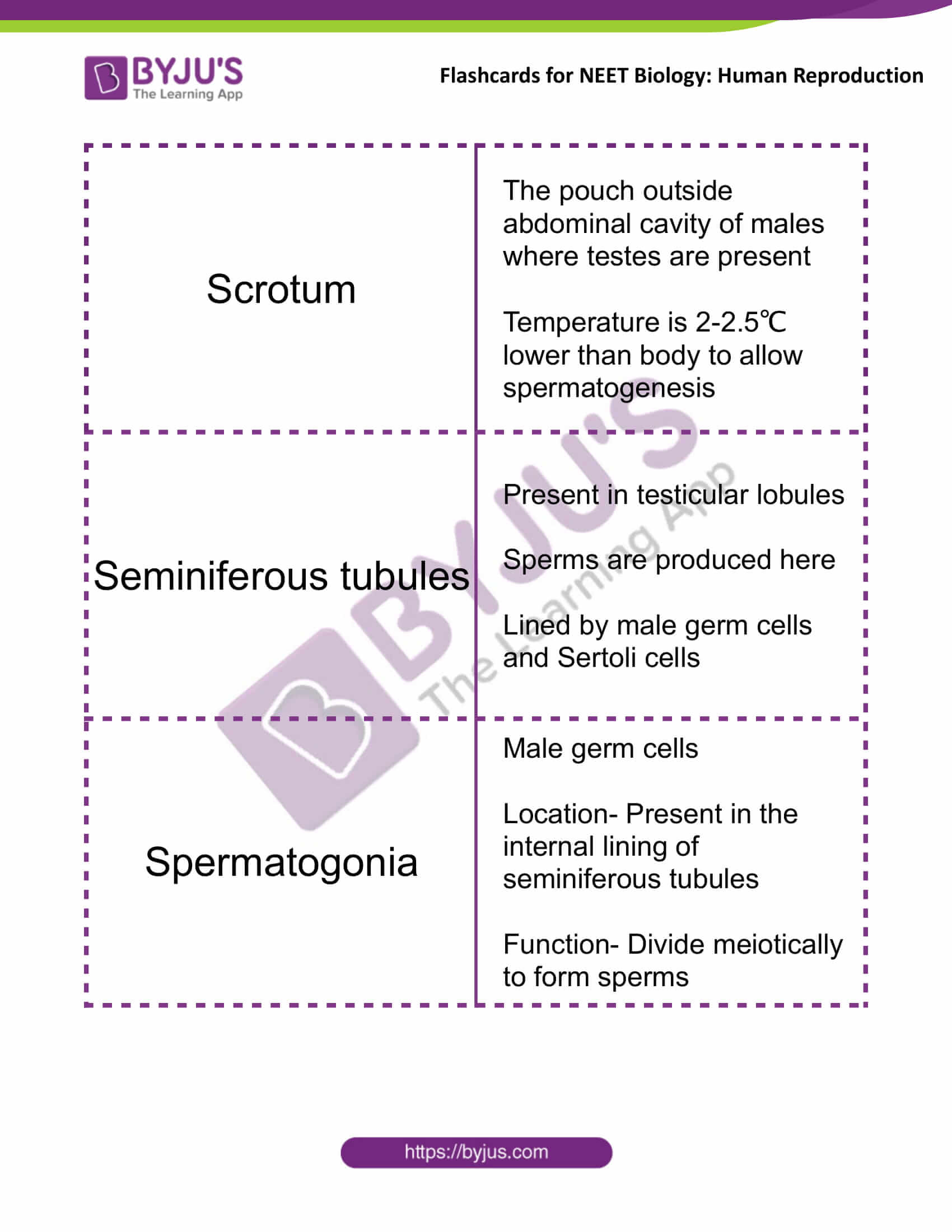
| Scrotum | The pouch outside abdominal cavity of males where testes are present
Temperature is 2-2.5℃ lower than body to allow spermatogenesis |
| Seminiferous tubules | Present in testicular lobules
Sperms are produced here Lined by male germ cells and Sertoli cells |
| Spermatogonia | Male germ cells
Location- Present in the internal lining of seminiferous tubules Function- Divide meiotically to form sperms |
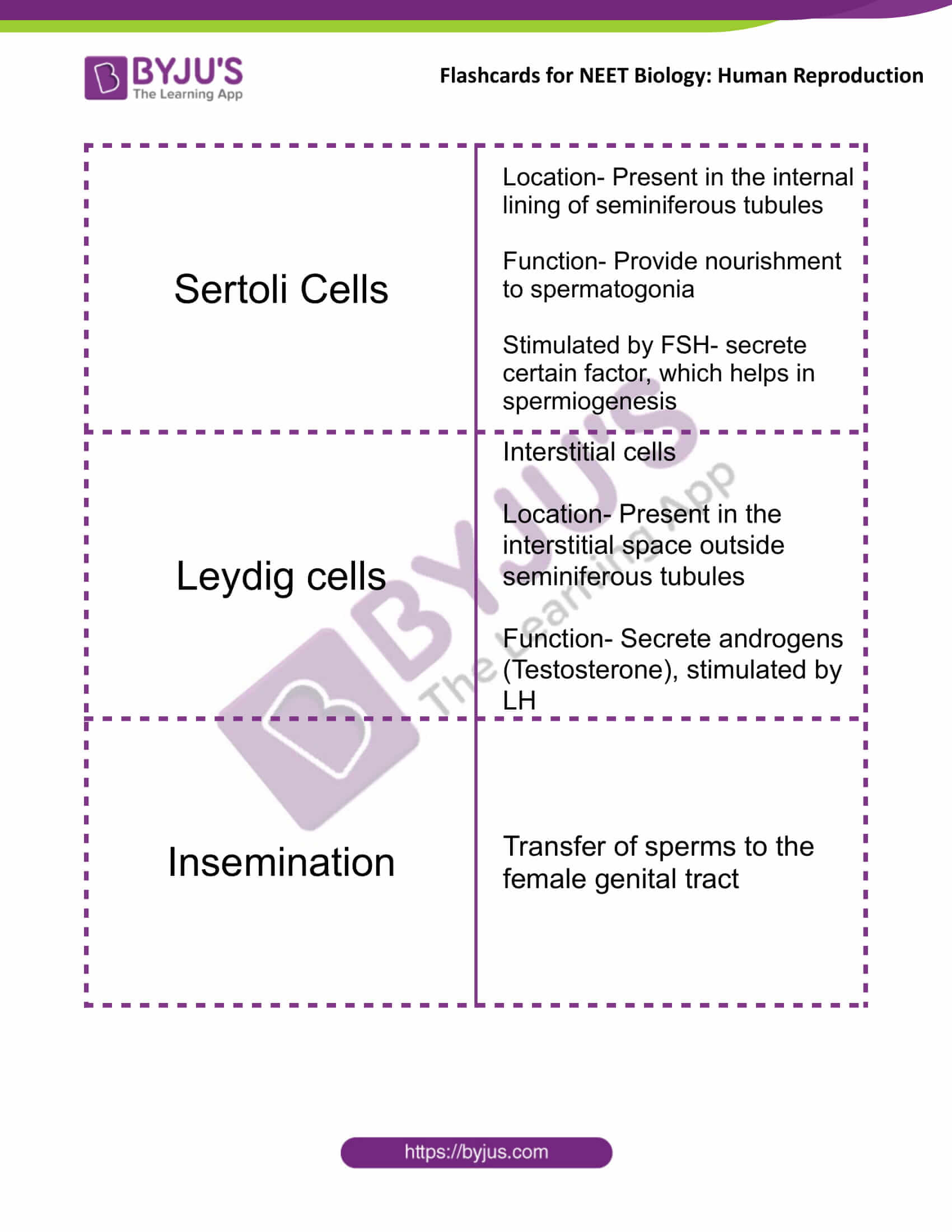
| Sertoli Cells | Location- Present in the internal lining of seminiferous tubules
Function- Provide nourishment to spermatogonia Stimulated by FSH- secrete certain factor, which helps in spermiogenesis |
| Leydig cells | Interstitial cells
Location- Present in the interstitial space outside seminiferous tubules Function- Secrete androgens (Testosterone), stimulated by LH |
| Insemination | Transfer of sperms to the female genital tract |
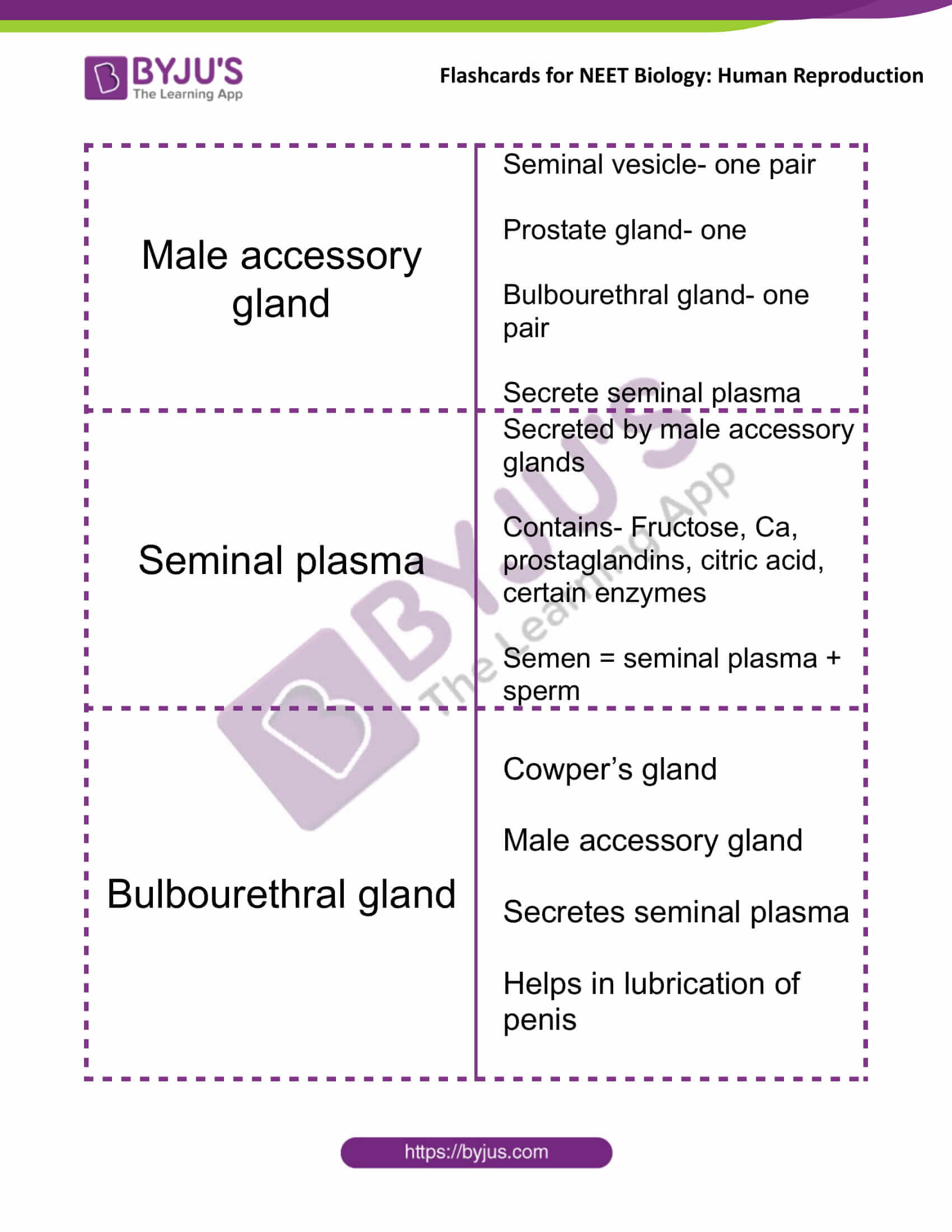
| Male accessory gland | Seminal vesicle- one pair
Prostate gland- one Bulbourethral gland- one pair Secrete seminal plasma |
| Seminal plasma | Secreted by male accessory glands
Contains- Fructose, Ca, prostaglandins, citric acid, certain enzymes Semen = seminal plasma + sperm |
| Bulbourethral gland | Cowper’s gland
Male accessory gland Secretes seminal plasma Helps in lubrication of penis |
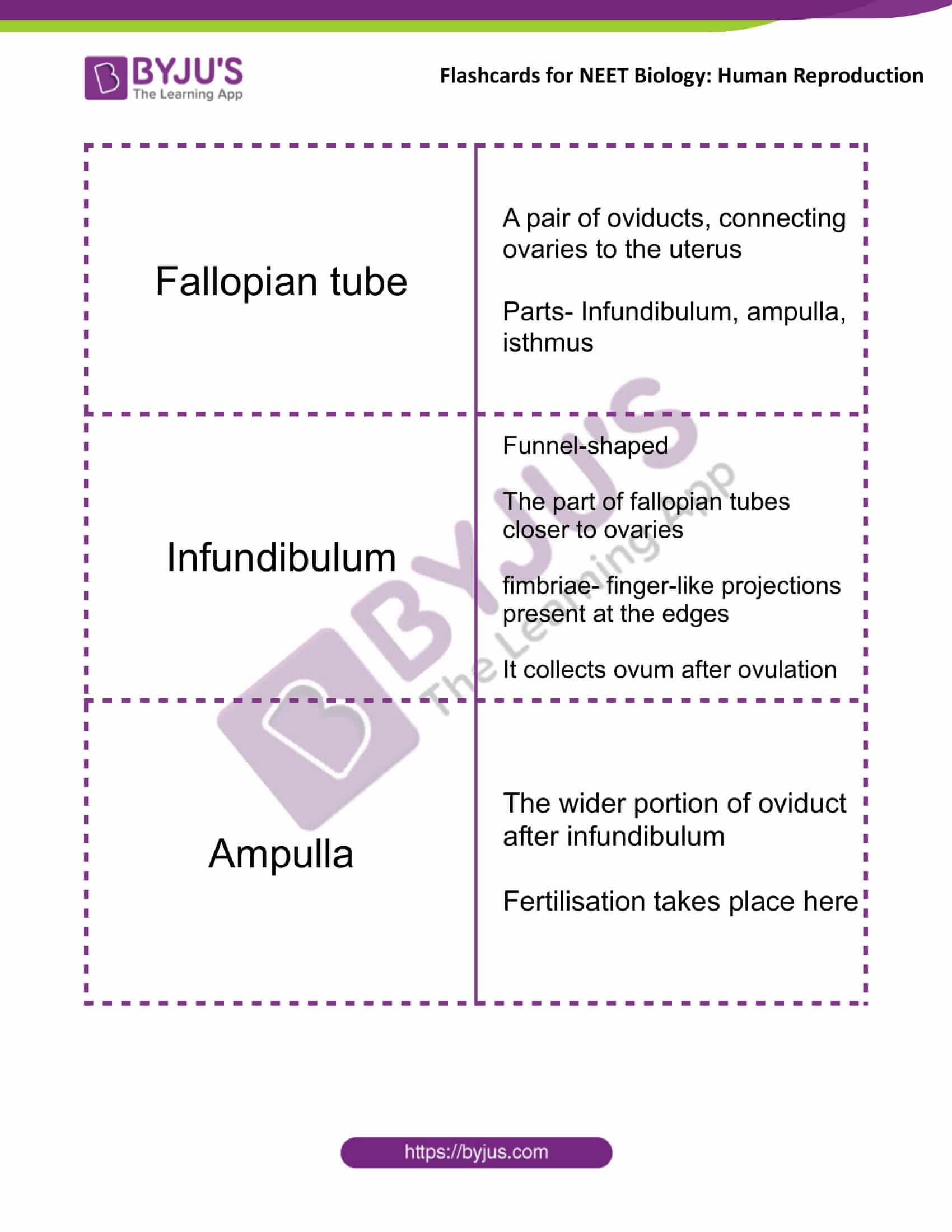
| Fallopian tube | A pair of oviducts, connecting ovaries to the uterus
Parts- Infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus |
| Infundibulum | Funnel-shaped
The part of fallopian tubes closer to ovaries fimbriae- finger-like projections present at the edges It collects ovum after ovulation |
| Ampulla | The wider portion of oviduct after infundibulum
Fertilisation takes place here |
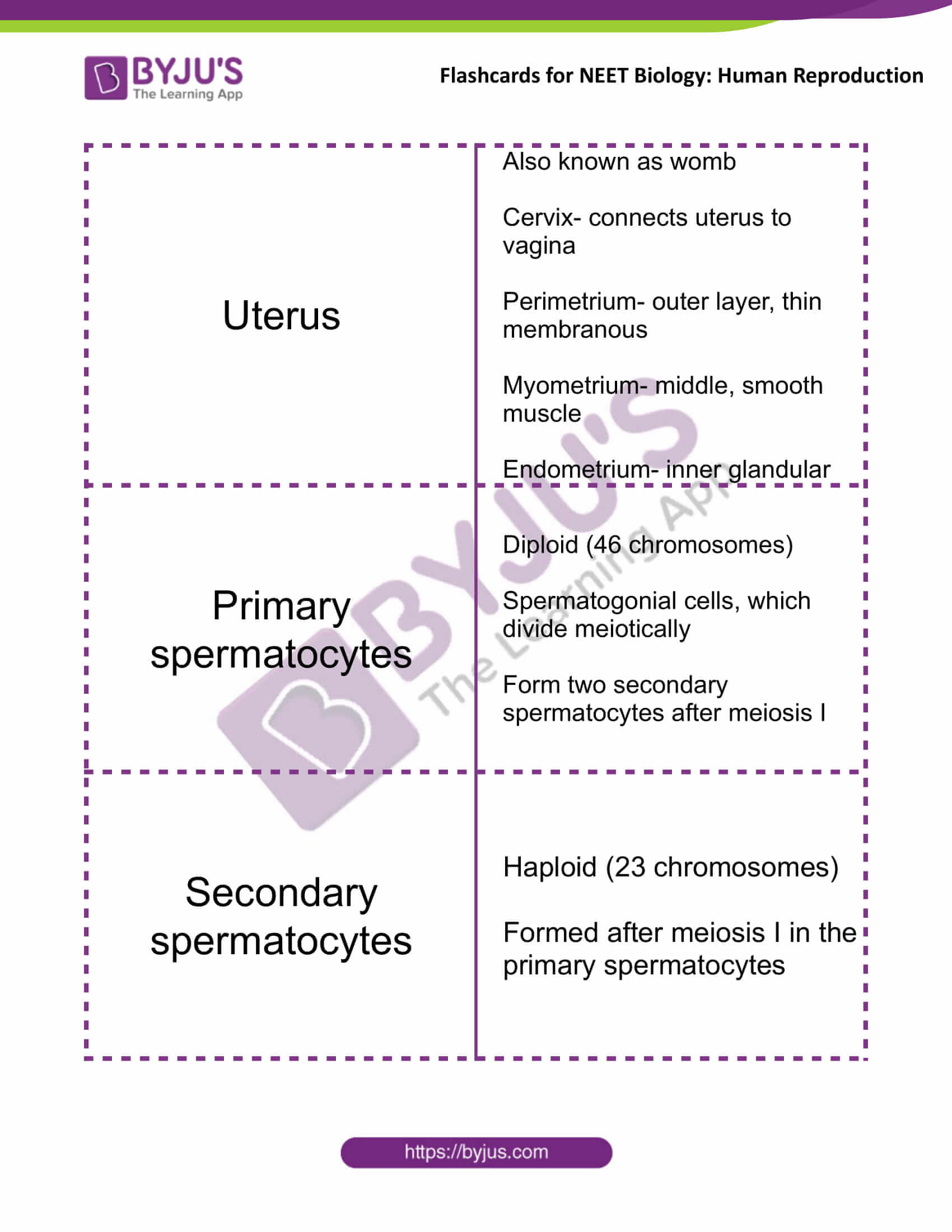
| Uterus | Also known as womb
Cervix- connects uterus to vagina Perimetrium- outer layer, thin membranous Myometrium- middle, smooth muscle Endometrium- inner glandular |
| Primary spermatocytes | Diploid (46 chromosomes)
Spermatogonial cells, which divide meiotically Form two secondary spermatocytes after meiosis I |
| Secondary spermatocytes | Haploid (23 chromosomes)
Formed after meiosis I in the primary spermatocytes |
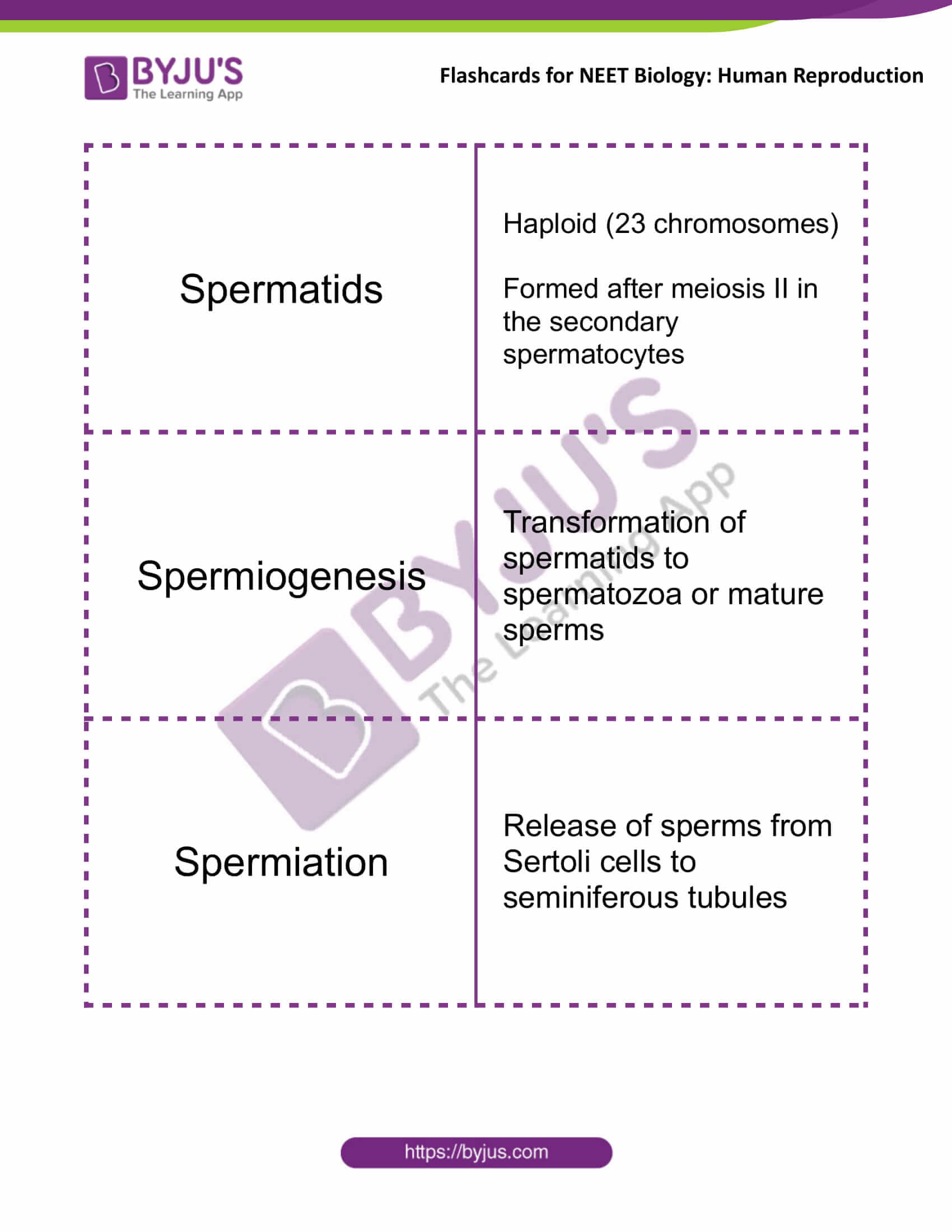
| Spermatids | Haploid (23 chromosomes)
Formed after meiosis II in the secondary spermatocytes |
| Spermiogenesis | Transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa or mature sperms |
| Spermiation | Release of sperms from Sertoli cells to seminiferous tubules |
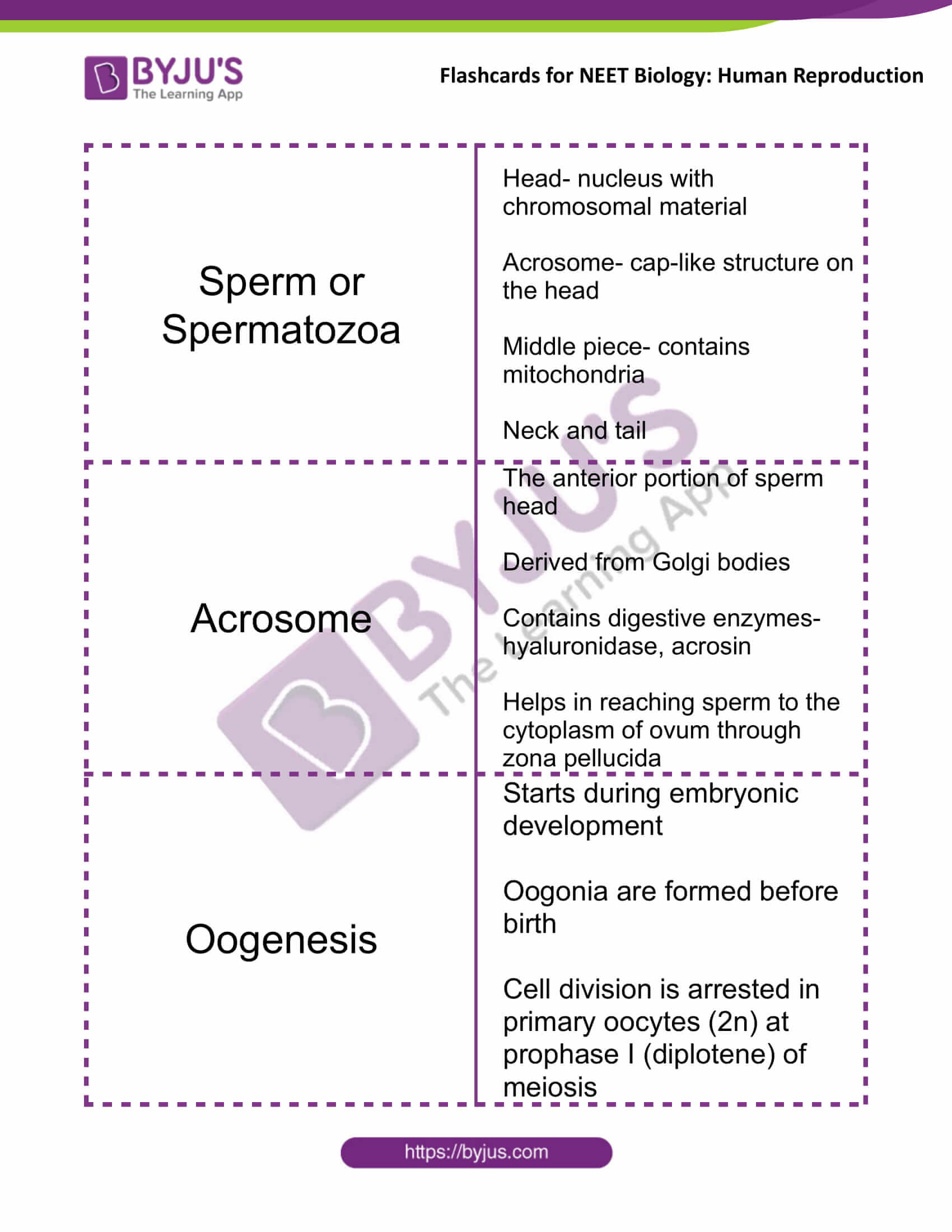
| Sperm or Spermatozoa | Head- nucleus with chromosomal material
Acrosome- cap-like structure on the head Middle piece- contains mitochondria Neck and tail |
| Acrosome | The anterior portion of sperm head
Derived from Golgi bodies Contains digestive enzymes- hyaluronidase, acrosin Helps in reaching sperm to the cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida |
| Oogenesis | Starts during embryonic development
Oogonia are formed before birth Cell division is arrested in primary oocytes (2n) at prophase I (diplotene) of meiosis |
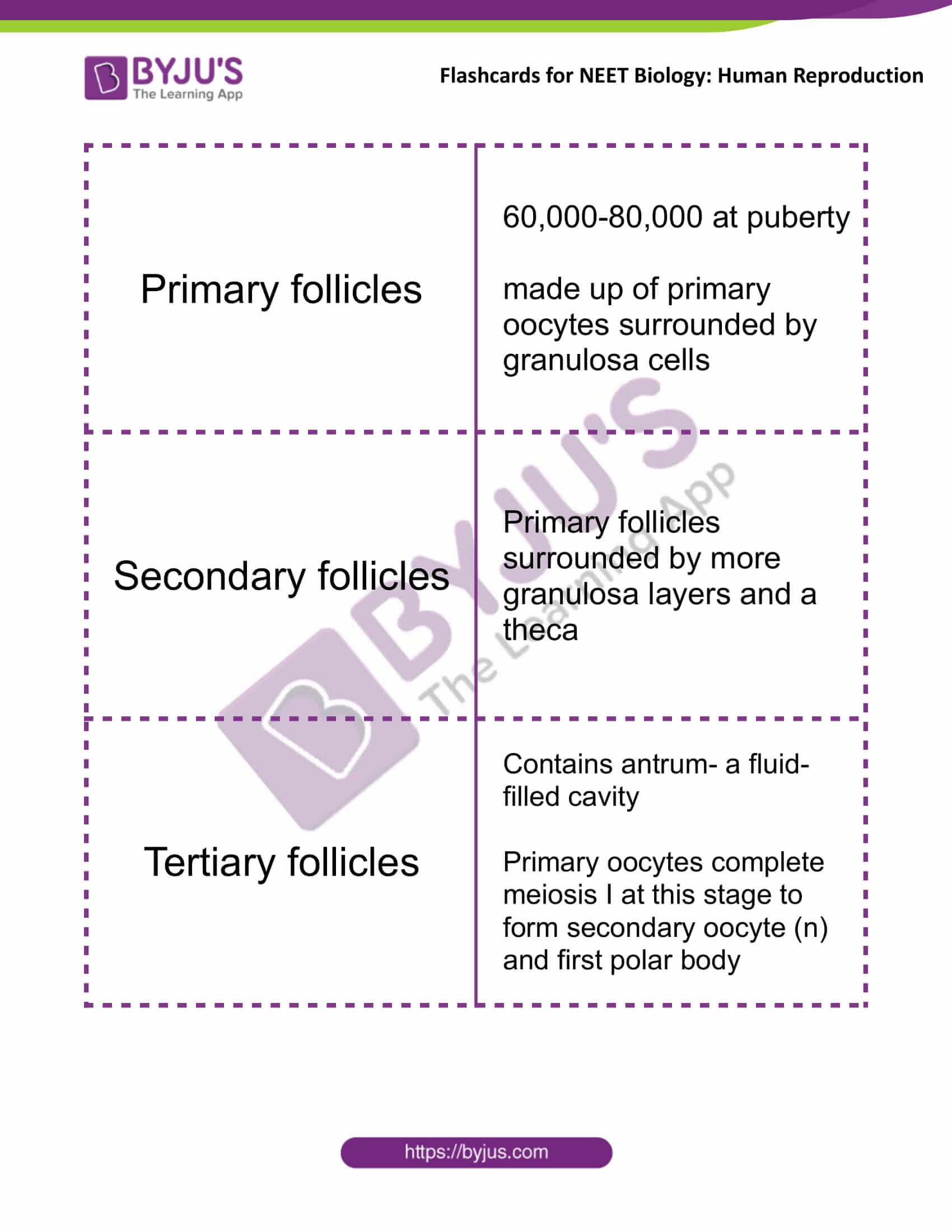
| Primary follicles | 60,000-80,000 at puberty
made up of primary oocytes surrounded by granulosa cells |
| Secondary follicles | Primary follicles surrounded by more granulosa layers and a theca |
| Tertiary follicles | Contains antrum- a fluid-filled cavity
Primary oocytes complete meiosis I at this stage to form secondary oocyte (n) and first polar body |
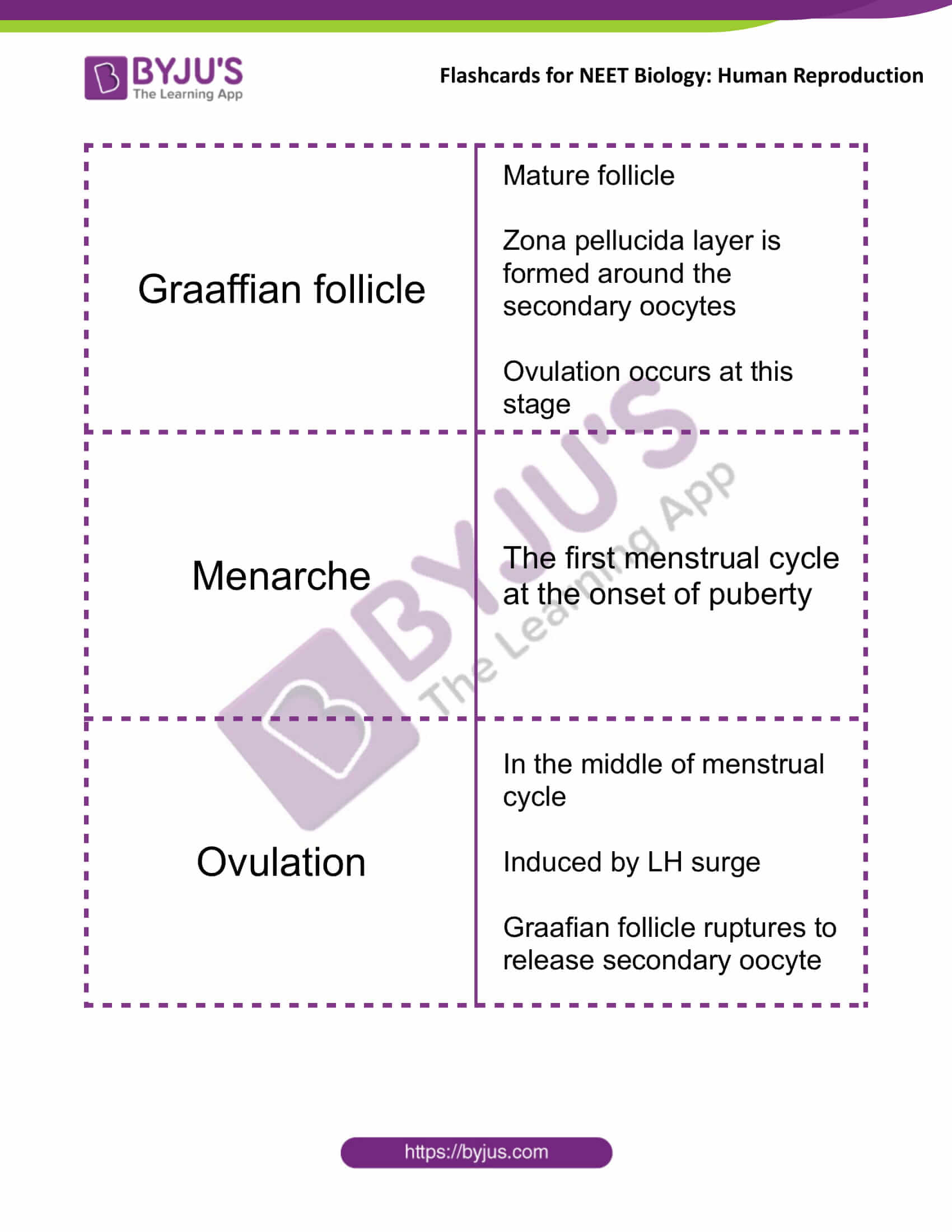
| Graaffian follicle | Mature follicle
Zona pellucida layer is formed around the secondary oocytes Ovulation occurs at this stage |
| Menarche | The first menstrual cycle at the onset of puberty |
| Ovulation | In the middle of menstrual cycle
Induced by LH surge Graafian follicle ruptures to release secondary oocyte |
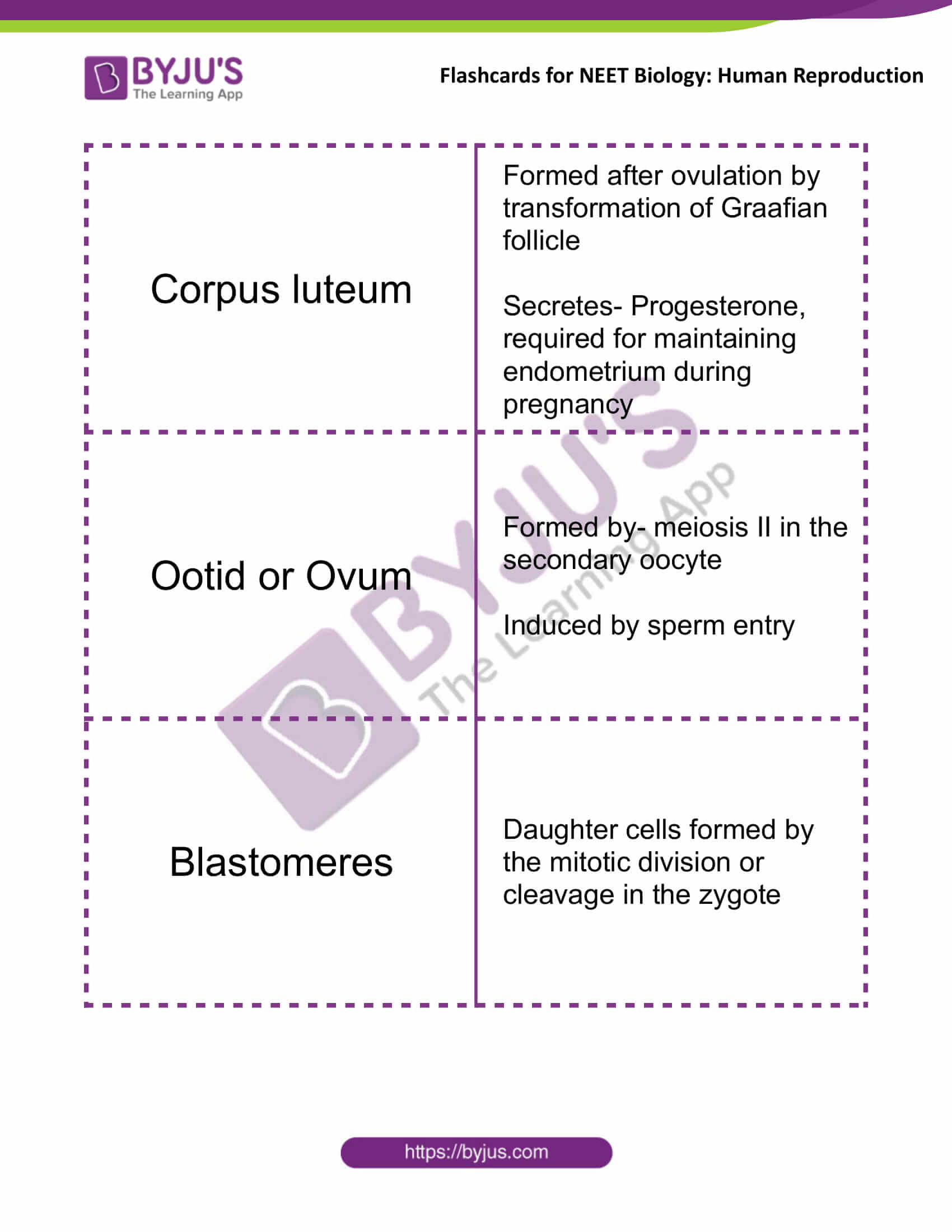
| Corpus luteum | Formed after ovulation by transformation of Graafian follicle
Secretes- Progesterone, required for maintaining endometrium during pregnancy |
| Ootid or Ovum | Formed by- meiosis II in the secondary oocyte
Induced by sperm entry |
| Blastomeres | Daughter cells formed by the mitotic division or cleavage in the zygote |
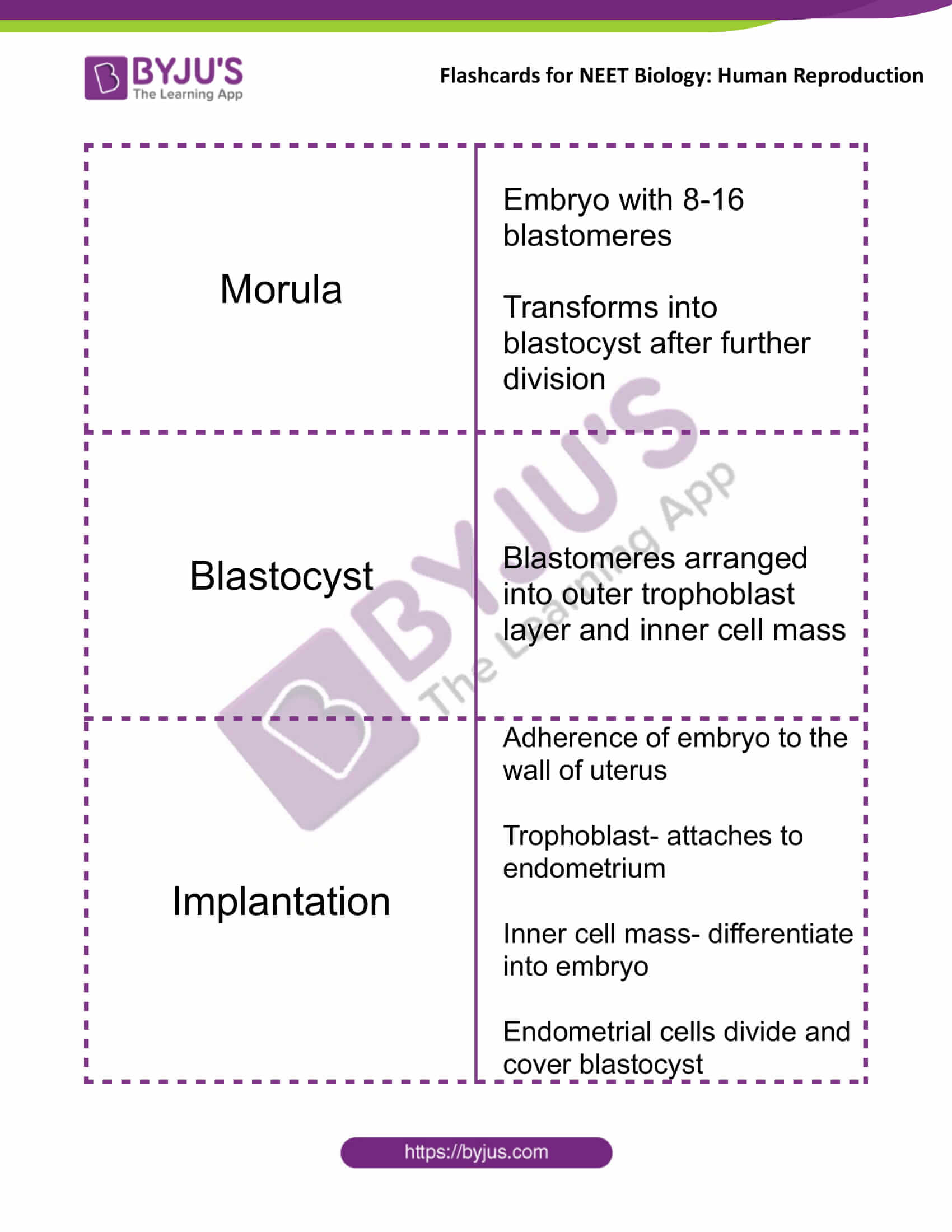
| Morula | Embryo with 8-16 blastomeres
Transforms into blastocyst after further division |
| Blastocyst | Blastomeres arranged into outer trophoblast layer and inner cell mass |
| Implantation | Adherence of embryo to the wall of uterus
Trophoblast- attaches to endometrium Inner cell mass- differentiate into embryo Endometrial cells divide and cover blastocyst |
| Placenta | Formed by interdigitated chorionic villi and uterine tissue
A connecting link between developing embryo and mother, IgG can cross placenta Facilitate gaseous exchange and removal of excretory waste Secretes hormones- hCG, estrogens, progestogens |
| Chorionic villi | Finger-like projections on trophoblast formed after implantation |
| Embryonic development | First month- heart is formed
Second month- limbs and digits First trimester- external genital organs and most of the other organs Fifth month- hair on the head and movement of foetus Second trimester- body hair, eyelids, eyelashes |
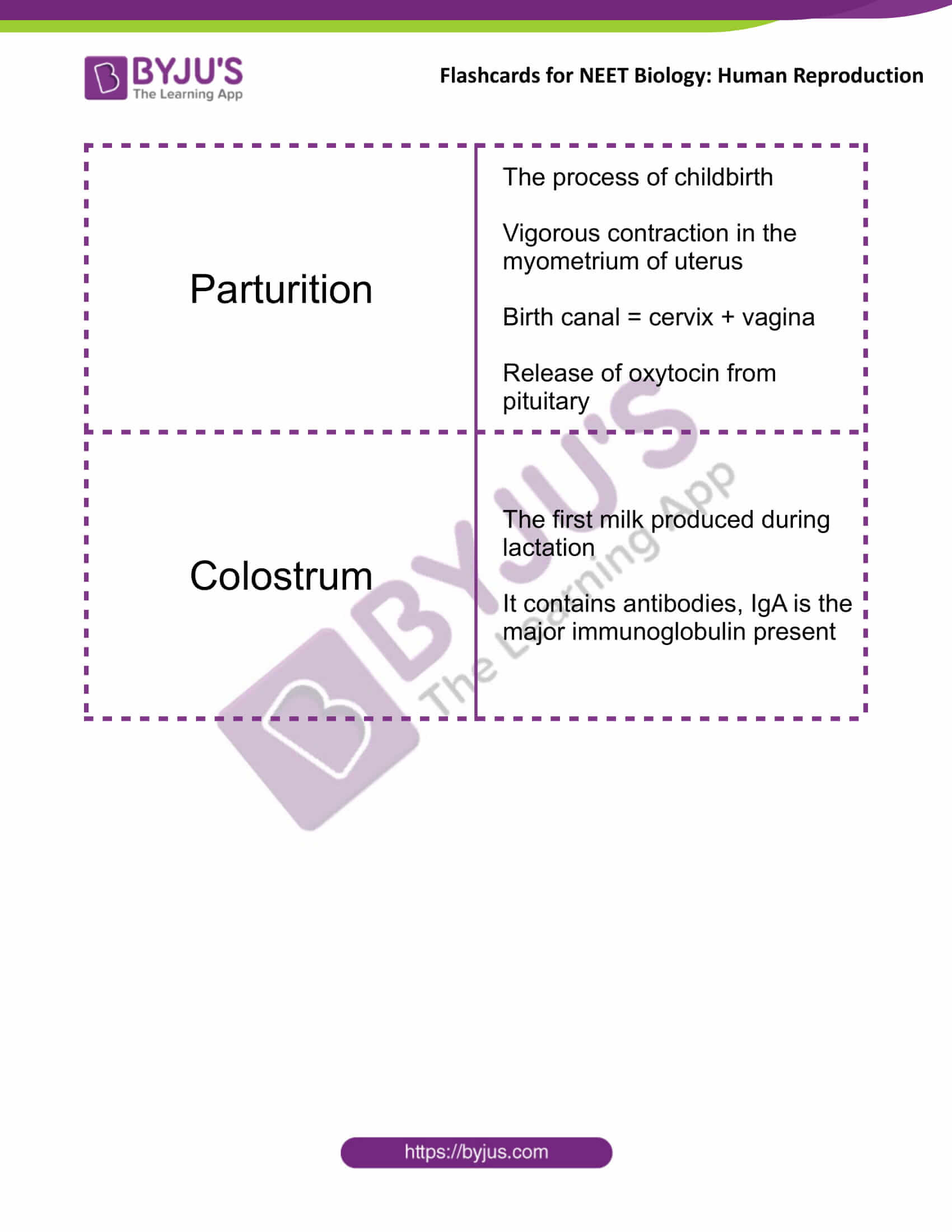
| Parturition | The process of childbirth
Vigorous contraction in the myometrium of uterus Birth canal = cervix + vagina Release of oxytocin from pituitary |
| Colostrum | The first milk produced during lactation
It contains antibodies, IgA is the major immunoglobulin present |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Videos:



Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Reproduction In Organisms
NEET Flashcards: Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
NEET Flashcards: Reproductive Health

Comments