Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Excretory Products and their Elimination. These flashcards on Excretory Products and their Elimination are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Excretory Products and their Elimination, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Recommended Videos:


Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Excretory Products and their Elimination
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Excretory Products and their Elimination | NEET exams |
| Ammonotelic animals | Aquatic amphibians, aquatic insects, bony fishes
Ammonia is the most toxic excretory product and requires a large amount of water |
| Ureotelic animals | Terrestrial amphibians, marine fishes and mammals
Produced in liver and filtered by kidneys for excretion |
| Uricotelic animals | Insects, land snails, reptiles and birds
Least toxic and requires minimum water for excretion |
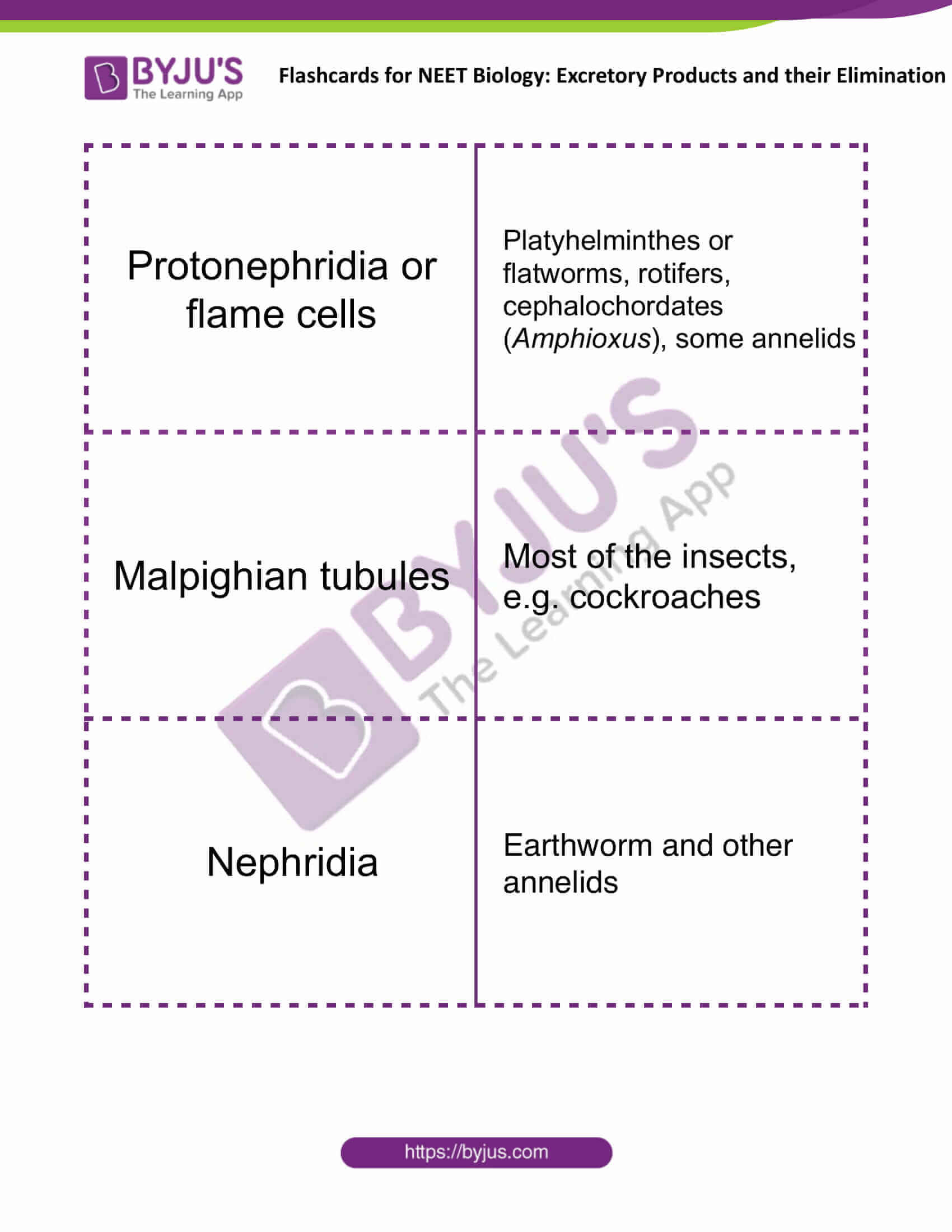
| Protonephridia or flame cells | Platyhelminthes or flatworms, rotifers, cephalochordates (Amphioxus), some annelids |
| Malpighian tubules | Most of the insects, e.g. cockroaches |
| Nephridia | Earthworm and other annelids |
| Antennal or green glands | Crustaceans including prawns |
| Columns of Bertini | Renal columns of cortical tissues present between medullary pyramids |
| Renal corpuscle or malpighian body | Made up of-
Glomerulus- tuft of capillaries of the afferent arteriole Bowman’s capsule- cup-like structure, which encloses glomerulus |
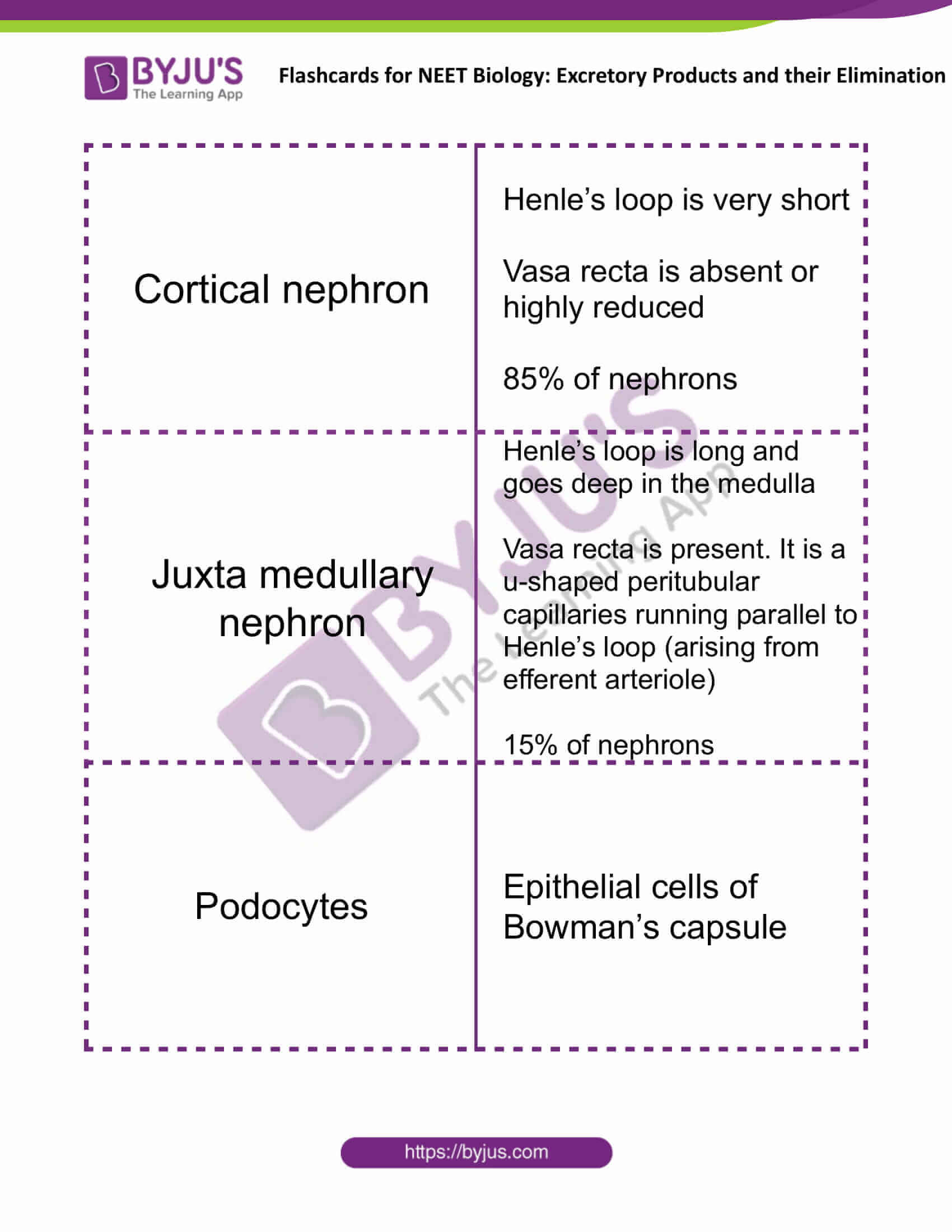
| Cortical nephron | Henle’s loop is very short
Vasa recta is absent or highly reduced 85% of nephrons |
| Juxta medullary nephron | Henle’s loop is long and goes deep in the medulla
Vasa recta is present. It is a u-shaped peritubular capillaries running parallel to Henle’s loop (arising from efferent arteriole) 15% of nephrons |
| Podocytes | Epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule |
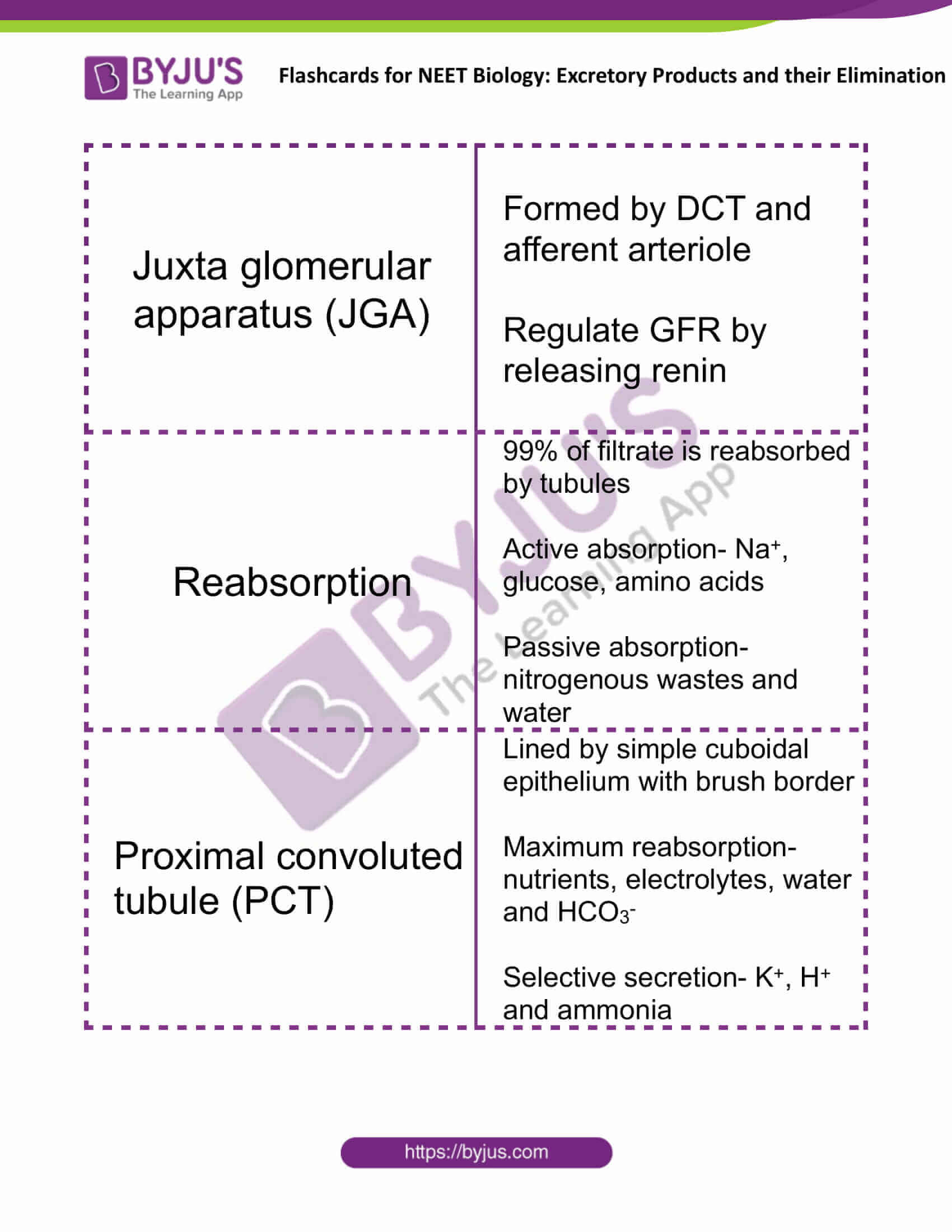
| Juxta glomerular apparatus (JGA) | Formed by DCT and afferent arteriole
Regulate GFR by releasing renin |
| Reabsorption | 99% of filtrate is reabsorbed by tubules
Active absorption- Na+, glucose, amino acids Passive absorption- nitrogenous wastes and water |
| Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) | Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium with brush border
Maximum reabsorption- nutrients, electrolytes, water and HCO3– Selective secretion- K+, H+ and ammonia |
| Henle’s loop | Helps in maintaining high osmolarity of interstitial medullary fluid and concentration of the filtrate
Descending limb- water reabsorption Ascending limb- electrolytes reabsorption |
| Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) | Reabsorption of Na+, water and HCO3–
Selective secretion- K+, H+ and ammonia |
| Collecting duct | Reabsorption of water and some urea
Selective secretion- K+, H+ |
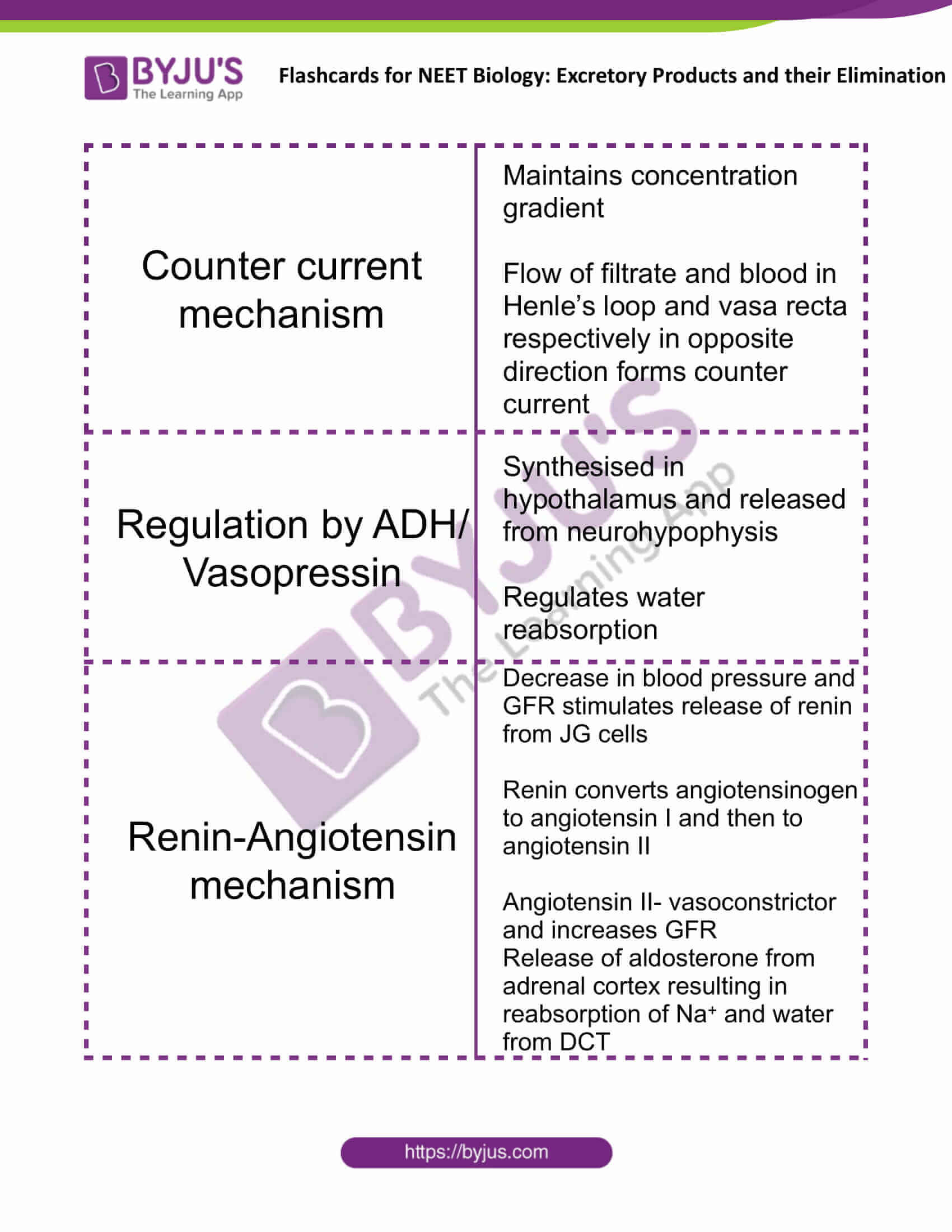
| Counter current mechanism | Maintains concentration gradient
Flow of filtrate and blood in Henle’s loop and vasa recta, respectively in opposite direction forms counter current |
| Regulation by ADH/ Vasopressin | Synthesised in hypothalamus and released from neurohypophysis
Regulates water reabsorption |
| Renin-Angiotensin mechanism | Decrease in blood pressure and GFR stimulates release of renin from JG cells
Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I and then to angiotensin II Angiotensin II- vasoconstrictor and increases GFR Release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex resulting in reabsorption of Na+ and water from DCT |
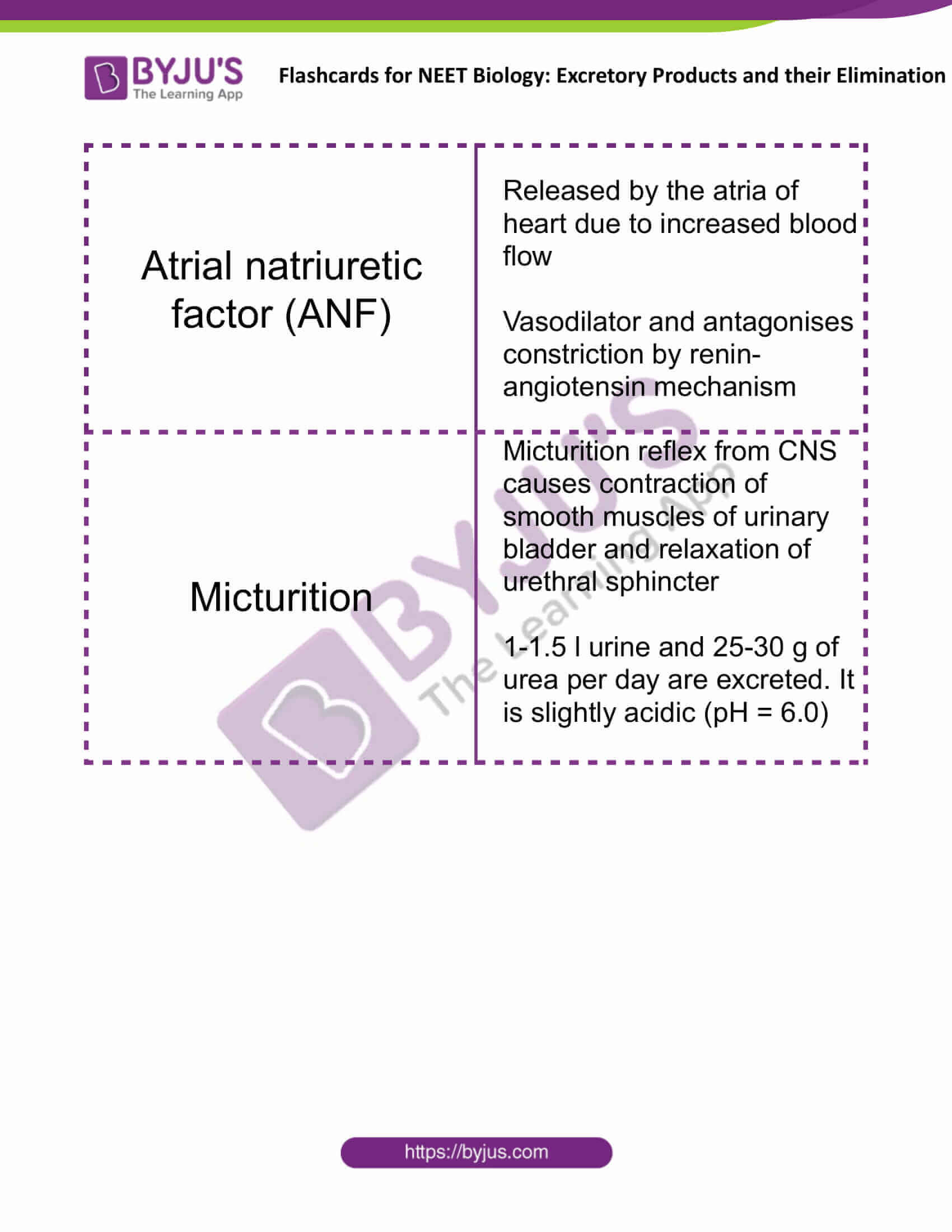
| Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) | Released by the atria of heart due to increased blood flow
Vasodilator and antagonises constriction by renin-angiotensin mechanism |
| Micturition | Micturition reflex from CNS causes contraction of smooth muscles of urinary bladder and relaxation of urethral sphincter
1-1.5 l urine and 25-30 g of urea per day are excreted. It is slightly acidic (pH = 6.0) |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Digestion And Absorption
NEET Flashcards: Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
NEET Flashcards: Body Fluids And Circulation



Comments