Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Human Health and Disease. These flashcards on Human Health and Disease are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Human Health and Disease, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Human Health and Disease
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Human Health and Disease | NEET exams |
| Human Health and Disease | |
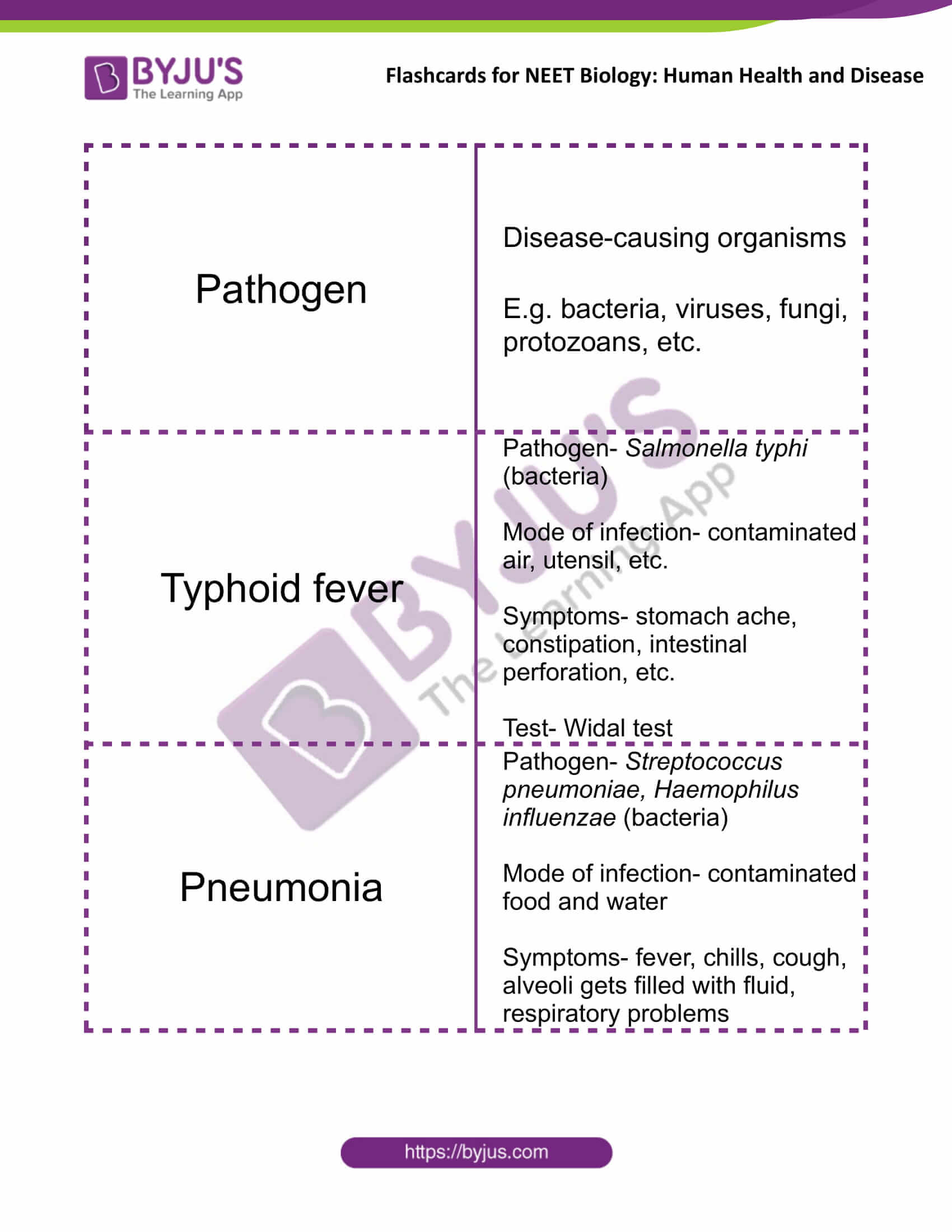
| Pathogen | Disease-causing organisms
E.g. bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoans, etc. |
| Typhoid fever | Pathogen- Salmonella typhi (bacteria)
Mode of infection- contaminated air, utensil, etc. Symptoms- stomach ache, constipation, intestinal perforation, etc. Test- Widal test |
| Pneumonia | Pathogen- Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (bacteria)
Mode of infection- contaminated food and water Symptoms- fever, chills, cough, alveoli gets filled with fluid, respiratory problems |
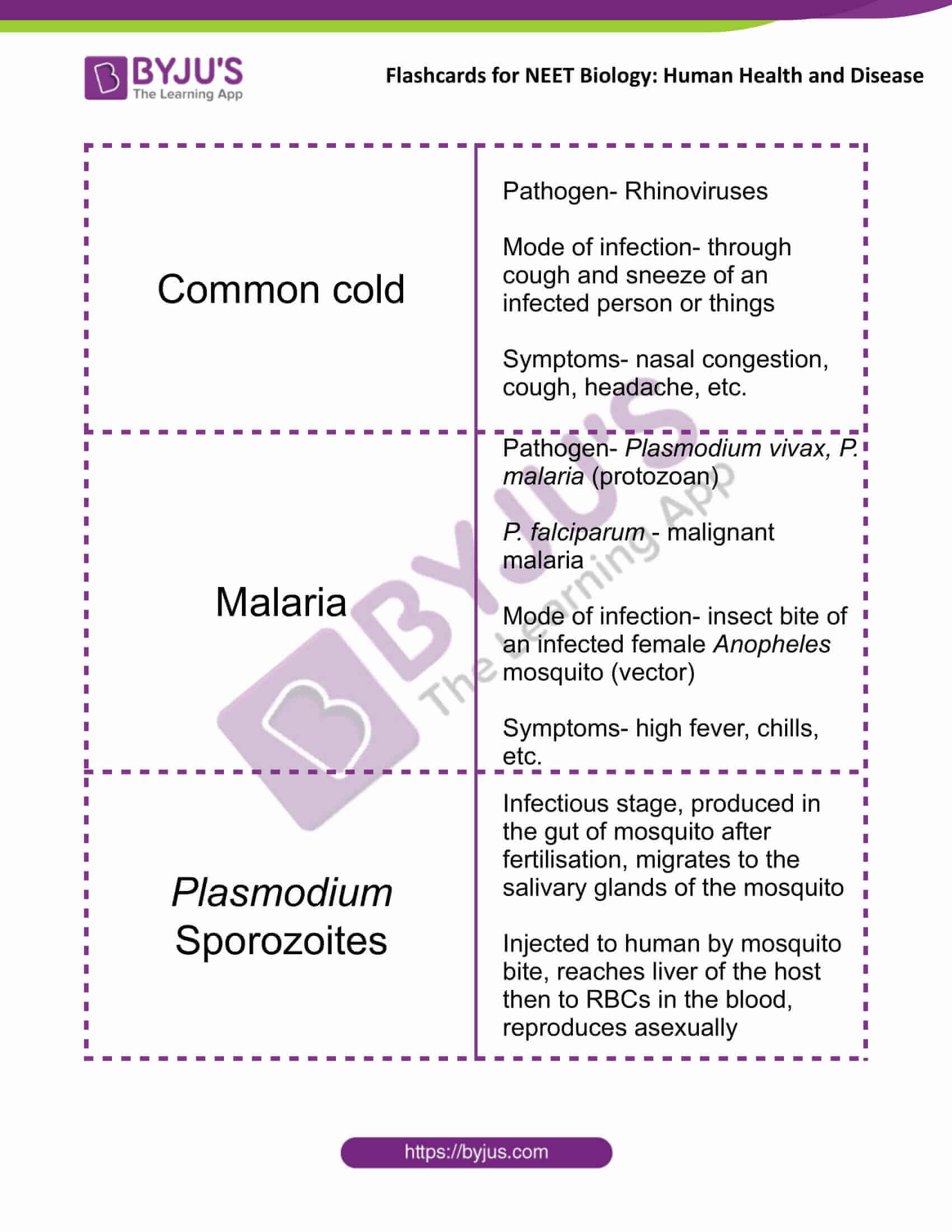
| Common cold | Pathogen- Rhinoviruses
Mode of infection- through cough and sneeze of an infected person or things Symptoms- nasal congestion, cough, headache, etc. |
| Malaria | Pathogen- Plasmodium vivax, P. malaria (protozoan)
P. falciparum – malignant malaria Mode of infection- insect bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito (vector) Symptoms- high fever, chills, etc. |
| Plasmodium Sporozoites | Infectious stage, produced in the gut of mosquito after fertilisation, migrates to the salivary glands of the mosquito
Injected to human by mosquito bite, reaches liver of the host then to RBCs in the blood, reproduces asexually |
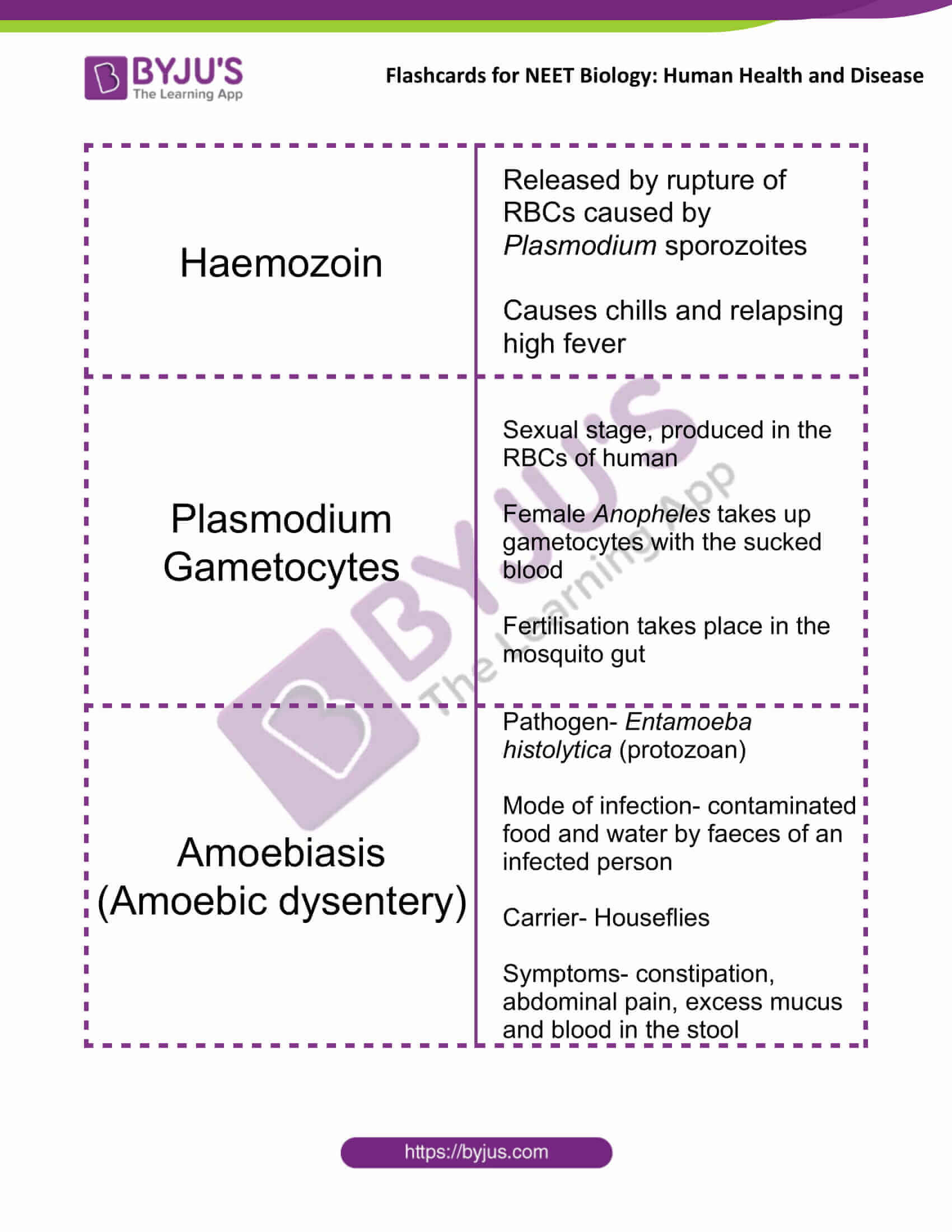
| Haemozoin | Released by rupture of RBCs caused by Plasmodium sporozoites
Causes chills and relapsing high fever |
| Plasmodium Gametocytes | Sexual stage, produced in the RBCs of human
Female Anopheles takes up gametocytes with the sucked blood Fertilisation takes place in the mosquito gut |
| Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery) | Pathogen- Entamoeba histolytica (protozoan)
Mode of infection- contaminated food and water by faeces of an infected person Carrier- Houseflies Symptoms- constipation, abdominal pain, excess mucus and blood in the stool |
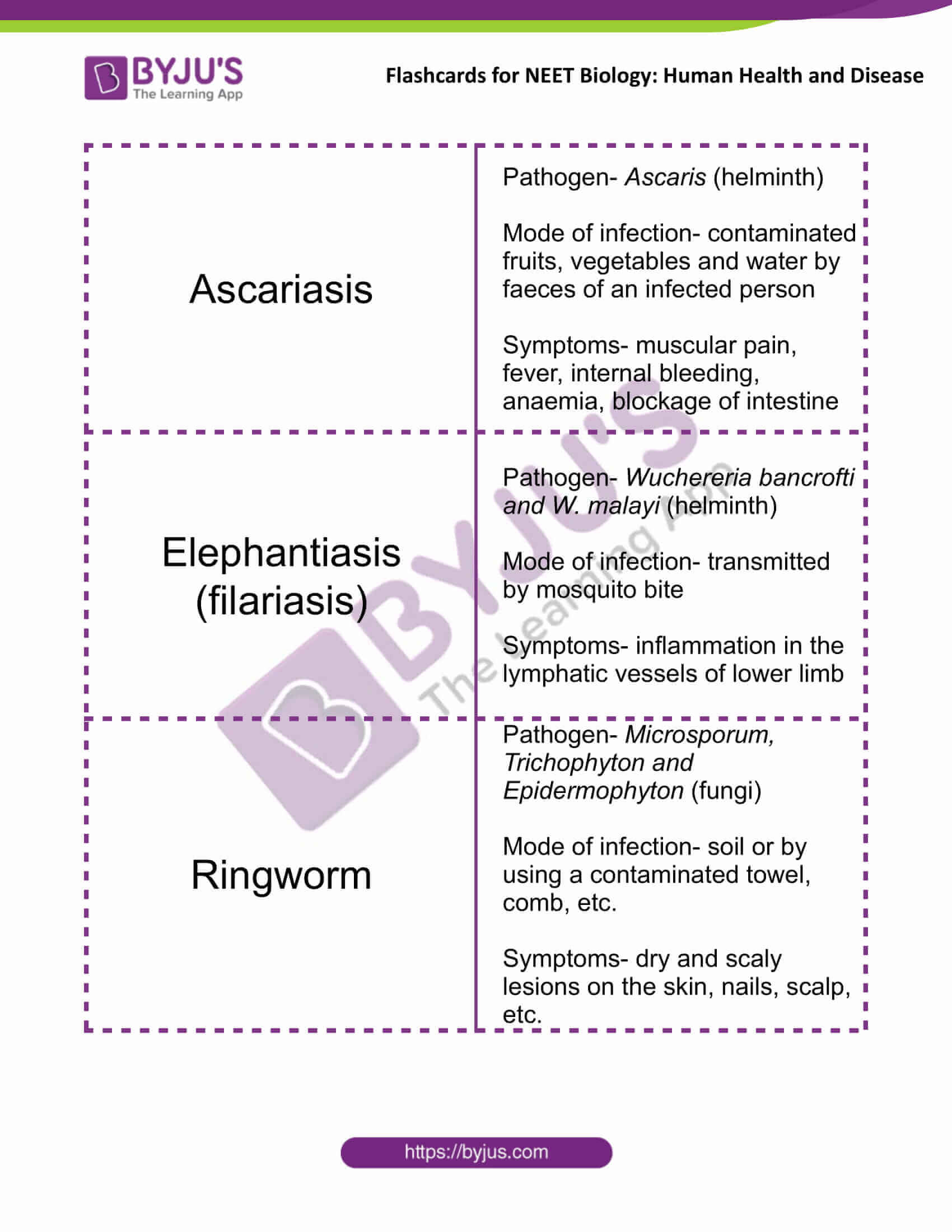
| Ascariasis | Pathogen- Ascaris (helminth)
Mode of infection- contaminated fruits, vegetables and water by faeces of an infected person Symptoms- muscular pain, fever, internal bleeding, anaemia, blockage of the intestine |
| Elephantiasis (filariasis) | Pathogen- Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi (helminth)
Mode of infection- transmitted by mosquito bite Symptoms- inflammation in the lymphatic vessels of lower limb |
| Ringworm | Pathogen- Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton (fungi)
Mode of infection- soil or by using a contaminated towel, comb, etc. Symptoms- dry and scaly lesions on the skin, nails, scalp, etc. |
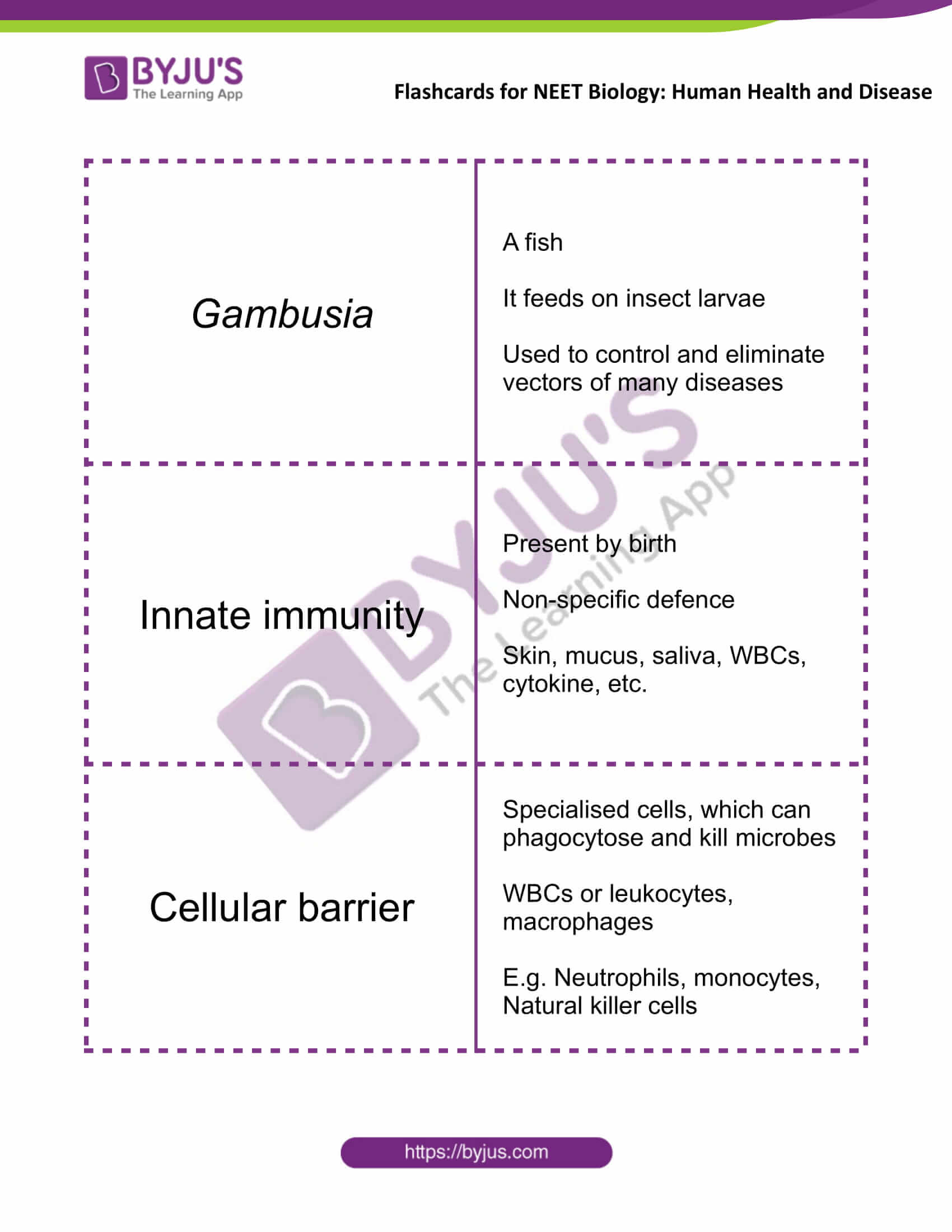
| Gambusia | A fish
It feeds on insect larvae Used to control and eliminate vectors of many diseases |
| Innate immunity | Present by birth
Non-specific defence Skin, mucus, saliva, WBCs, cytokine, etc. |
| Cellular barrier | Specialised cells, which can phagocytose and kill microbes
WBCs or leukocytes, macrophages E.g. Neutrophils, monocytes, Natural killer cells |
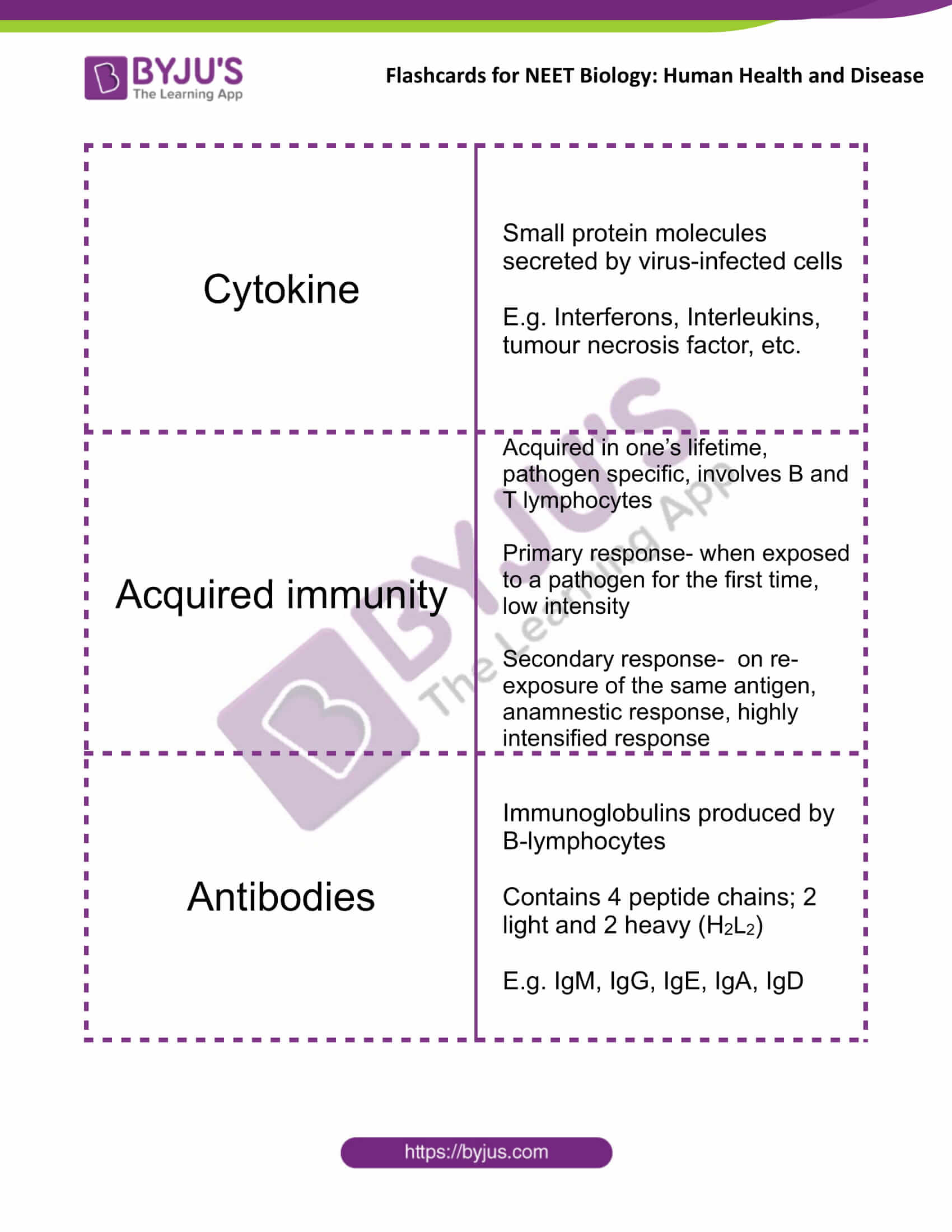
| Cytokine | Small protein molecules secreted by virus-infected cells
E.g. Interferons, Interleukins, tumour necrosis factor, etc. |
| Acquired immunity | Acquired in one’s lifetime, pathogen-specific, involves B and T lymphocytes
Primary response- when exposed to a pathogen for the first time, low intensity Secondary response- on re-exposure of the same antigen, anamnestic response, highly intensified response |
| Antibodies | Immunoglobulins produced by B-lymphocytes
Contains 4 peptide chains; 2 light and 2 heavy (H2L2) E.g. IgM, IgG, IgE, IgA, IgD |
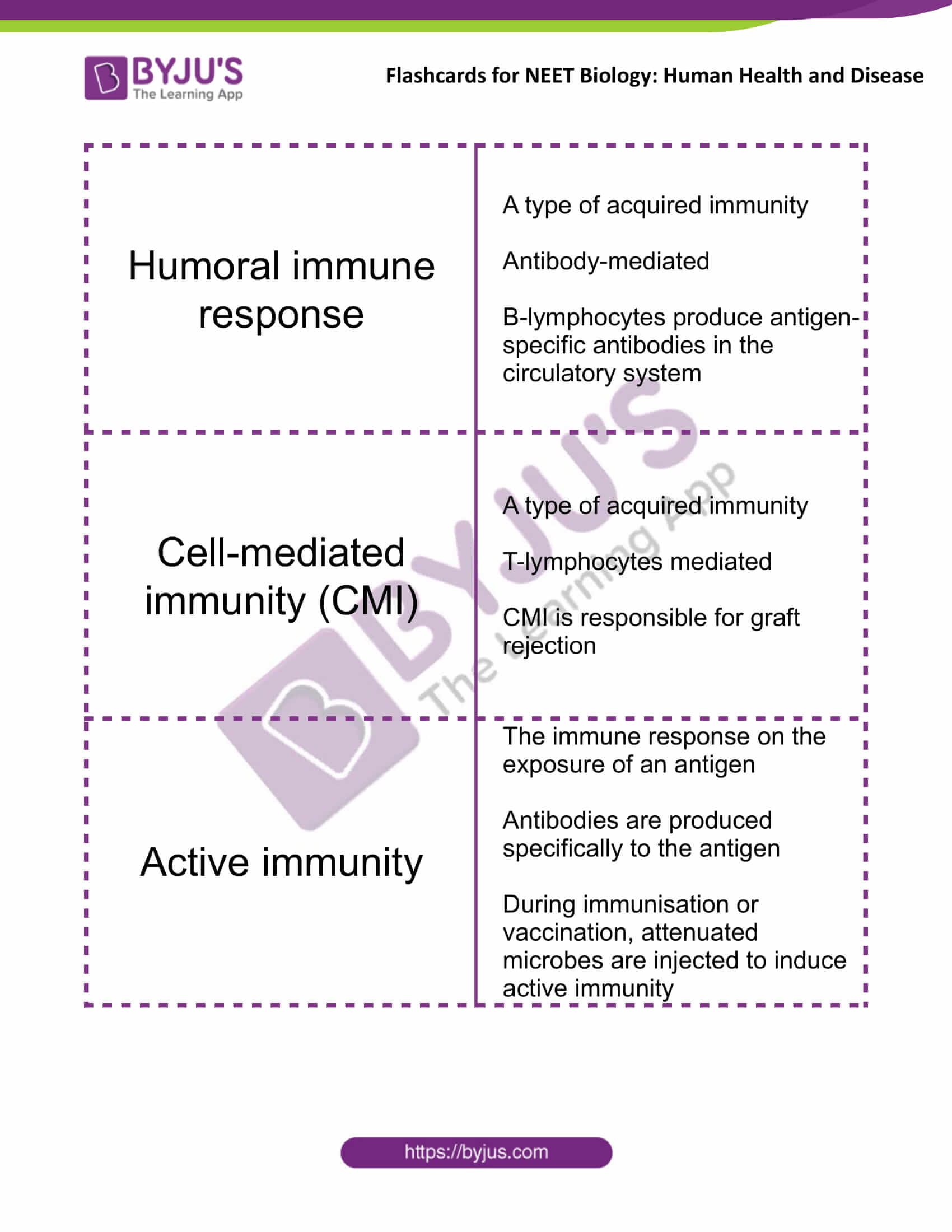
| Humoral immune response | A type of acquired immunity
Antibody-mediated B-lymphocytes produce antigen-specific antibodies in the circulatory system |
| Cell-mediated immunity (CMI) | A type of acquired immunity
T-lymphocytes mediated CMI is responsible for graft rejection |
| Active immunity | The immune response on the exposure of an antigen
Antibodies are produced specifically to the antigen During immunisation or vaccination, attenuated microbes are injected to induce active immunity |
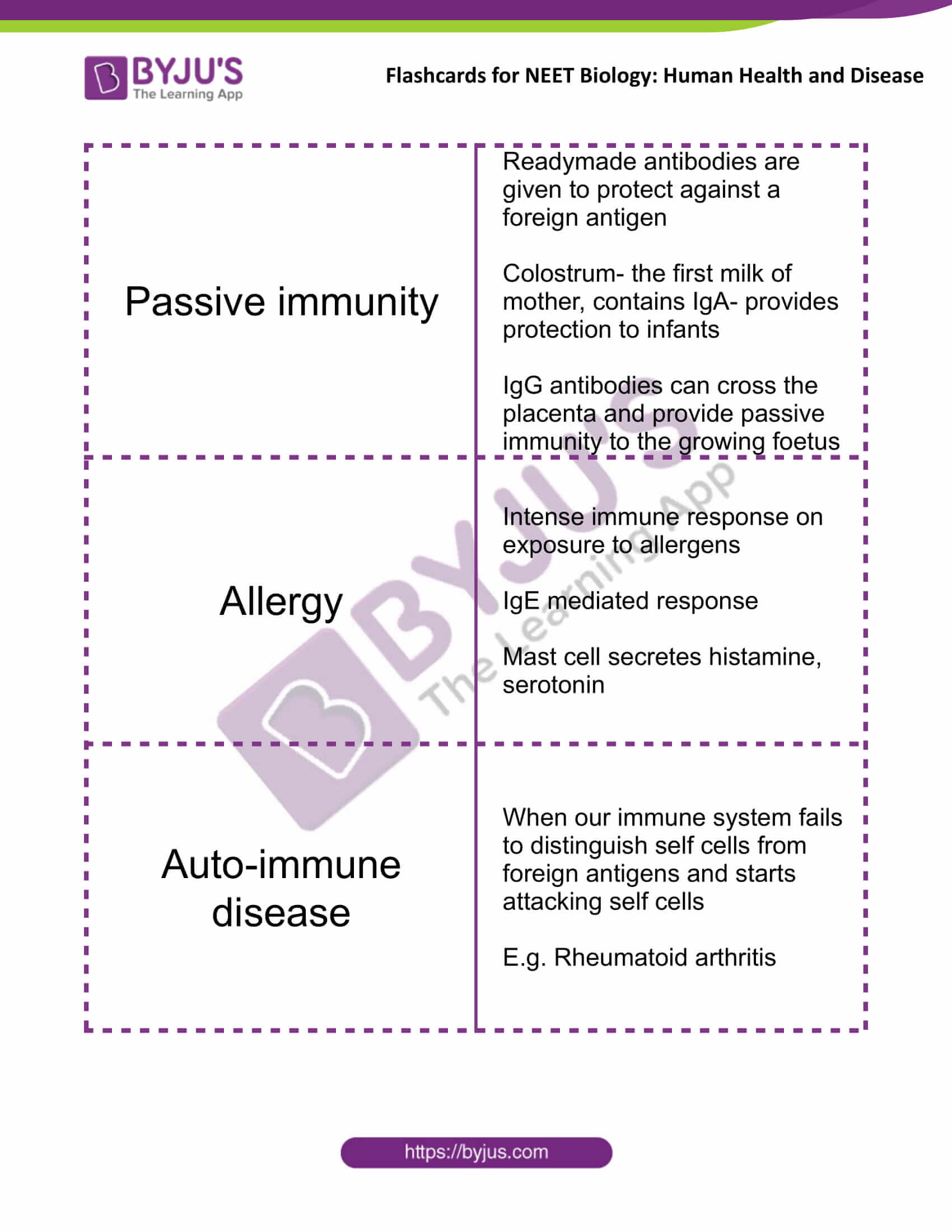
| Passive immunity | Readymade antibodies are given to protect against a foreign antigen
Colostrum- the first milk of mother, contains IgA- provides protection to infants IgG antibodies can cross the placenta and provide passive immunity to the growing foetus |
| Allergy | Intense immune response on exposure to allergens
IgE mediated response Mast cell secretes histamine, serotonin |
| Auto-immune disease | When our immune system fails to distinguish self cells from foreign antigens and starts attacking self cells
E.g. Rheumatoid arthritis |
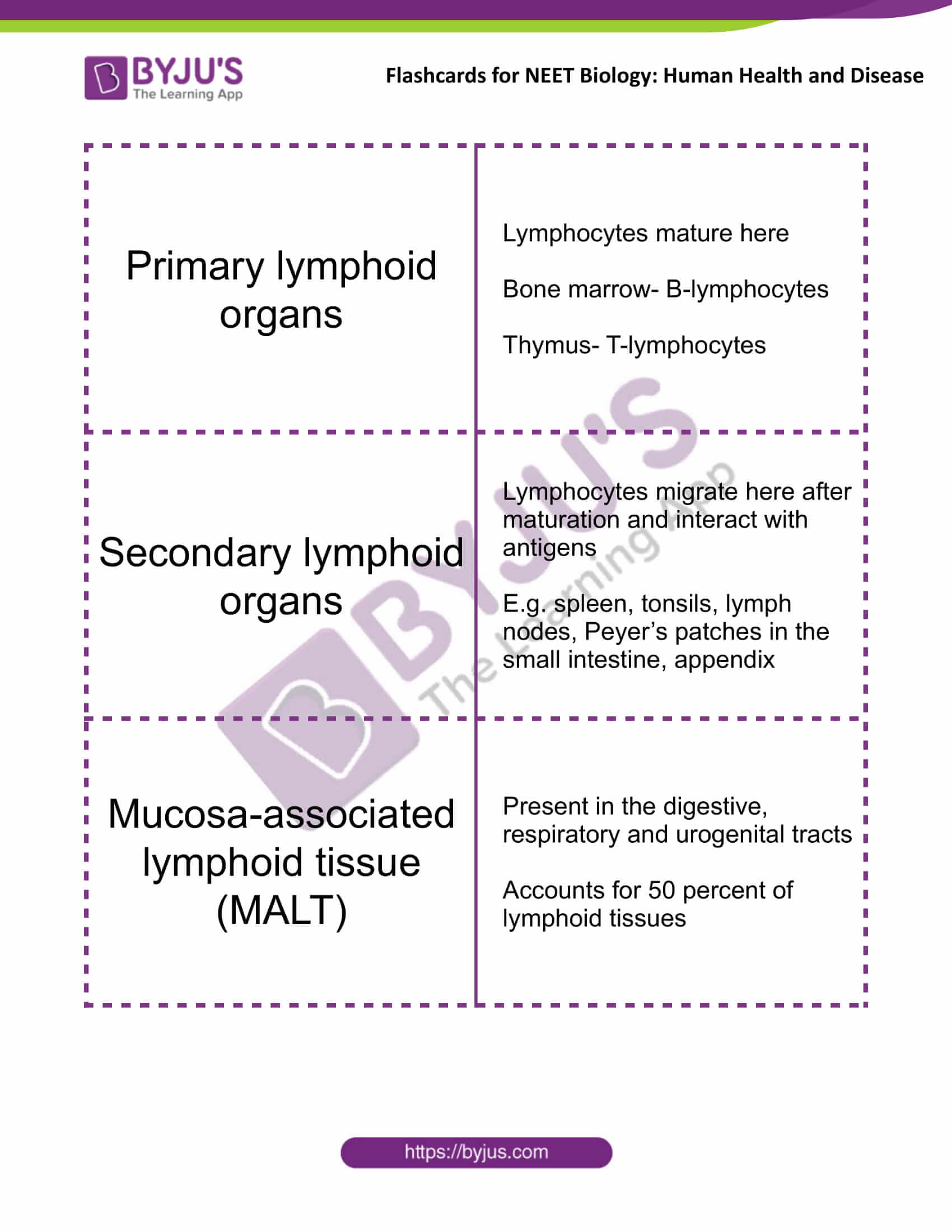
| Primary lymphoid organs | Lymphocytes mature here
Bone marrow- B-lymphocytes Thymus- T-lymphocytes |
| Secondary lymphoid organs | Lymphocytes migrate here after maturation and interact with antigens
E.g. spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes, Peyer’s patches in the small intestine, appendix |
| Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) | Present in the digestive, respiratory and urogenital tracts
Accounts for 50 percent of lymphoid tissues |
| AIDS | Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Caused by HIV virus, a retrovirus Transmitted through body fluids, sexually, using infected needles and can cross placenta too Test- ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) |
| HIV replication | In Macrophages- forms DNA by reverse transcription and gets inserted into host cell genome producing multiple copies
In TH cells- replicate and attacks other T-lymphocytes, decreasing the number of T-lymphocytes |
| Tumours | Cells, lose regulatory mechanism and contact inhibition, show uncontrolled division and proliferation
Benign- remain confined to the original location Malignant- neoplastic cells, invade surrounding tissues |
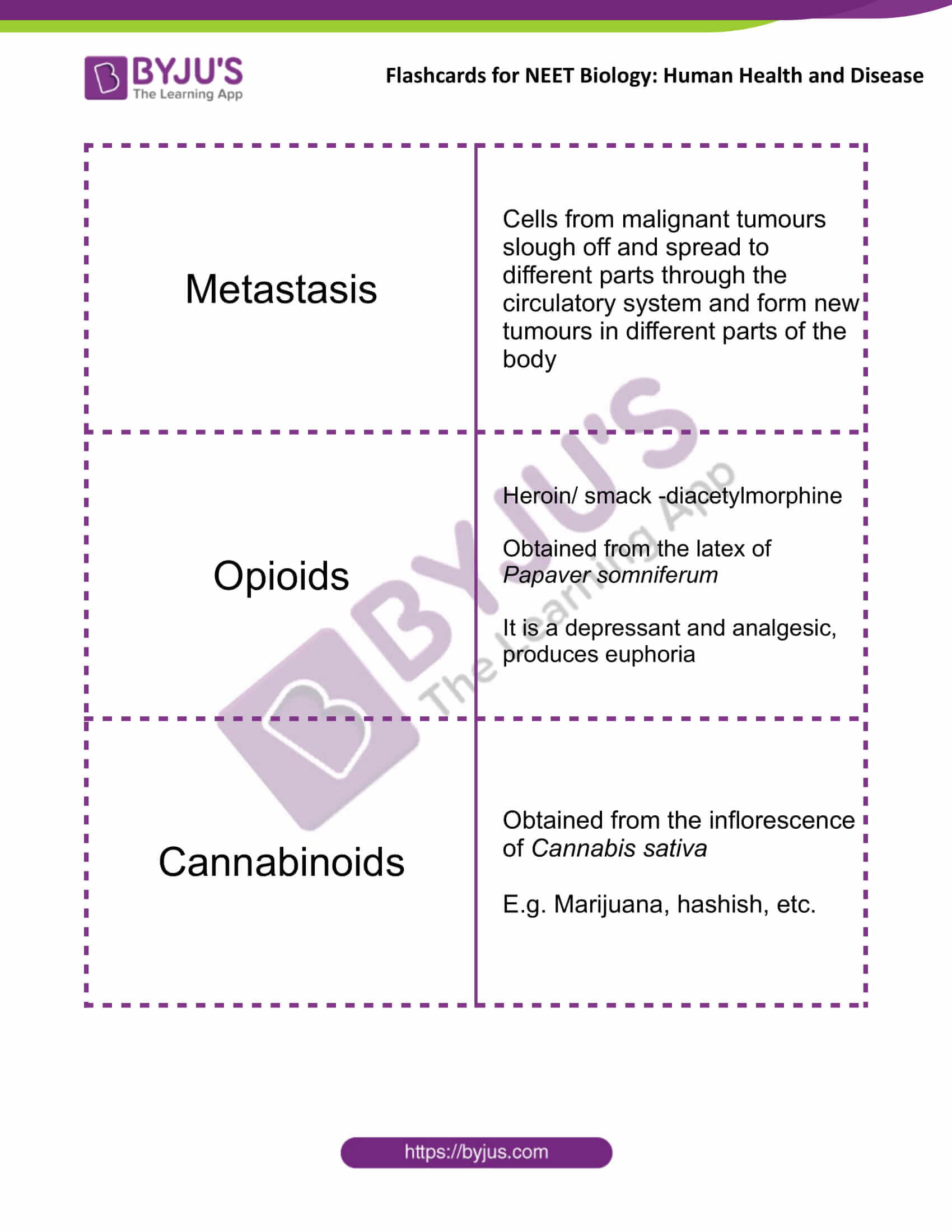
| Metastasis | Cells from malignant tumours slough off and spread to different parts through the circulatory system and form new tumours in different parts of the body |
| Opioids | Heroin/ smack -diacetylmorphine
Obtained from the latex of Papaver somniferum It is a depressant and analgesic, produces euphoria |
| Cannabinoids | Obtained from the inflorescence of Cannabis sativa
E.g. Marijuana, hashish, etc. |
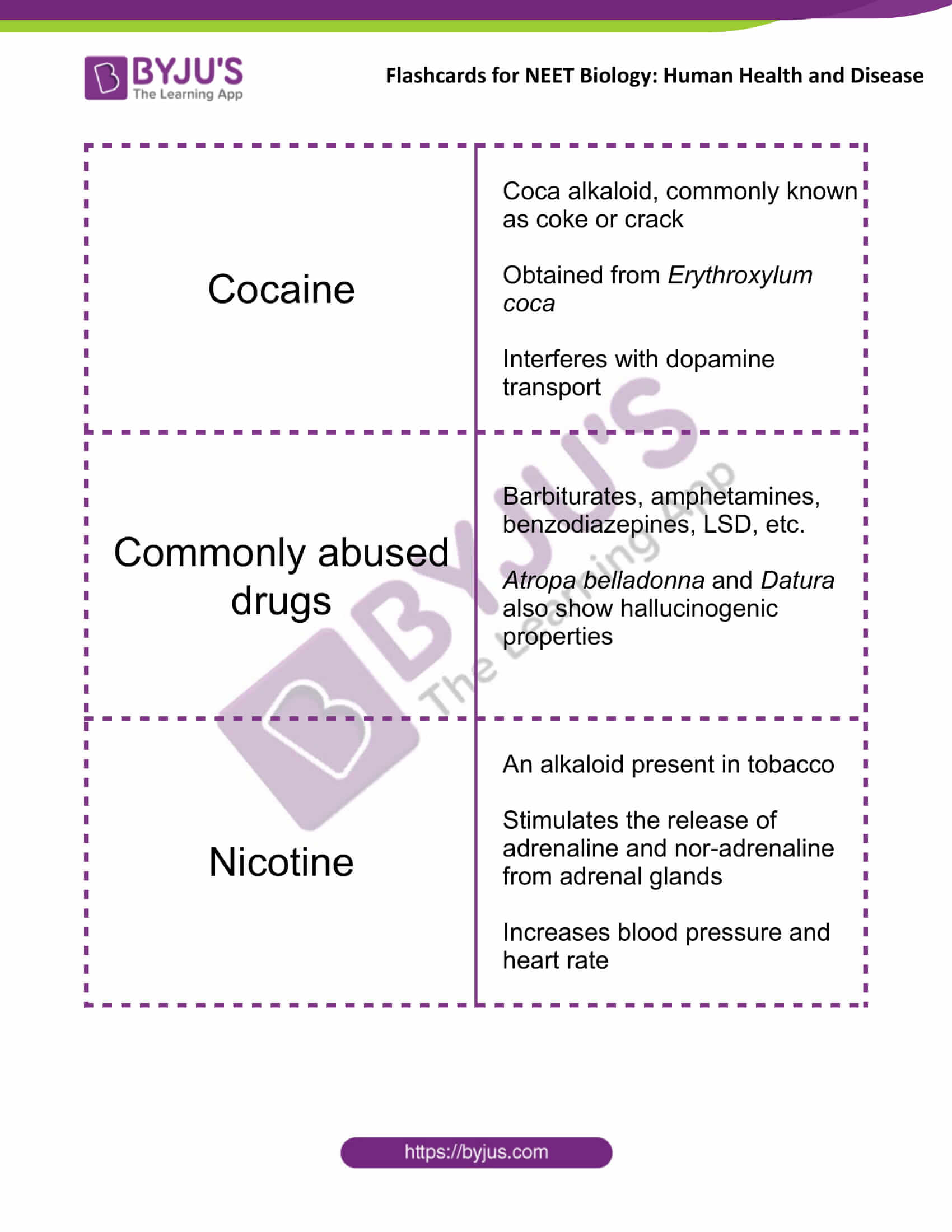
| Cocaine | Coca alkaloid, commonly known as coke or crack
Obtained from Erythroxylum coca Interferes with dopamine transport |
| Commonly abused drugs | Barbiturates, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, LSD, etc.
Atropa belladonna and Datura also show hallucinogenic properties |
| Nicotine | An alkaloid present in tobacco
Stimulates the release of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline from adrenal glands Increases blood pressure and heart rate |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Principles Of Inheritance And Variation
NEET Flashcards: Molecular Basis Of Inheritance
NEET Flashcards: Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production
NEET Flashcards: Microbes In Human Welfare
Recommended video:


Comments