Hibiscus is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. It is a large genus covering hundreds of species native to tropical and subtropical regions with warm temperate features across the world.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Morphology of Flowering Plants
Download Now
Table of Content:
Floral Formula
A floral formula is the numeric representation of different floral structures that constitute a flower. It is used to describe a flower using some signs and symbols, in order to designate various floral parts.
The floral formula of Hibiscus rosa sinensis (China rose flower) is as follows:
Br Brl ⊕ ⚥ K( 5 ) C( 5 ) A(∞)
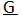 ( 5 )
( 5 )
Systematic Position Of Malvaceae
Division: Embryophyta Siphonogama
Sub Division: Angiospermae
Class: Dicotyledonaea
Subclass: Archichlamydeae
Order: Malvales
Family: Malvaceae
Features Of Malvaceae Species
Some Common Plants
| Common name | Scientific name |
| China rose flower or shoe flower | Hibiscus rosa sinensis |
| Cotton | Gossypium herbaceum |
| Lady’s finger | Hibiscus esculentus |
| Mallow | Malva sylvestris |
| Hina | Pavonia odorata |
| Indian tulip | Thespesia populnea |
Size And Distribution
The family includes nearly 25 genera and nearly 1500 species widely spread in tropical and temperate regions. In India alone, the Malvaceae family is represented by 22 genera and about 125 species.
Description Of The Family
Habitat: most members are terrestrial mesophytes
Habit: few are annuals (Malva, Althaea) or perennial herbs, some grow very tall (Lavatera). Some are shrubs such as Hibiscus rosa sinensis, Gossypium species or some are small trees such as Kydia, Thespesia populnea.
Root: Typically they possess a tap root system with profuse branching
Stem: aerial, branched, erect, herbaceous, cylindrical, and woody with young portions covered by satellite hairs or trichomes. Typically, the stem displays fibrous nature with much mucilaginous sap.
Leaf: leaves are simple, often lobed palmately and are alternate, petiolate, stipulate, cordate or ovate. The margin usually is entire or serrate, venation is unicostate or multicostate pinnately reticulate. Leaves are generally covered by stellate hair displaying mucilaginous ducts.
Inflorescence: typically cymose, solitary cymes in the leaf axil or raceme.
Flower: Bracteate, bracteolate, actinomorphic, showy, dichlamydeous, complete, pedicellate, heterochlamydeous bisexual, pentamerous and hypogynous, mucilage in floral structures.
Calyx: green, typically 5 sepals, gamosepalous showing valvate aestivation and odd sepal is posterior in position.
Epicalyx: additional calyx like whorl formed by bracteoles on the surface of the calyx. 5-8 bracteoles to the outer calyx, free and green. Number of bracteoles varies in different species.
Corolla: Petals 5, polypetalous bust basally adnate with the staminal column, variously colored, twisted aestivation.
Androecium: Number of stamens, monadelphous, filaments fuse to form a tubular staminal column around gynoecium, anthers reniform, monothecous, extrorse dehiscing transversally or longitudinally
Gynoecium: long, and simple style, slender passing through the staminal tube. Stigma 5, colored and capitate, pentacarpellary syncarpous, ovary superior, ovary pentalocular with several oculi per locule on the axile placentation. Style branches into many stigmata or twice the number, as that of carpels.
Fruit: Abortive mostly. Most members of this family exhibit production of capsules that can be a loculicidal capsule.
Seeds: one or more seeds per locule, exalbuminous with a curved embryo
Pollination: members of this family mainly exhibit entomophilous pollination, where flowers are colored brightly along with extrafloral nectaries.
Recommended Video:
Morphology of Flowering Plants | TOP 10 QUESTIONS | NEET

Also Explore:
| Floral Formula of Fabaceae |
| Floral Formula of Solanaceae |
| Floral Formula of Liliaceae |
Salient Features Of The Family
- Most members of the family exhibit fibrous stem
- Young stems and leaves will be covered by stellate trichomes
- Members anatomically show the presence of mucilaginous ducts
- Flowers characterized by the presence of epicalyx or collection of bracteoles
- Flowers show polypetalous condition with contorted aestivation
- Androecium displays numerous stamens, showing monadelphous conditions. Anthers are reniform and are monothecous. The staminal column encloses the gynoecium.
- The gynoecium is multicarpellary, multilocular, syncarpous, superior ovary with axile placentation
- The fruit is typically a schizocarp or capsule.
You just read about the floral formula of Hibiscus flower. For more such information, visit BYJU’S.
Related Links:
| Anatomy of Flowering Plants – Important Notes For NEET |
| Morphology Of Flowering Plants – Important Notes For NEET |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some characteristic features of Malvaceae?
The young stems and leaves of Malvaceae plants are covered by stellate trichomes. The inflorescence can be cymose, raceme or solitary cymes in the leaf axis. Also, they anatomically show the presence of mucilaginous ducts.
Which plants are included in Malvaceae?
This family includes various genera. The largest genera is the Hibiscus with approximately 300 species. Some familiar plants that come under Malvaceae are China rose flower, Indian tulip, Lady’s finger, Mallow, etc.

Comments