Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Digestion and Absorption. These flashcards on Digestion and Absorption are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Digestion and Absorption, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.


Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Digestion and Absorption
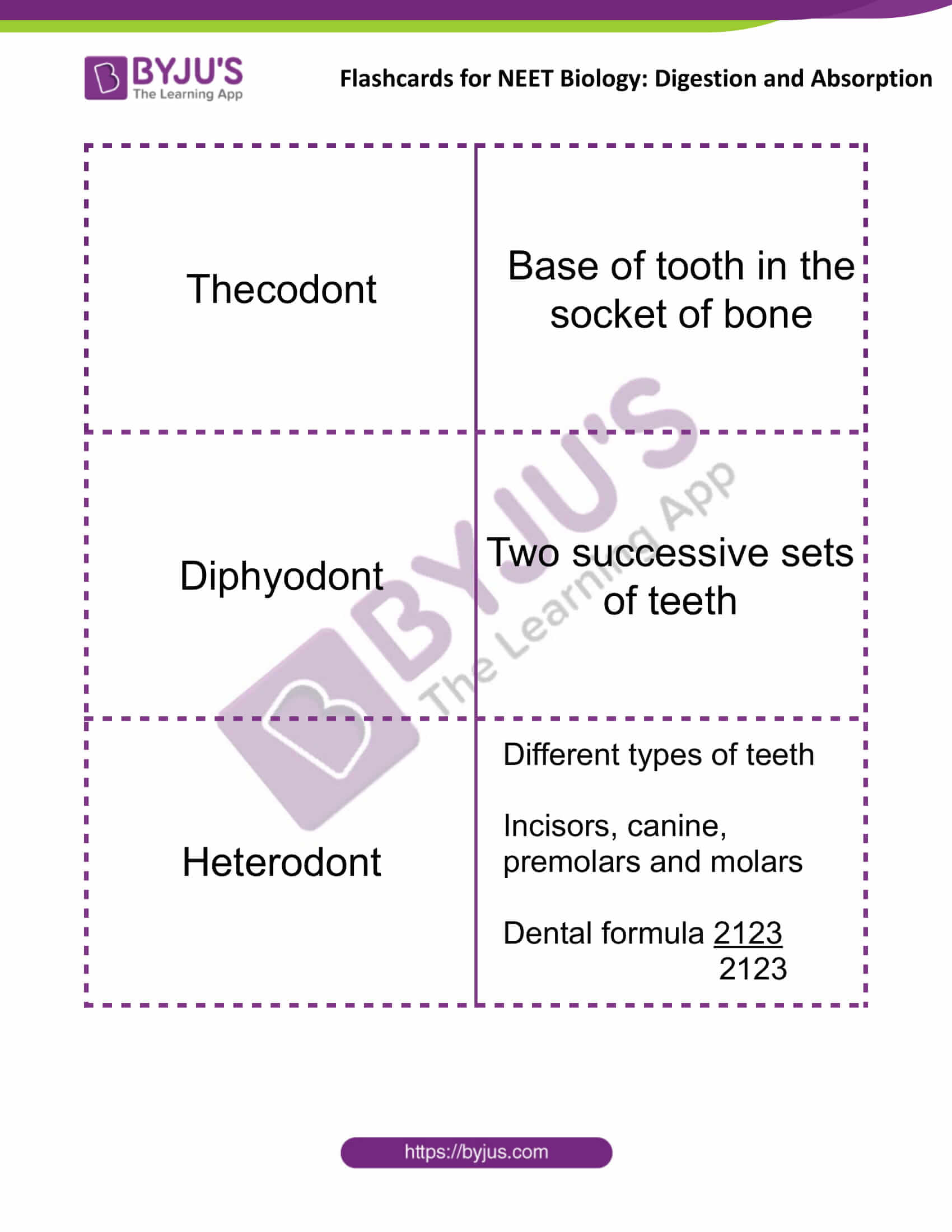
| Thecodont | The base of the tooth in the socket of bone |
| Diphyodont | Two successive sets of teeth |
| Heterodont | Different types of teeth
Incisors, canine, premolars and molars Dental formula 2123 2123 |
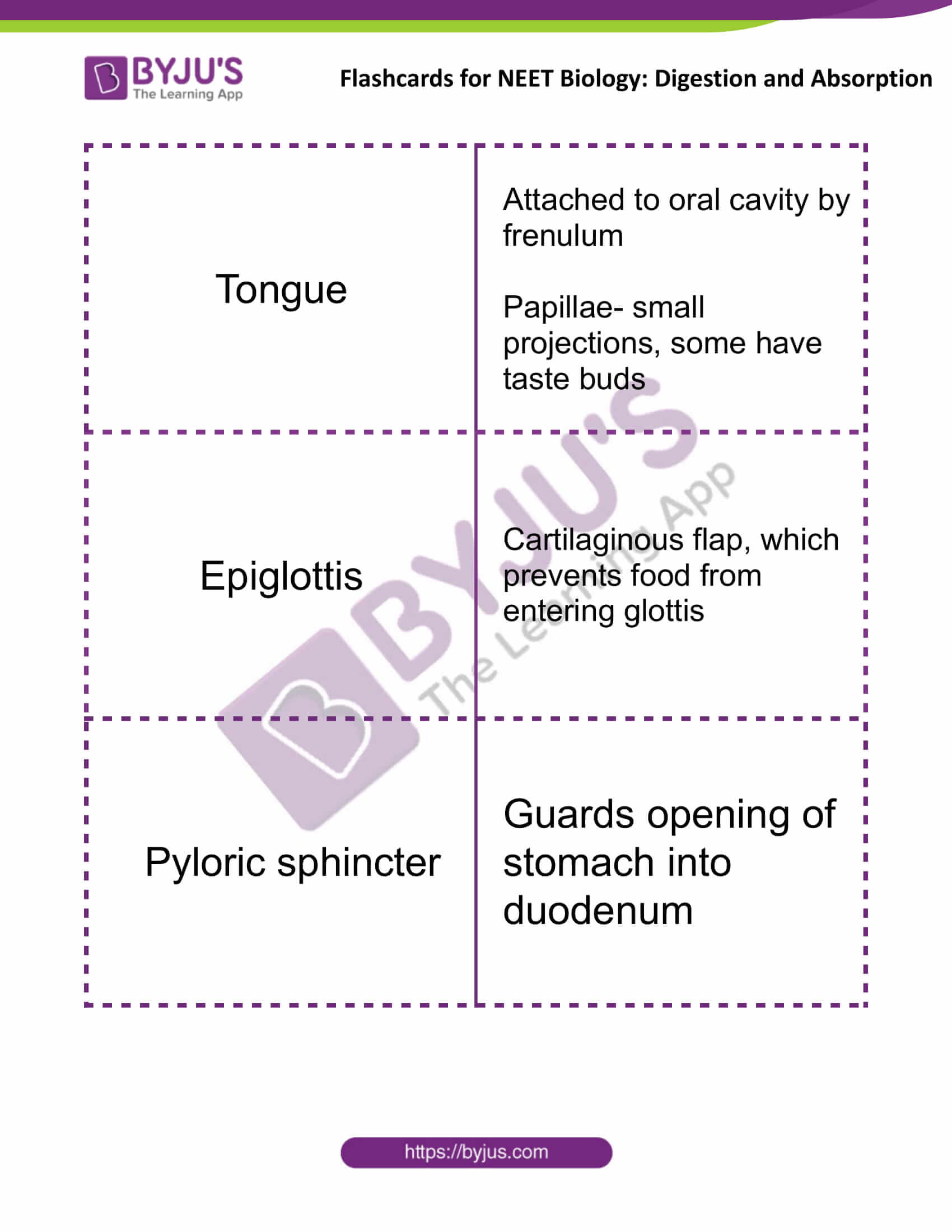
| Tongue | Attached to the oral cavity by the frenulum
Papillae- small projections, some have taste buds |
| Epiglottis | Cartilaginous flap, which prevents food from entering glottis |
| Pyloric sphincter | Guards opening of the stomach into the duodenum |
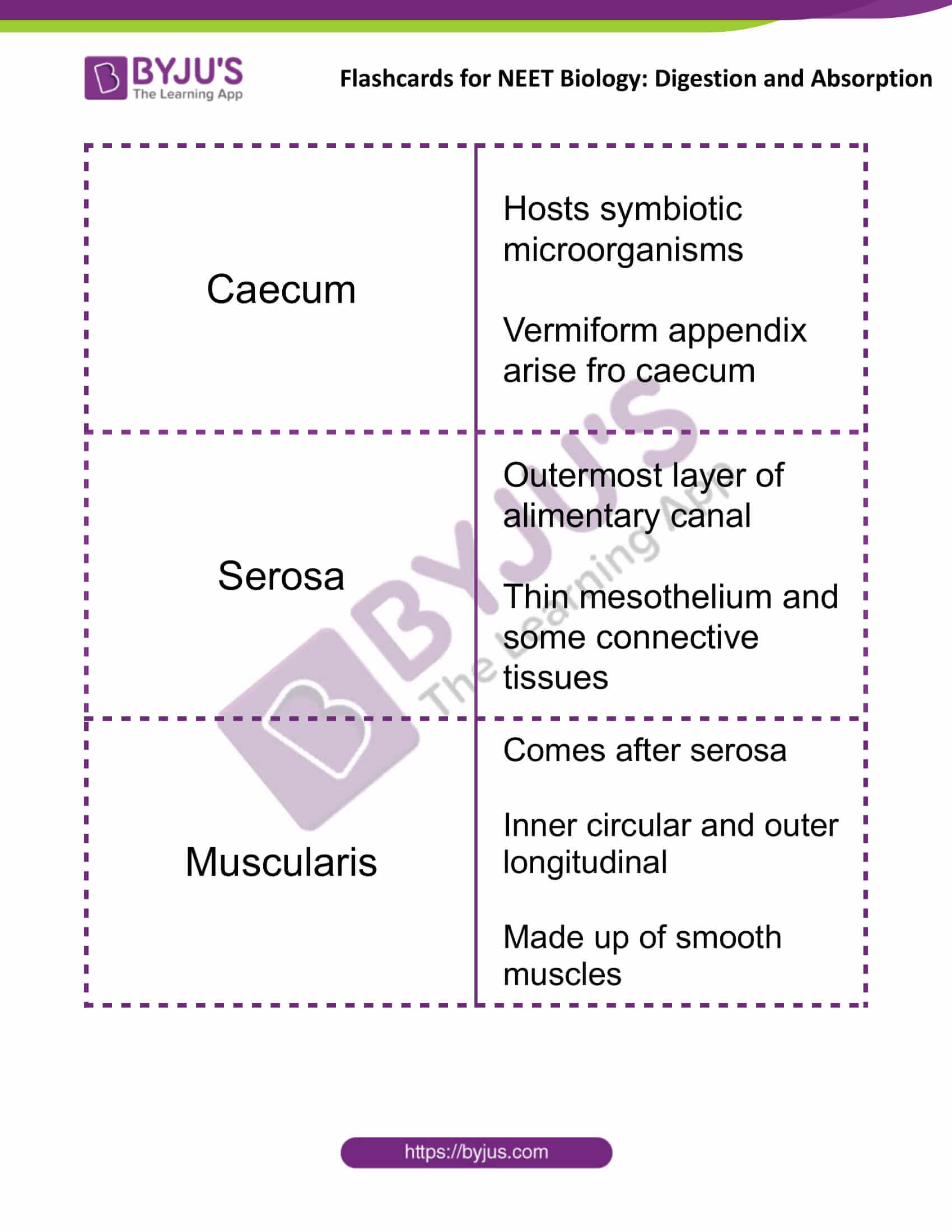
| Caecum | Hosts symbiotic microorganisms
Vermiform appendix arise fro caecum |
| Serosa | The outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Thin mesothelium and some connective tissues |
| Muscularis | Comes after serosa
Inner circular and outer longitudinal Made up of smooth muscles |
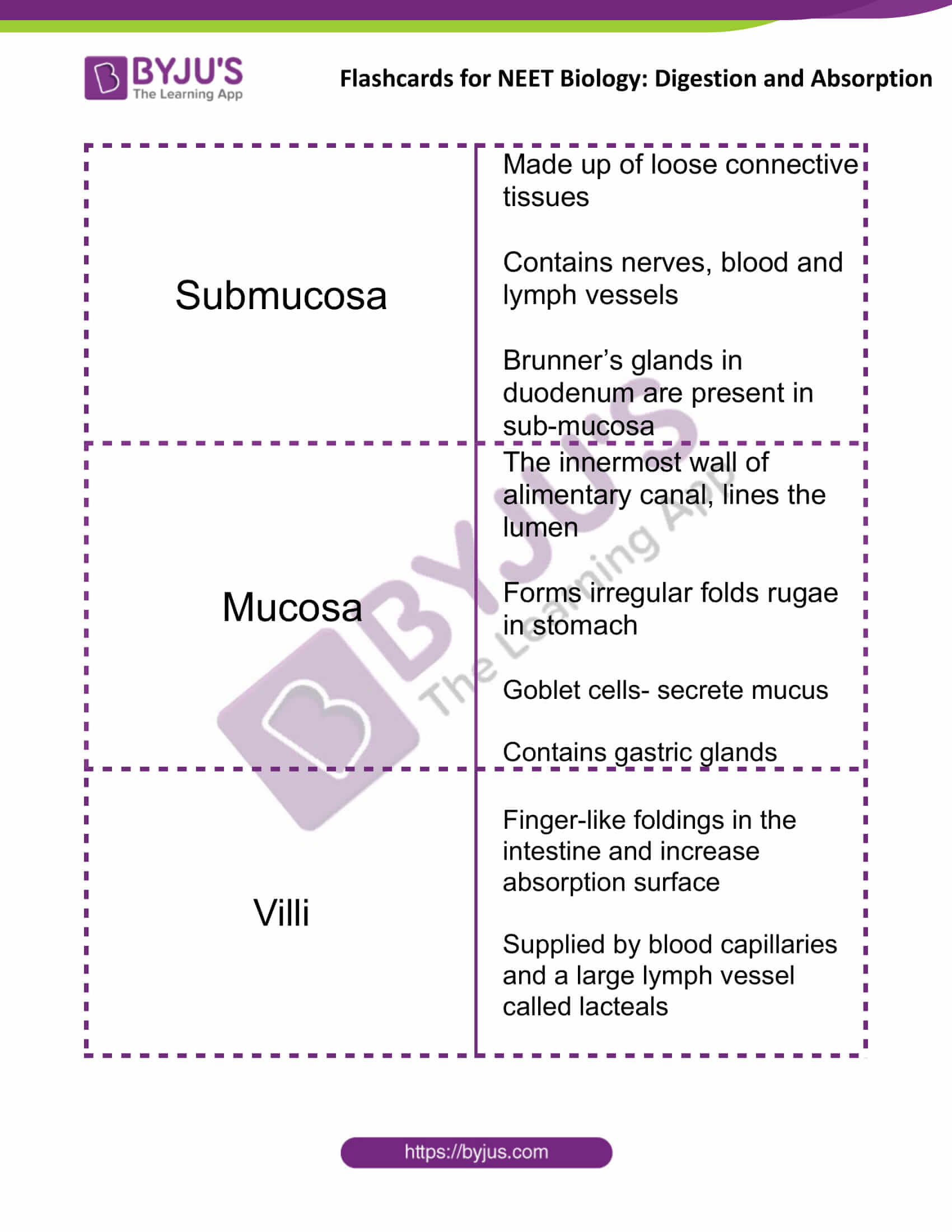
| Submucosa | Made up of loose connective tissues
Contains nerves, blood and lymph vessels Brunner’s glands in the duodenum are present in sub-mucosa |
| Mucosa | The innermost wall of the alimentary canal, lines the lumen
Forms irregular folds rugae in stomach Goblet cells- secrete mucus Contains gastric glands |
| Villi | Finger-like foldings in the intestine and increase absorption surface
Supplied by blood capillaries and a large lymph vessel called lacteals |
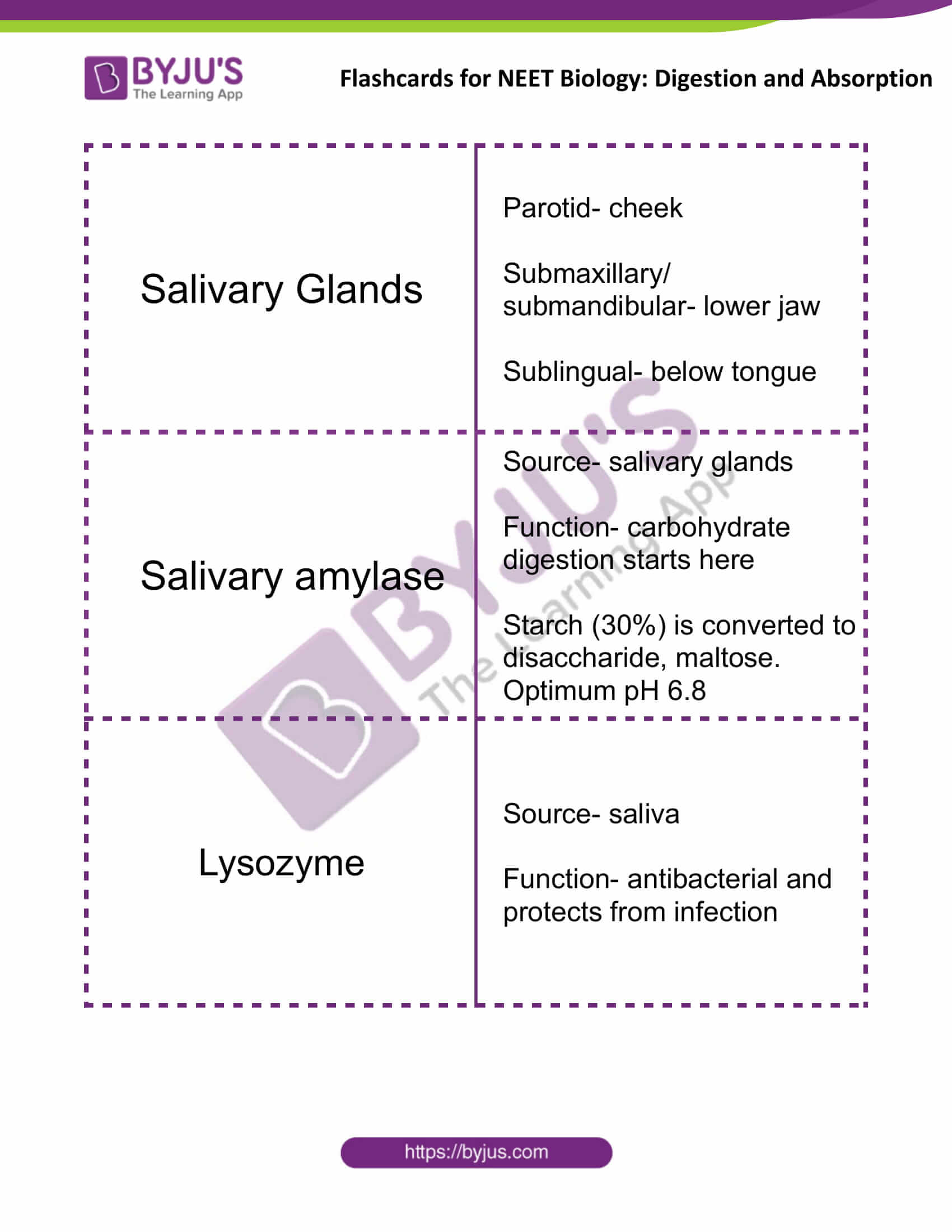
| Salivary Glands | Parotid- cheek
Submaxillary/ submandibular- lower jaw Sublingual- below the tongue |
| Salivary amylase | Source- salivary glands
Function- carbohydrate digestion starts here Starch (30%) is converted to disaccharide, maltose. Optimum pH 6.8 |
| Lysozyme | Source- saliva
Function- antibacterial and protects from infection |
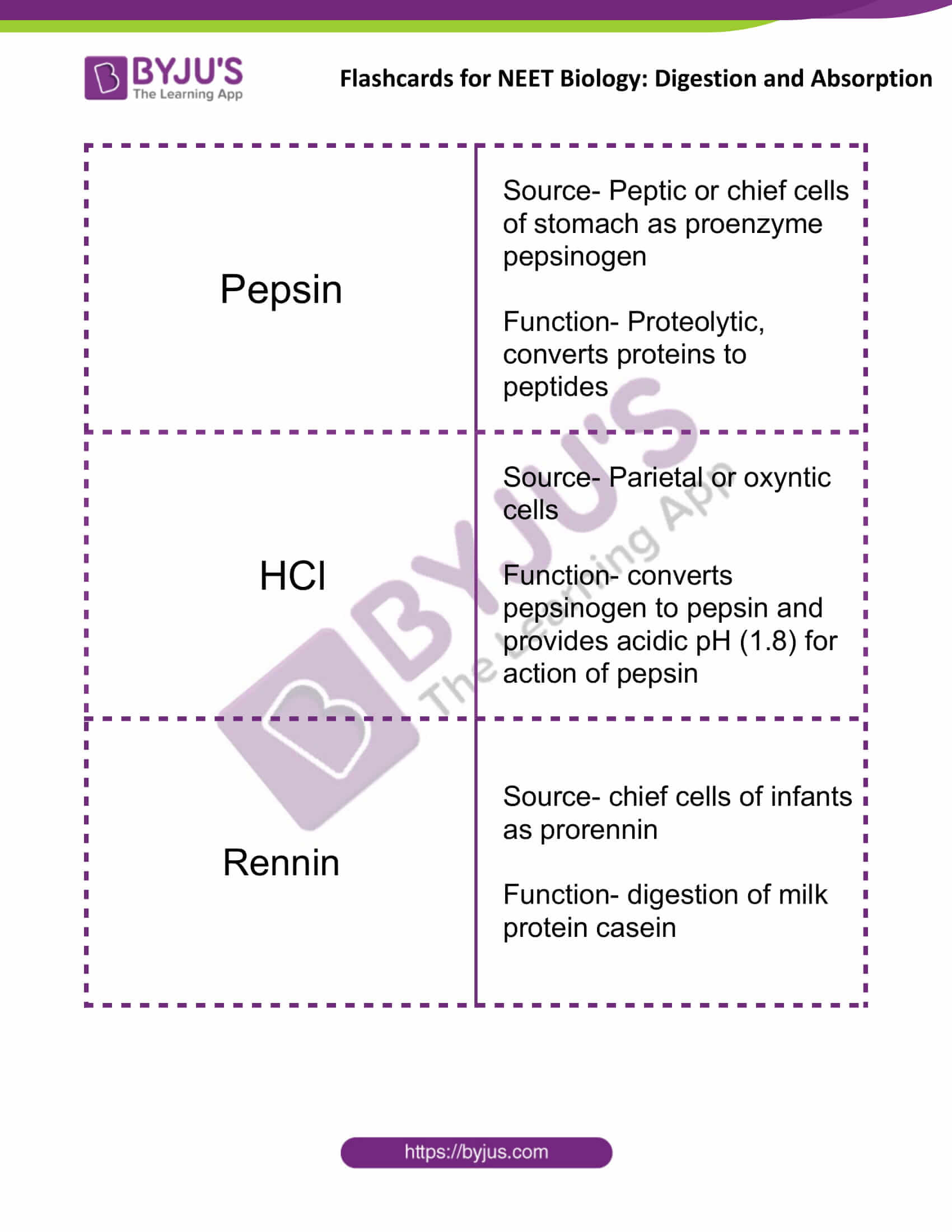
| Pepsin | Source- Peptic or chief cells of the stomach as proenzyme pepsinogen
Function- Proteolytic, converts proteins to peptides |
| HCl | Source- Parietal or oxyntic cells
Function- converts pepsinogen to pepsin and provides acidic pH (1.8) for the action of pepsin |
| Rennin | Source- chief cells of infants as prorennin
Function- digestion of milk protein casein |
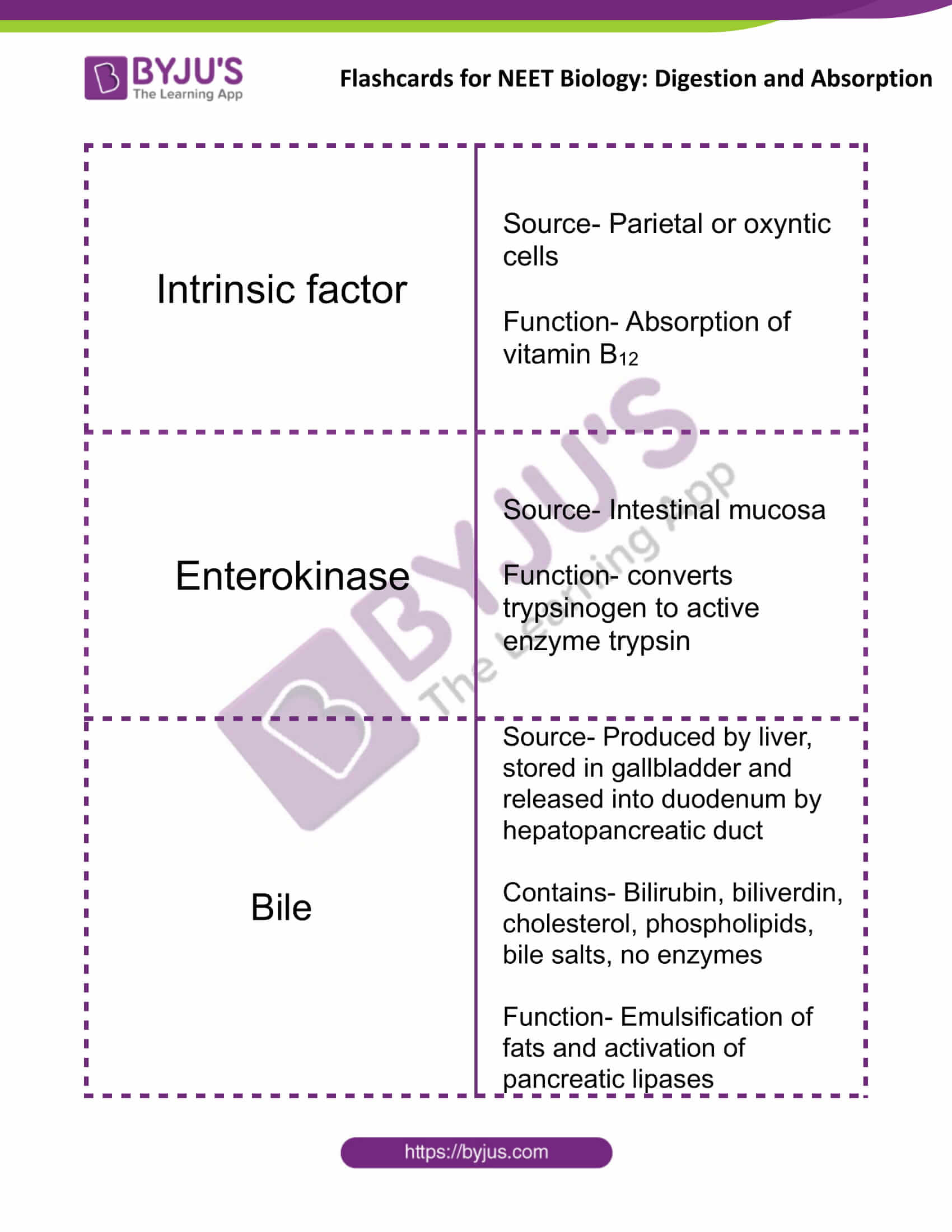
| Intrinsic factor | Source- Parietal or oxyntic cells
Function- Absorption of vitamin B12 |
| Enterokinase | Source- Intestinal mucosa
Function- converts trypsinogen to active enzyme trypsin |
| Bile | Source- Produced by liver, stored in gallbladder and released into duodenum by hepatopancreatic duct
Contains- Bilirubin, biliverdin, cholesterol, phospholipids, bile salts, no enzymes Function- Emulsification of fats and activation of pancreatic lipases |
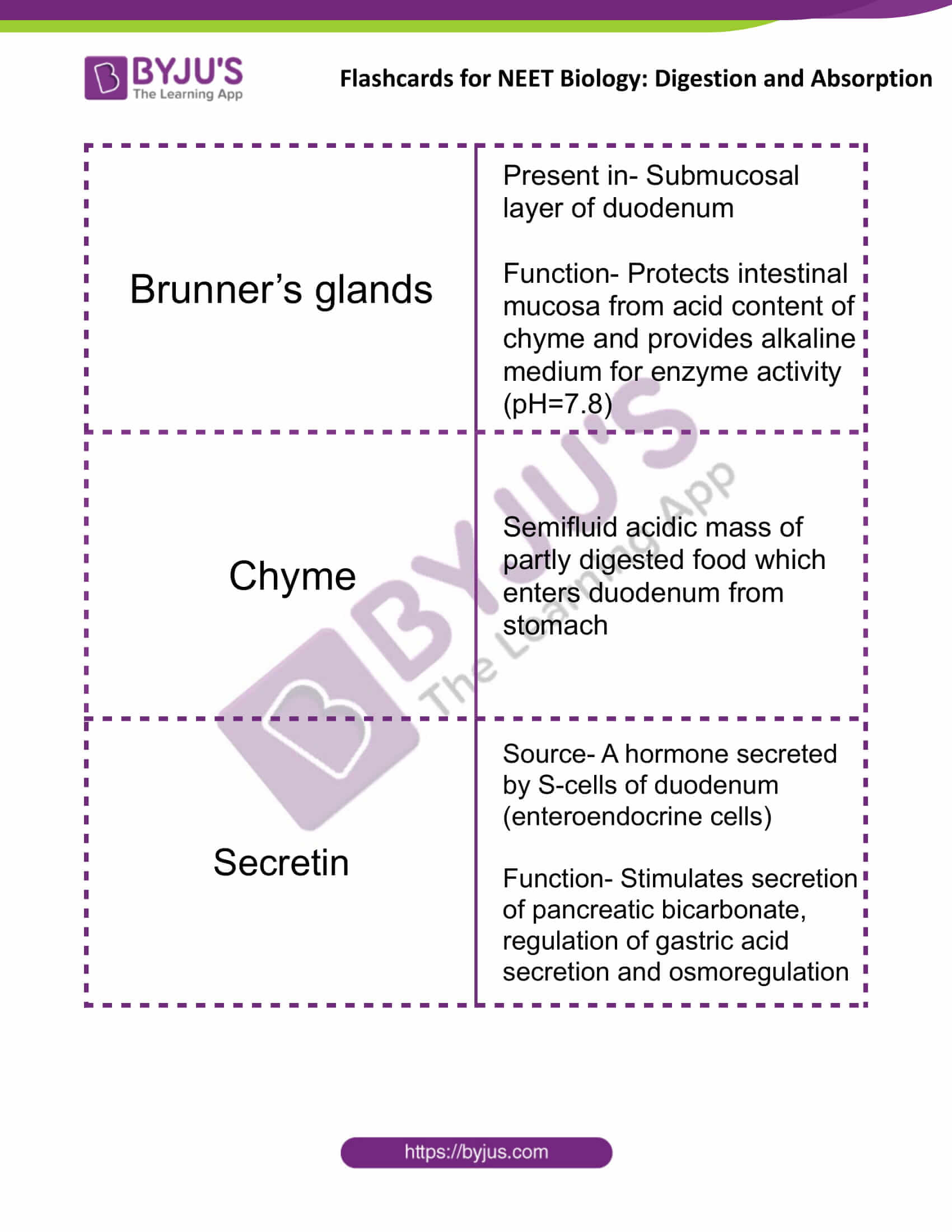
| Brunner’s glands | Present in- Submucosal layer of duodenum
Function- Protects intestinal mucosa from acid content of chyme and provides an alkaline medium for enzyme activity (pH=7.8) |
| Chyme | Semifluid acidic mass of partly digested food which enters duodenum from the stomach |
| Secretin | Source- A hormone secreted by S-cells of the duodenum (enteroendocrine cells)
Function- Stimulates secretion of pancreatic bicarbonate, regulation of gastric acid secretion and osmoregulation |
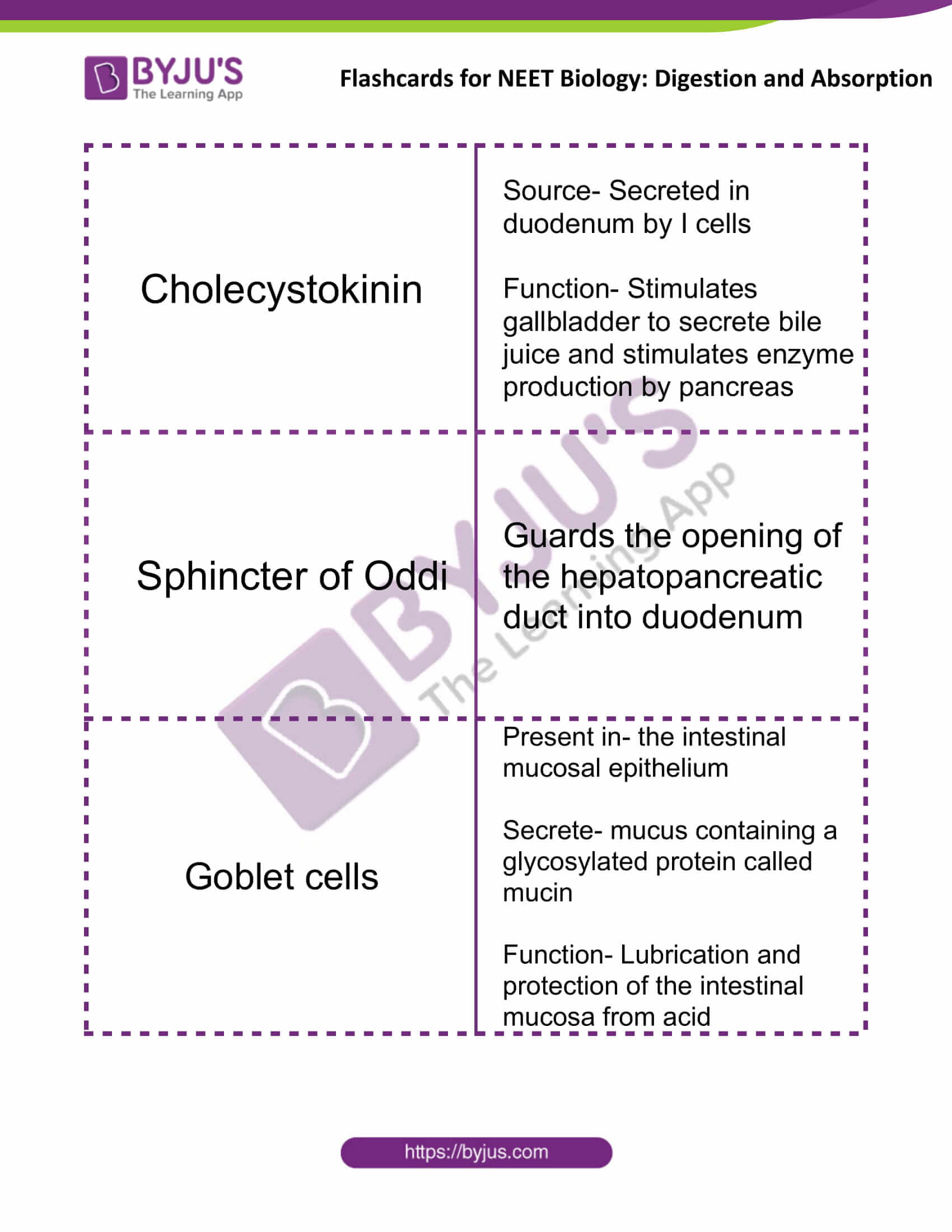
| Cholecystokinin | Source- Secreted in the duodenum by I cells
Function- Stimulates gallbladder to secrete bile juice and stimulates enzyme production by the pancreas |
| Sphincter of Oddi | Guards the opening of the hepatopancreatic duct into the duodenum |
| Goblet cells | Present in- the intestinal mucosal epithelium
Secrete- mucus containing a glycosylated protein called mucin Function- Lubrication and protection of the intestinal mucosa from acid |
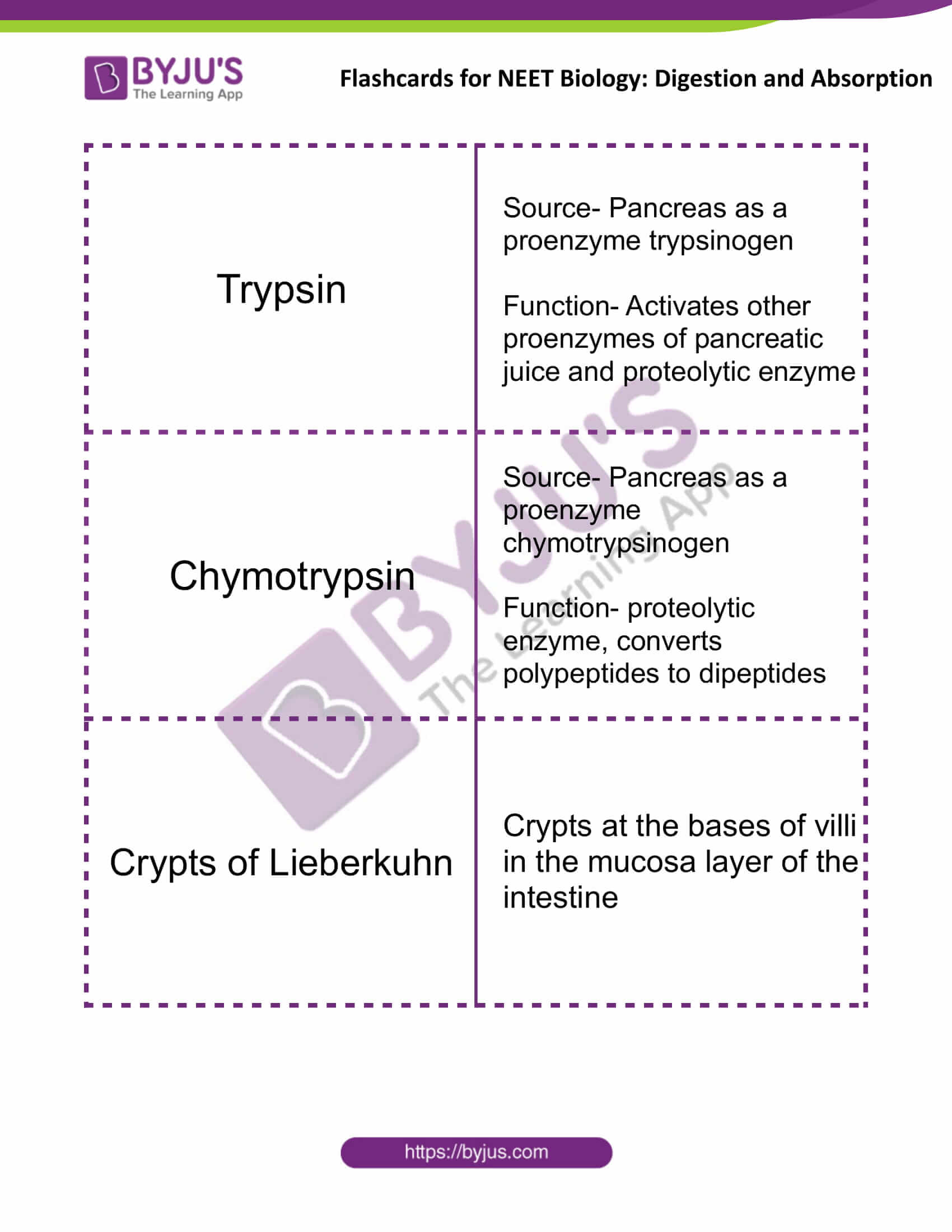
| Trypsin | Source- Pancreas as a proenzyme trypsinogen
Function- Activates other proenzymes of pancreatic juice and proteolytic enzyme |
| Chymotrypsin | Source- Pancreas as a proenzyme chymotrypsinogen
Function- proteolytic enzyme, converts polypeptides to dipeptides |
| Crypts of Lieberkuhn | Crypts at the bases of villi in the mucosa layer of the intestine |
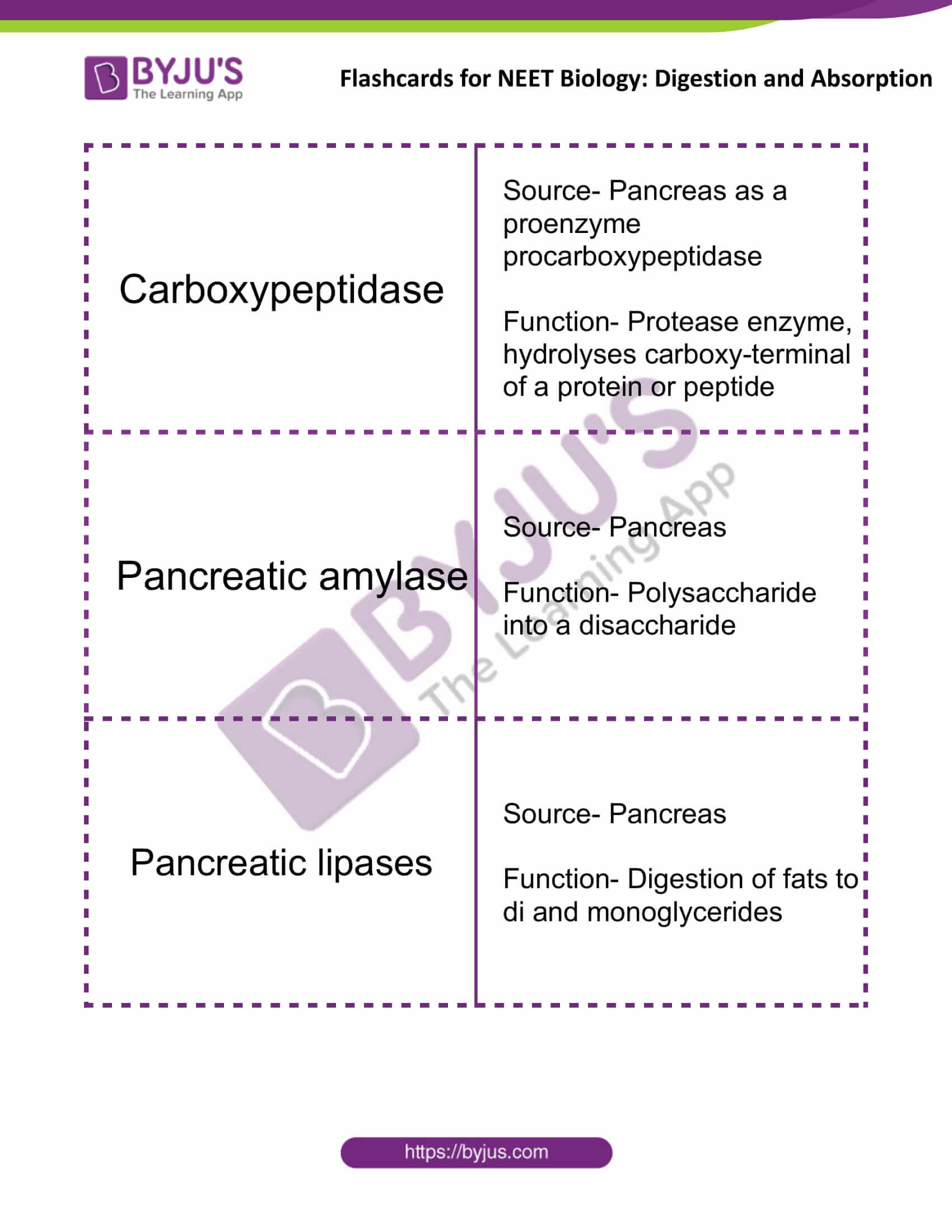
| Carboxypeptidase | Source- Pancreas as a proenzyme procarboxypeptidase
Function- Protease enzyme, hydrolyses carboxy-terminal of a protein or peptide |
| Pancreatic amylase | Source- Pancreas
Function- Polysaccharide into a disaccharide |
| Pancreatic lipases | Source- Pancreas
Function- Digestion of fats to di and monoglycerides |
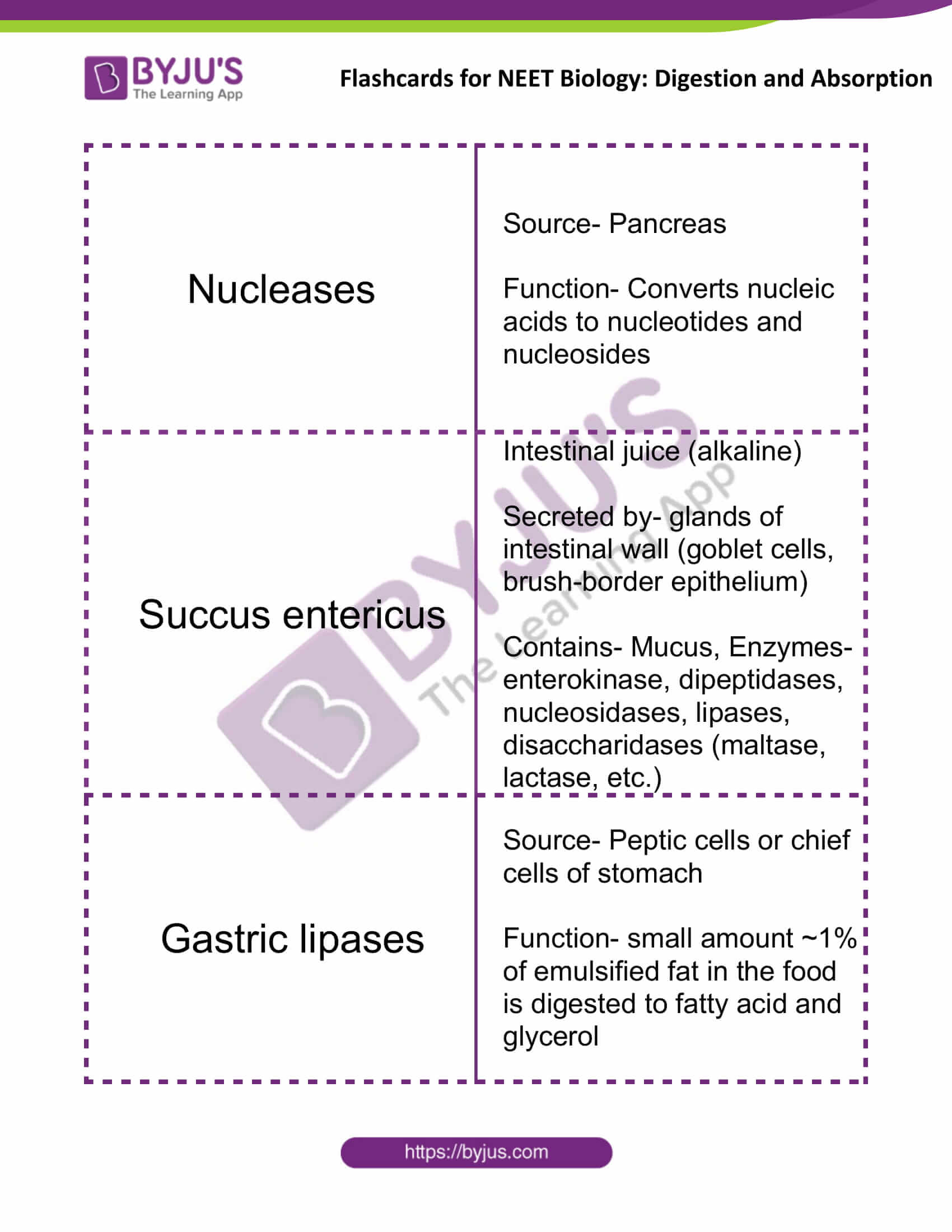
| Nucleases | Source- Pancreas
Function- Converts nucleic acids to nucleotides and nucleosides |
| Succus entericus | Intestinal juice (alkaline)
Secreted by- glands of the intestinal wall (goblet cells, brush-border epithelium) Contains- Mucus, Enzymes- enterokinase, dipeptidases, nucleosidases, lipases, disaccharidases (maltase, lactase, etc.) |
| Gastric lipases | Source- Peptic cells or chief cells of the stomach
Function- small amount ~1% of emulsified fat in the food is digested to fatty acid and glycerol |
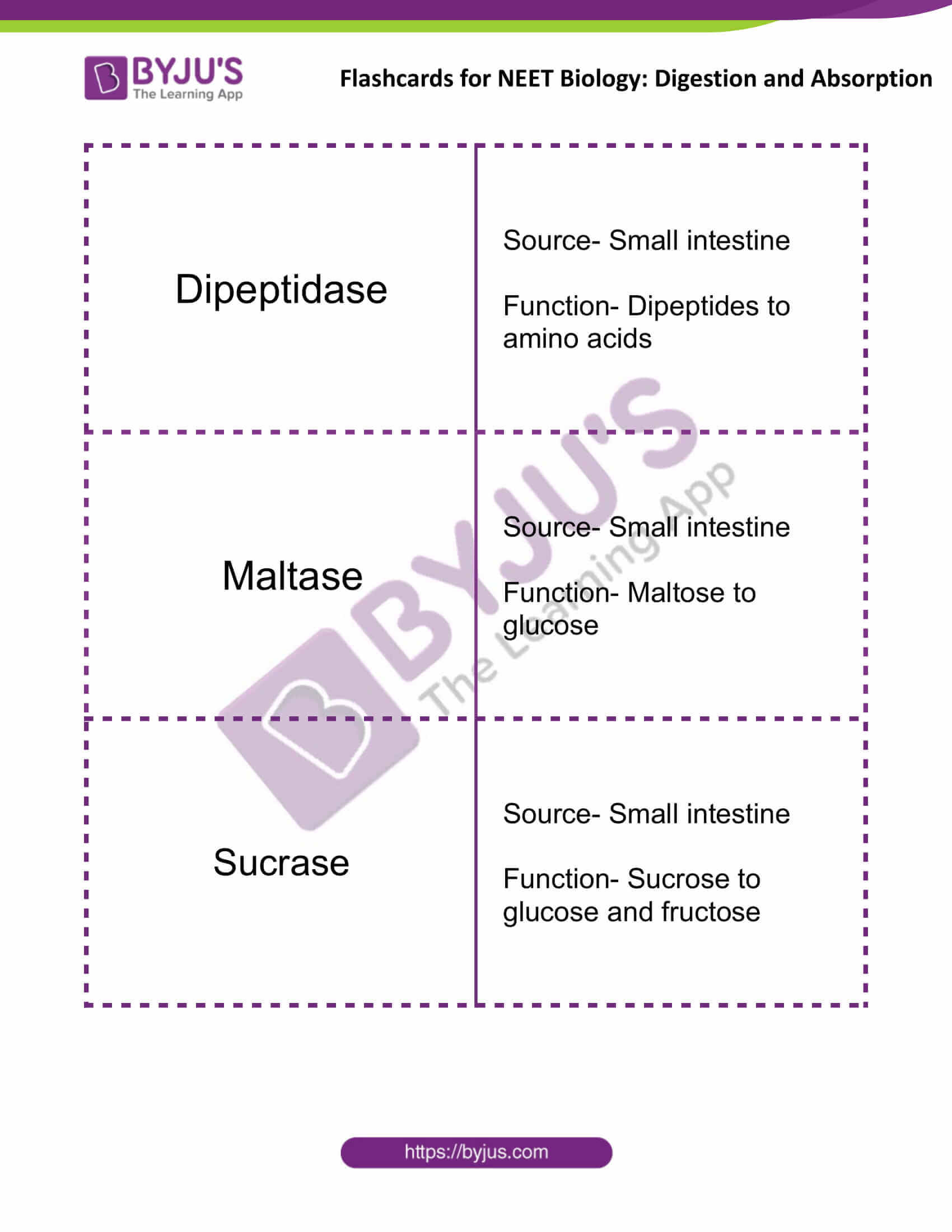
| Dipeptidase | Source- Small intestine
Function- Dipeptides to amino acids |
| Maltase | Source- Small intestine
Function- Maltose to glucose |
| Sucrase | Source- Small intestine
Function- Sucrose to glucose and fructose |
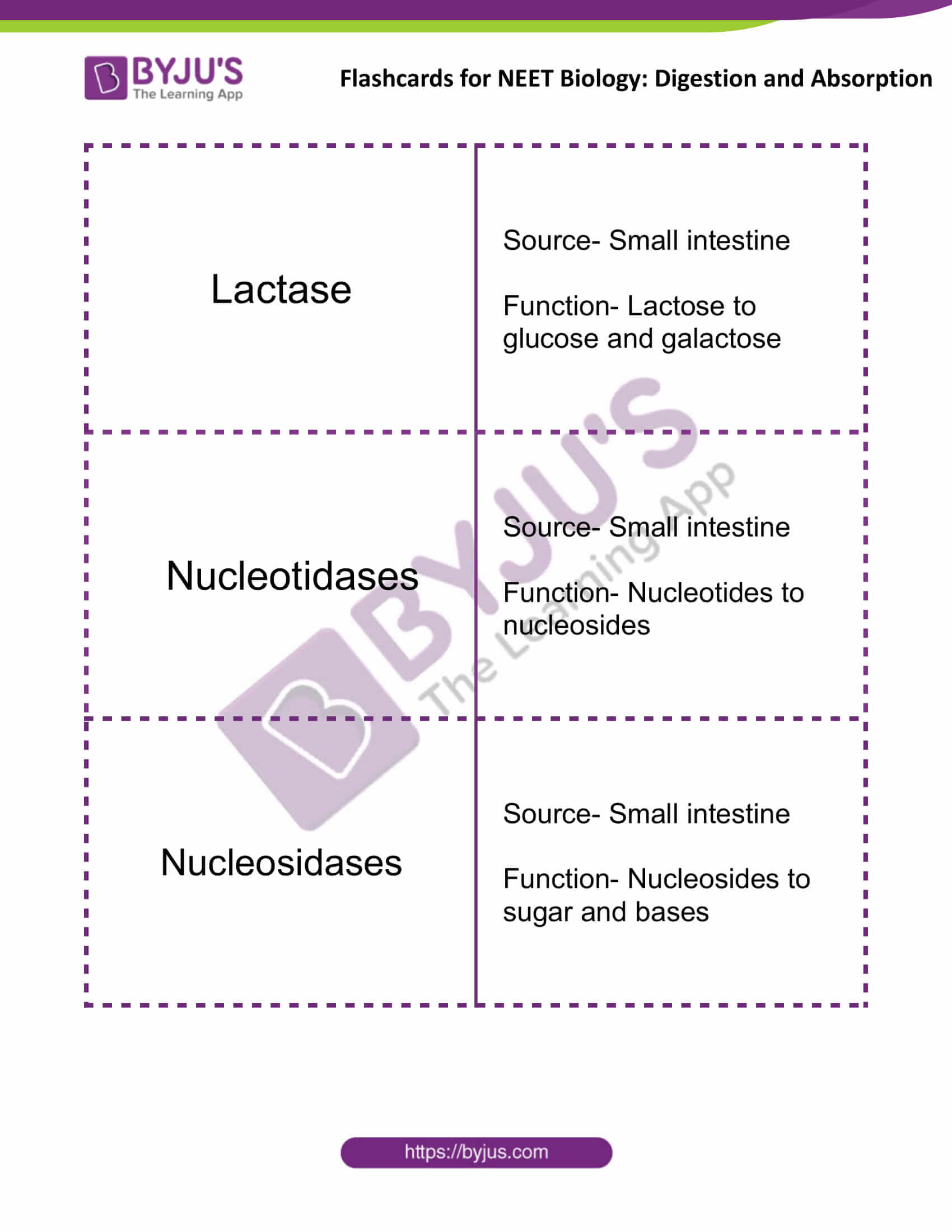
| Lactase | Source- Small intestine
Function- Lactose to glucose and galactose |
| Nucleotidases | Source- Small intestine
Function- Nucleotides to nucleosides |
| Nucleosidases | Source- Small intestine
Function- Nucleosides to sugar and bases |
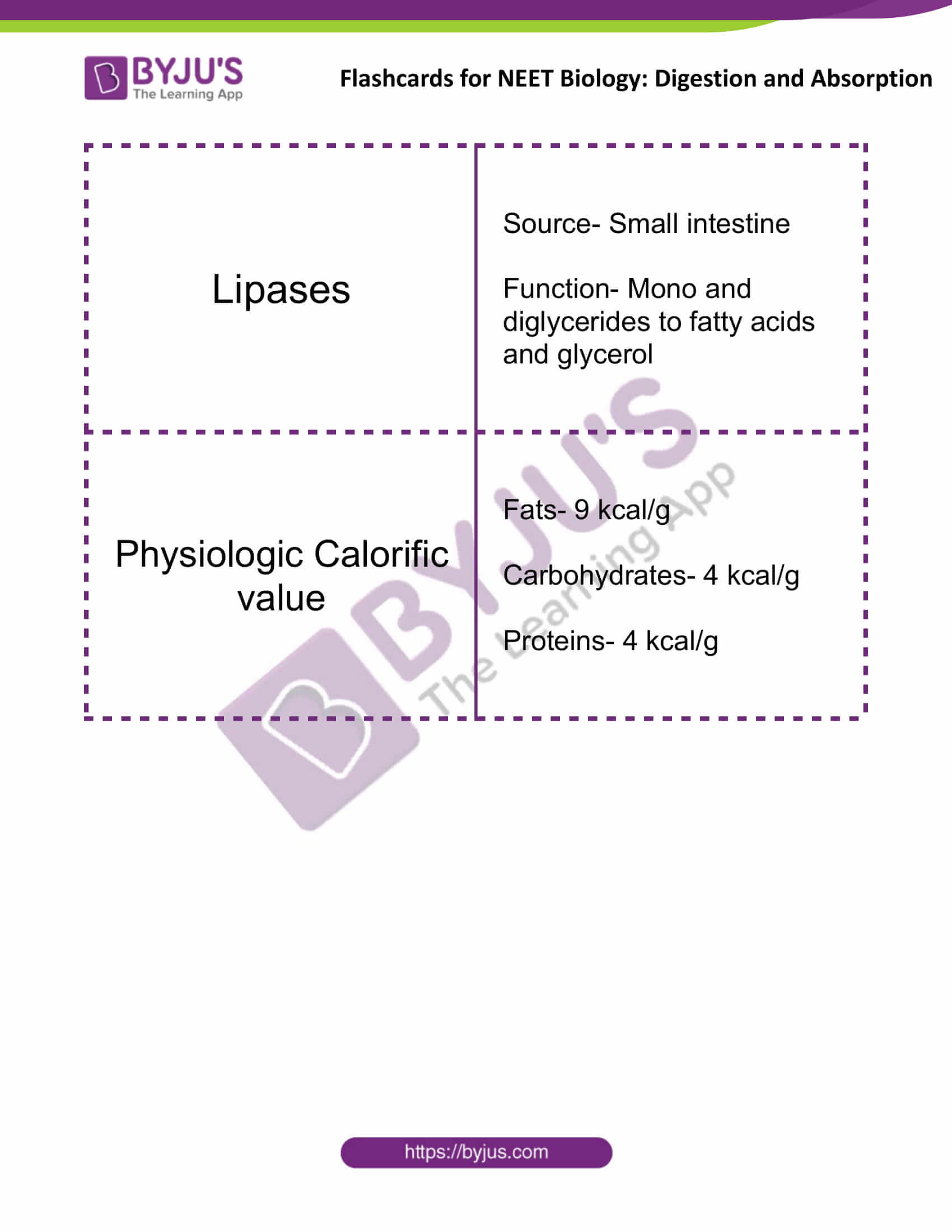
| Lipases | Source- Small intestine
Function- Mono and diglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol |
| Physiologic Calorific value | Fats- 9 kcal/g
Carbohydrates- 4 kcal/g Proteins- 4 kcal/g |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
NEET Flashcards: Body Fluids And Circulation
NEET Flashcards: Excretory Products And Their Elimination
NEET Flashcards: Locomotion And Movement
NEET Flashcards: Neural Control And Coordination

Comments