JEE Main 2019 solved Maths paper solutions are given on this page. The solutions are given in a step by step manner so that students can easily understand the problems. These solutions are prepared by subject experts. Students are recommended to revise and learn these solutions, so that they can easily improve their problem-solving skills. These solutions can be downloaded in PDF format for free.
JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
April Paper – Maths
1. The sum of coefficients of even powers of x in (x+√(x3-1)6 + x-√(x3-1)6)
A) 23
B) 24
C) 18
D) 21
(x+√(x3-1)6 + x-√(x3-1)6) = 2[6C0x6 +6C2x4(x3-1)+6C4x2(x3-1)2 +6C6(x3-1)3]
= 2[x6+15x4(x3-1)+15x2(x6-2x3+1)+(x3-1)3]
= 2[x6+15x7-15x4+15x8-30x5+15x2+x9-3x6+3(x3-1)]
Terms with even power of x =
\(\begin{array}{l}2\left[ {{x}^{6}}-15{{x}^{4}}+15{{x}^{8}}+15{{x}^{2}}-3{{x}^{6}}-1 \right]\end{array} \)
Therefore Sum of coefficients = 2(1-15+15+15-3-1) = 24
Answer: B
2. Let sin(α-β) = 5/13 and cos (α+β) = 3/5 where α, β ∈ (0, π/4) then tan 2α
A) 63/16
B) 61/16
C) 65/16
D) 32/9
sin(α-β) = 5/13
cos (α-β) = 12/13
cos(α+β) = 3/5
sin(α+β) = 4/5
tan 2α = tan[(α+β)+(α-β)]
= (4/3)+(5/12)÷(1-(4/3)×(5/12))
= 63/16
Answer: A
3.The line x+y = n, n∈N, makes intercepts with x2+y2 = 16. Then the sum of squares of all possible intercepts
A) 105/4
B) 105
C) 210
D) 105/2
x2+y2 = 16
Centre = (0,0)
OA = P
Radius = 4
P = n/√2

To make the intercepts n/√2 < 4
n< 4√2
Length of intercepts = √(r2-p2)
AB = √(16-n2/2)
Length of chord BC = 2√(16-n2/2) = √(64-2n2)
Square of intercepts = (64-2n2 ), n∈N
Possible value of n = 1,2,3,4,5
Sum of square of intercepts = (64-2)+(64-8)+(64-18)+(64-32)+(64-50)
= 62+56+46+32+50
= 210
Answer: C
4. \(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{\sin \frac{5x}{2}}{\sin \frac{x}{2}}}.\,dx=\end{array} \)
A) x+2sin x+sin 2x+c
B) x+2cos x+sin 2x+c
C) x-2sin x+sin 2x+c
D) x+2sin x-sin 2x+c
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{\sin \frac{5x}{2}}{\sin \frac{x}{2}}}.\,dx\end{array} \)
= \(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{2\sin \frac{5x}{2}.\cos \frac{x}{2}}{2\sin \frac{x}{2}.\cos \frac{x}{2}}}.\,dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{\sin 3x+\sin 2x}{\sin 2\left( \frac{x}{2} \right)}}.\,dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{\sin 3x}{\sin x}}.\,dx+\int{\frac{\sin 2x}{\sin x}}.\,dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\int{\frac{3\sin x-4{{\sin }^{3}}x}{\sin x}}.\,dx+\int{\frac{2\sin x\cos x}{\sin x}}dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}3\int{dx-4\int{{{\sin }^{2}}x.\,dx}}+2\int \cos x dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}3x-4\int{\frac{1-\cos 2x}{2}}.\,dx+2\sin x\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}3x-2x+\sin 2x+2\sin x+c\end{array} \)
= x+2 sinx+sin 2x +c
Answer: A
5. The area bounded by the curve y ≤ x2+3x, 0 ≤ y ≤ 4, 0 ≤ x ≤3 is
A) 59/6
B) 57/4
C) 59/3
D) 57/6

y = x2+3x
y = 4
x2+3x= 4 = 0
x2+3x-4 = 0
x = 1 or x = -4
Area =
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int\limits_{0}^{1}{\left( {{x}^{2}}+3x \right).\,dx}\end{array} \)
+ area of rectangle
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\left[ \frac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+\frac{3{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{1}+2\left( 4 \right)\end{array} \)
= (1/3)+(3/2)+8
= 59/6
Answer: A
6. “If you are born in India then you are citizen of India” contrapositive of this statement is
A) If you are born in India then you are not citizen of India
B) If you are not citizen of India then you are not born in India
C) If you are citizen of India then you are not born in India
D) If you are citizen of India then you are born in India
Statement:
\(\begin{array}{l}p\Rightarrow q\end{array} \)
Contrapositive:
\(\begin{array}{l}\tilde{\ }p\Rightarrow \,\tilde{\ }q\end{array} \)
Therefore answer is if you are not citizen of India then you are not born in India.
Answer: B
7. \(\begin{array}{l}A=\left[ \begin{matrix} \cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha \\ \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha \\ \end{matrix} \right]\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}{{A}^{32}}=\left[ \begin{matrix} 0 & -1 \\ 1 & 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right]\end{array} \)
. then α may be
A) 0
B) π/32
C) π/64
D) π/16
A =
\(\begin{array}{l}\left[ \begin{matrix} \cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha \\ \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha \\ \end{matrix} \right]\end{array} \)
A2 =
\(\begin{array}{l}\left[ \begin{matrix} \cos 2\alpha & -\sin 2\alpha \\ \sin 2\alpha & \cos 2\alpha \\ \end{matrix} \right]\end{array} \)
An =
\(\begin{array}{l}\left[ \begin{matrix} \cos \,n\alpha & -\sin \,n\alpha \\ \sin \,n\alpha & \cos \,n\alpha \\ \end{matrix} \right]\end{array} \)
cos 32α = 0 and sin 32α = 1
32α = π/2
α = π/64
Answer: C
8. Shortest distance between the curves y2 = x-2 and y = x is
A) greater than 4
B) less than 2
C) greater than 3
D) greater than 2
y2 = x-2
Differentiating we get,
2y (dy/dx) = 1
(dy/dx) = 1/2y
Slope of the line y = x is 1.
Slope of the tangent to the curve = 1/2y
1/2y = 1
→ y = 1/2
→ K = 1/2
∴ N = (9/4, 1/2)
Minimum distance = MN = perpendicular distance from point N to line y = x
\(\begin{array}{l}\left| \frac{a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}} \right|\end{array} \)
= \(\begin{array}{l}\left| \frac{1\left( \frac{9}{4} \right)-1\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)}{\sqrt{1+1}} \right|\end{array} \)
= 7/4√2 which is less than 2.
Answer: B
9. \(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\sin^{2} x}{\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{1+\cos x}}=\end{array} \)
A) √2
B) 2
C) 4
D) 4√2
Rationalise the denominator
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}x\left[ \sqrt{2}+\sqrt{1+\cos x} \right]}{2-\left( 1+\cos x \right)}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}x\left( \sqrt{2}+\sqrt{1+\cos x} \right)}{1-\cos x}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{Lt}}\,\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}x\left( \sqrt{2}+\sqrt{1+\cos x} \right)}{2{{\sin }^{2}}\frac{x}{2}}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{Lt}}\,\frac{{{\sin }^{2}}x}{{{x}^{2}}}.\frac{1}{2}\frac{1}{{{\left( \frac{\sin \frac{x}{2}}{\frac{x}{2}} \right)}^{2}}\times \frac{1}{4}}\left( \sqrt{2}+\sqrt{1+\cos x} \right)\end{array} \)
= (4/2) √2+√(1+1)
= 4√2
Answer: D
10. How many 9 digit numbers can be formed by using the digits 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4 such that odd numbers occur at even places.
A) 160
B) 175
C) 180
D) 220

Even places = 4
Odd numbers = 3
Even numbers = 6
Therefore number of numbers =
\(\begin{array}{l}=4{{c}_{3}}\times \frac{3!}{2!}\times \frac{6!}{4!2!}=180\end{array} \)
Answer: C
11. Let g(x) = ln x and \(\begin{array}{l}f\left( x \right)=\left( \frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right)\end{array} \)
then \(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{g\left[ f\left( x \right) \right]}.\,dx=\end{array} \)
A) ln 1
B) ln 2
C) ln e
D) ln 4
g(f(x)) =
\(\begin{array}{l}g\left[ \frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right]\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\ell n\left( \frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right)\end{array} \)
I =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{g\left[ f\left( x \right) \right]}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{\ell n\left( \frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right)}\,dx\end{array} \)
..(1)
We have
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)}=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( a+b-x \right)}\end{array} \)
I =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{\ell n\left( \frac{1+x\cos x}{1-x\cos x} \right)}\end{array} \)
..(2)
Add (1) and (2)
2I =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{\left[ \ell n\left( \frac{1+x\cos x}{1-x\cos x} \right)+\left( \frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right) \right]}\,dx\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{\ell n}\left( \frac{1+x\cos x}{1-x\cos x}.\frac{1-x\cos x}{1+x\cos x} \right)\,dx\end{array} \)
Because log ab = log a + log b
2I =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\limits_{-\frac{\pi }{4}}^{\frac{\pi }{4}}{\ell n}\,1=0\end{array} \)
Answer: A
12. The sum of the series 2. 20C0 + 5.20C1+8.20C2+62.20C20 is equal to
A) 16.222
B) 8.222
C) 8.221
D) 16.221
2. 20C0 + 5.20C1+8.20C2+62.20C20
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum\limits_{r=0}^{20}{\left( 3r+2 \right)20{{C}_{r}}}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}3\sum\limits_{r=0}^{20}{r.\,20{{C}_{r}}}+2.\sum\limits_{r=0}^{20}{20{{C}_{r}}}.\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}3.20\sum\limits_{r=1}^{20}{19{{C}_{r-1}}+2\left( 20{{C}_{0}}+20{{C}_{1}}+…+20{{C}_{20}} \right)}\end{array} \)
= 60.219+2.220
= 221(15+1)
= 221.16
Answer: D
13. Sum of natural numbers between 100 and 200 whose HCF with 91 should be more than 1.
A) 1121
B) 3210
C) 3121
D) 1520
Given numbers: 101, 102, 103, … 198, 199
91=13 × 7
HCF of 91 and a number is more than 1 means the number should be either multiple of 7 or 13.
Therefore sum of the numbers = (Numbers divisible by 7) + (Numbers divisible by 13) – (Numbers divisible by 91)
= (105+112+…+196 +( 104+117+…195 )-( 182)
= (14/2)[105+196]+(8/2)[104+195]-182
= 7(301)+4(299)-182
= 2107+1196-182
= 3121
Answer: C
14. If mean and variance of 7 variates are 8 and 16 respectively and five of them are 2, 4, 10, 12, 14 then the product of remaining two variates is
A) 49
B) 48
C) 45
D) 40
Let the remaining two variates be x and y
Given mean = 8
(x+y+2+4+10+12+14)/7 = 8
x+y+42 = 56
x+y = 14 ..(1)
Given variance = 16
[(x2+y2+4+16+100+144+196)/7] – 82 = 16
(x2+y2+460)/7 = 80
(x2+y2+460) = 560
(x2+y2) = 100 ..(2)
(x+y)2-2xy = 100
Substitute (1) in above equation
142-2xy = 100
196-2xy = 100
2xy = 96
xy = 48
Answer: B
15. If α and β are the roots of x2-2x+2 = 0 then the minimum value of n such that (α/β)n = 1
A) 4
B) 3
C) 2
D) 5
x2-2x+2 = 0
x2-2x+1+1 = 0
(x-1)2 = -1
(x-1) = ±i
x = 1+i or 1-i
Let α = 1+i
β = 1-i
(α/β) = (1+i)/(1-i)
= (1+i)2/2
= (1+i2+2i)/2
= (1-1+2i)/2
= i
(α/β)n = in = 1
Least value of n is 4.
Answer: A
16. Let y = y(x) be the solution of the differential equation, (x2+1)2dy/dx + 2x(x2+1)y = 1 such that y(0) = 0. If √a y(1) = π/32, then the value of a is:
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/16
D) 1
(x2+1)2dy/dx + 2x(x2+1)y = 1
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}+\frac{2x}{{{x}^{2}}+1}.\,y=\frac{1}{{{\left( {{x}^{2}}+1 \right)}^{2}}}\end{array} \)
dy/dx +Py = Q
P = 2x/x2+1
Q = 1/(x2+1)2
I.F =
\(\begin{array}{l}e^{\int \frac{2x}{1+x^{2}}}dx\end{array} \)
= 1+x2
The general solution of linear differential equation is
y.(I.F) =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int Q.(I.F)dx+C\end{array} \)
y(1+x2) =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int \frac{1}{1+x^{2}}dx+C\end{array} \)
= tan-1 x+C
At x = 0, y = 0
0(1) = tan-10+C
C = 0
y.(x2+1) = tan-1x
put x = 1
y.(2) = tan-11
y.(2) = π/4
y = π/8
(1/4)y = π/32
i.e √a = ¼
a = 1/16
Answer: C
17. If f(x) = log((1-x)/(1+x)) then f(2x/1+x2) is equal to
A) f(x)
B) 2f(x)
C) -2f(x)
D) [f(x)]2
f(x) =
\(\begin{array}{l}\log \left( \frac{1-x}{1+x} \right)\end{array} \)
f(2x/1+x2) =
\(\begin{array}{l}\log \left[ \frac{1-\frac{2x}{1+{{x}^{2}}}}{1+\frac{2x}{1+{{x}^{2}}}} \right]\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\log \left( \frac{1+{{x}^{2}}-2x}{1+{{x}^{2}}+2x} \right)\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\log {{\left( \frac{1-x}{1+x} \right)}^{2}}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}2\: log\left( \frac{1-x}{1+x} \right)\end{array} \)
= 2 f(x)
Answer: B
18. Given that \(\begin{array}{l}A\subset B\end{array} \)
then identify the correct statement.
A) \(\begin{array}{l}P\left( \frac{A}{B} \right)=P\left( A \right)\end{array} \)
B) \(\begin{array}{l}P\left( \frac{A}{B} \right)\le P\left( A \right)\end{array} \)
C) \(\begin{array}{l}P\left( \frac{A}{B} \right)\ge P\left( A \right)\end{array} \)
D) \(\begin{array}{l}P\left( \frac{A}{B} \right)=P\left( A \right)-P\left( B \right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}P\left( \frac{A}{B} \right)=\frac{P\left( A\cap B \right)}{P\left( B \right)}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{P\left( A \right)}{P\left( B \right)}\ge P\left( A \right)\end{array} \)
19. Find the value of ‘c’ for which the following equations have non-trivial solutions.
cx-y-z = 0
-cx+y-cz = 0
x+y-cz = 0
A) 1/2
B) -1
C) 2
D) 0
For non trivial solutions,
\(\begin{array}{l}\left| \begin{matrix} c & -1 & -1 \\ -c & 1 & -c \\ 1 & 1 & -c \\ \end{matrix} \right|=0\end{array} \)
c(-c+c) +1(c2+c)-1(-c-1) = 0
c2+c+c+1 = 0
(c+1)2 = 0
c+1 = 0
c = -1
Answer: B
20. Let \(\begin{array}{l}2y={{\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}\left( \frac{\sqrt{3}\cos x+\sin x}{\cos x-\sqrt{3}\sin x} \right) \right]}^{2}}\end{array} \)
then \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}=\end{array} \)
A) x-(π/6)
B) x+(π/6)
C) 2x-(π/6)
D) 2x-(π/3)
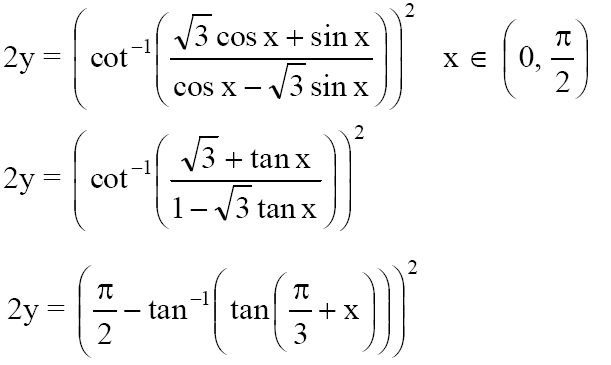
2y = [(π/2) -(π/3)+x]2
2y = [(π/6)-x]2
Differentiating we get,
2 dy/dx = 2[(π/6)-x](-1)
dy/dx = x-(π/6)
Answer: A
21. Let S1 is set of minima and S2 is set of maxima for the curve y = 9x4+12x3-36x2-25 then
A) S1 = {-2,-1} S2 = {0}
B) S1 = {-2,1} S2 = {0}
C) S1 = {-2,1} S2 = {-1}
D) S1 = {-2,2} S2 = {0}
y = 9x4+12x3-36x2-25
dy/dx = 36x3 + 36x2-72x
= 36x(x2+x-2)
= 36x(x2+2x-x-2)
= 36x(x+2)(x-1)
Critical points are 0,-2,1
At {-2,1} -> points of minima
{0} -> points of maxima.
Answer: B
22. Let f:[0,2] -> R be a twice differentiable functions such that f’’(x) >0 for all x ∈ (0,2). If f(x) = f(x)+f(2-x). then f is:
A) Increasing in (0, 1) and decreasing in (1, 2)
B) Decreasing in (0, 1) and increasing in (1, 2)
C) Increasing in (0, 2)
D) Decreasing in (0, 2)
Given f’’(x) >0, x ∈(0,2)
i.e f’(x) is an increasing function
f(x) = f(x)+f(2-x)
f’(x) = f’(x)-f’(2-x)
f(x) is increasing (x) > 0
f’(x)-f’(2-x) >0
f’(x) > f’(2-x)
x > 2-x
2x > 2
x>1
i.e x ∈ (1,2)
f(x) is decreasing (x) < 0
f’(x)-f’(2-x) <0
f’(x) < f’(2-x)
x < 2-x
2x < 2
x <1
i.e x ∈ (0,1)
Answer: B
23. Let vertices of the triangle ABC is A(0, 0), B(0, 1) and C(x, y) and perimeter is 4 then locus of ‘C’ is
A) 9x2 + 8y2+8y = 16
B) 8x2 + 9y2+9y = 16
C) 9x2 + 8y2-8y = 16
D) 8x2 + 9y2-9x = 16

Given AB+AC+BC = 4
1+
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}\end{array} \)
= 4
√(x2+y2)2 = (3-√(x2+(y-1)2)2
x2+y2 = 9+x2+y2-2y+1-6√(x2+(y-1)2)
3√(x2+(y-1)2) = 5-y
9(x2+(y-1)2 = (5-y)2
9x2+8y2-8y = 16
Answer: C
24. A point on the straight line, 3x + 5y = 15 which is equidistant from the coordinate axes will lie only in
A) 1st, 2nd and 4th quadrants
B) 1st and 2nd quadrants
C) 4th quadrants
D) 1st quadrants
3x+5y = 15 is the equation of the straight line.
If x = y
3x+5x = 15
8x = 15
x = 15/8
y = 15/8
P(15/8, 15/8) lies in 1st quadrant.
If x = -y
3x-5x = 15
-2x = 15
x = -15/2
y = 15/2
Q(-15/2, 15/2) lies in 2nd quadrant.
Answer: B
25. The perpendicular distance of point ( 2,-1,4) from the line \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x+3}{10}=\frac{y-2}{-7}=\frac{z}{1}\end{array} \)
lies between
A) (2, 3)
B) (3, 4)
C) (4, 5)
D) (1, 2)

Let A be (2,-1,4).
Direction ratio of AB = (10λ-5, -7λ+3, λ-4)
Drs of given line = (10, -7, 1)
10(10λ-5)-7(-7λ+3)+(λ -4) = 0
100λ -50+49-21+λ-4 = 0
150λ = 75
λ = 1/2
Point B (2, -3/2, 1/2)
Length AB = 5/√2
= 3.53
Answer: B
26. If a plane passes through intersection of planes 2x-y-4 = 0 and y+2z-4 = 0 and also passes through the point (1, 1, 0). Then the equation of the plane is
A) x-y-z = 0
B) 2x-z = 0
C) x+2z-1 = 0
D) x-z-1 = 0
Required equation of the plane is (2x-y-4)+λ(y+2z-4) = 0
Given it pass through (1,1,0)
(2-1-4)+λ(1+0-4) = 0
λ= -1
(2x-y-4)-(y+2z-4) = 0
2x-2y-2z = 0
x-y-z = 0
Answer: A
27. The sum of the solutions of the equation |√x-2|+√x(√x-4)+2 = 0, (x>0) is equal to
A) 4
B) 10
C) 9
D) 12
Given equation is |√x-2|+√x(√x-4)+2 = 0, (x>0)
Put √x = t
|t-2|+t(t-4)+2 = 0
If t ≥2
t-2+t2-4t+2 = 0
t2-3t = 0
t(t-3) = 0
t = 3 or t = 0
t = 0 not possible
if t = 3, x = 9
If t < 2
2-t+t2-4t+2 = 0
t2-5t+4 = 0
t = 1 or t = 4
t = 4 not possible
so t = 1
x = 1
Sum of solution = 9+1 = 10
Answer: B
28. If the tangents on the ellipse 4x2+y2 = 8 at the points (1,2) and (a,b) areperpendicular to each other, then a2 is equal to
A) 2/17
B) 64/17
C) 128/17
D) 4/17
The equation of the ellipse 4x2+y2 = 8
dy/dx = -4x/y
The tangent at (1,2) and (a,b) are perpendicular
(-y/2)(-4a/b) = -1
b = -8a ..(i)
(a,b) is on the ellipse.
4a2+b2 = 8 [from eq(i)]
4a2+64a2 = 8
a2 = 8/68 = 2/17
Answer: A
29. Find the magnitude of projection of vector \(\begin{array}{l}2\hat{i}+3\hat{j}+\hat{k}\end{array} \)
on a vector which is perpendicular to the plane containing vectors \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k}\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{i}+2\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\end{array} \)
A) √3/2
B) √(3/2)
C) 3√6
D) √6
The vector perpendicular to given vectors is
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}=\begin{vmatrix} \hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k}\\ 1 & 1 & 1\\ 1 & 2 & 3 \end{vmatrix}\end{array} \)
So
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}= \hat{i}-2\hat{j}+\hat{k}\end{array} \)
Projection of vector b in direction of vector a =
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\left | \vec{a} .\vec{b}\right |}{\left | \vec{a} \right |}\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\left | (\hat{i}-2\hat{j}+\hat{k} ).(2\hat{i}+3\hat{j}+\hat{k})\right |}{\left | \sqrt{6} \right |}\end{array} \)
= 2-6+1/√6
= 3/√6
= √(3/2)
Answer: B
30. If α = cos-1(3/5), β = tan-1 (1/3), where 0<α, β < π/2, then α-β is equal to:
A) tan-1(9/5√10)
B) sin-1(9/5√10)
C) tan-1(9/15)
D) cos-1(9/5√10)
α = cos-1(3/5) = tan-1(4/3)
β = tan-1 (1/3)
α-β = tan-1(4/3) – tan-1 (1/3)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan ^{-1}\left ( \frac{\frac{4}{3}-\frac{1}{3}}{1+\frac{4}{3}\times \frac{1}{3}} \right )\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan ^{-1}\left ( \frac{1}{1+\frac{4}{9}} \right )\end{array} \)
= tan-1(9/13)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\sin ^{-1}\frac{9}{\sqrt{13^{2}+9^{2}}}\end{array} \)
= sin-1(9/√250)
= sin-1(9/5√10)
Answer: B
Video Lessons – Maths Paper April
Download PDF 
carouselExampleControls112
























Comments