JEE Main 2020 Maths paper September 2 Shift 2 solutions are available on this page. Students are recommended to go through these solutions so that they can improve their understanding of concepts and at the same time develop greater speed for solving problems. Using this paper and solutions to revise and practice will help students to find out their weaker areas and concentrate more on improving them. These solutions can be easily downloaded in PDF format for free.
JEE Main 2020 Question Papers
September 2 Shift 2 – Maths
Download PDF 
September 2 Shift 2 – Maths
Question 1.Let f:R -> R be a function which satisfies f(x+y) = f(x)+f(y) for all x, y ∈ R. If f(1) = 2 and g(n) = \(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{k=1}^{n-1}f(k)\end{array} \)
, n ∈ N then the value of n for which g(n) = 20 is
a) 9
b) 5
c) 4
d) 20
f(1) = 2
f(x+y) = f(x)+f(y)
x = y = 1
f(2) = 2+2 = 4
x = 2, y = 1
f(3) = 4+2 = 6
g(n) = f(1)+f(2)+………+f(n-1)
= 2+4+6+ ….+ 2(n-1)
= 2Ʃ(n-1)
= 2(n-1)n/2
= n(n-1)
= n2-n
n2-n = 20
n2-n-20 = 0
(n-5)(n+4) = 0
n = 5
Answer:(b)
Question 2. If the sum of first 11 terms of an A.P, a1,a2,a3… is 0 (a1 ≠ 0) then the sum of the A.P, a1, a3 , a5…a23 is ka1, where k is equal to
a) -121/10
b) -72/5
c) 72/5
d) 121/10
Given
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{k=1}^{11}a_{k}=0\end{array} \)
11a+55d = 0
a+5d = 0
d = -a/5
Now a1+a3+….+ a23 = ka1
12a+d (2+4+6+…..+22) = ka
12a+2d×66 = ka
12(a+11d) = ka
12(a+11(-a/5)) = ka
12(1-11/5) = k
k = -72/5
Answer: (b)
Question 3. Let EC denote the complement of an event E. Let E1, E2 and E3 be any pair wise independent events with P(E1)>0 and P(E1 ∩ E2 ∩ E3) = 0. Then P(E2C ∩ E3C/E1) is equal to:
a) P(E3C)- P(E2C)
b) P(E3)- P(E2C)
c) P(E3C)- P(E2)
d) P(E2C)+ P(E3)
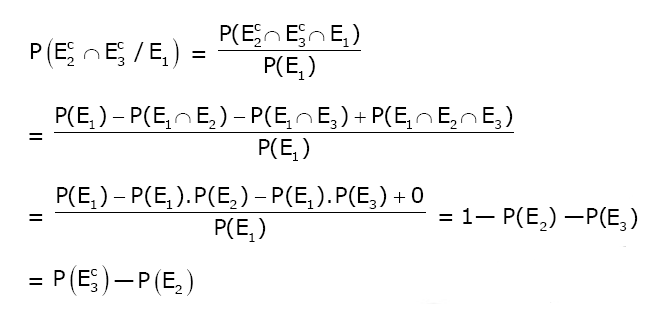
Answer: (c)
Question 4. If the equation cos4θ+sin4θ+λ = 0 has real solutions for θ, then λ lies in the interval:
a) (-1/2, -1/4]
b) [-1,-1/2]
c) [-3/2, -5/4]
d) (-5/4, -1)
cos4θ+sin4θ+λ = 0
λ = -{1-(1/2)sin22θ}
2(λ+1) = sin22θ
0 ≤2(λ+1) ≤1
0 ≤λ+1 ≤1/2
-1≤ λ ≤ -1/2
Answer: (b)
Question 5. The area (in sq. units) of an equilateral triangle inscribed in the parabola y2 = 8x, with
one of its vertices on the vertex of this parabola, is:
a) 128√3
b) 192√3
c) 64√3
d) 256√3
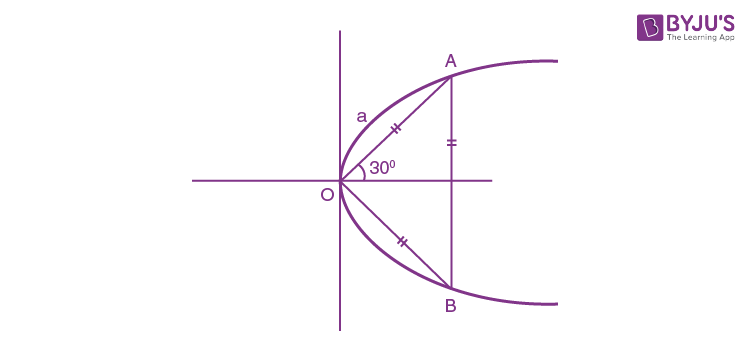
A: (a cos 300, a sin 300) lies on parabola
(a2/4) = 8×a√3/2
a = 16√3
Area of equilateral triangle, Δ = (√3/4)a2
Δ= (√3/4)×16×16×3
Δ= 192√3
Answer: (b)
Question 6. The imaginary part of (3+2√-54)1/2-(3-2√-54)1/2 can be:
a) √6
b) -2√6
c) 6
d) -√6
(3+2i√54)1/2-(3-i2√54)1/2
= (9+6i2+2×3i√6)1/2-(9+6i2-2×3i√6)1/2
= ((3+√6i)2)1/2 -((3-√6i)2)1/2
= (3+√6i)( 3-√6i)
= -2√6i
Answer: (b)
Question 7.A plane passing through the point (3,1,1) contains two lines whose direction ratios are (1, -2, 2) and (2, 3, -1) respectively. If this plane also passes through the point (α,-3,5), then α is equal to:
a) -5
b) 10
c) 5
d) -10
Required plane is
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{vmatrix} x-3 &y-1 & z-1\\ 1& -2& 2\\ 2& 3 &-1 \end{vmatrix}=0\end{array} \)
-4(x-3)+5(y-1)+7(z-1) = 0
4x-5y-7z = 0
(α, -3,5) lies on 4x-5y-7z = 0
α = 5
Answer: (c)
Question 8.Let A = {X= (x,y,z)T: PX = 0 and x2+y2+z2 = 1}, where P = \(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 1\\ -2 & 3 & -4\\ 1 & 9& -1 \end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
then the set A:
a) contains more than two elements.
b) is a singleton.
c) contains exactly two elements.
d) is an empty set.
Clearly |P|= 0
PX = 0 has infinite solutions
The line concurrence passes through (0,0,0) which is centre of sphere x2+y2+z2 = 1.
Diameter will intersect at two points.
two solutions (exactly) exist.
Answer: (c)
Question 9. The equation of the normal to the curve y = (1+x)2y +cos2(sin -1x) at x = 0 is:
a) y+4x = 2
b) 2y+x = 4
c) x+4y = 8
d) y = 4x+2
At x = 0, y = 1+cos2(0) = 2
P;(0,2)
y = (1+x)2y+cos2(sin-1x)
y = (1+x)2y+cos(cos-1√(1-x2))2
= (1+x)2y+ (√(1-x2))2
y = (1+x)2y+1-x2
Differentiating w.r.t x
Now y’ = (1+x)2y {(2y/1+x)+ln(1+x)2y’}-2x
y’ at (0,2) = 4-0 = 4
N0: y-2 = (-1/4)(x-0)
N0: 4y-8 = -x
x+4y = 8
Answer: (c)
Question 10. Consider a region R = {(x,y)∈R2 : x2 ≤y ≤ 2x}. If a line y = α divides the area of region R into two equal parts, then which of the following is true.?
a) α3-6α2+16 = 0
b) 3α2-8α3/2+8 = 0
c) α3-6α3/2-16 = 0
d) 3α2-8α+8 = 0
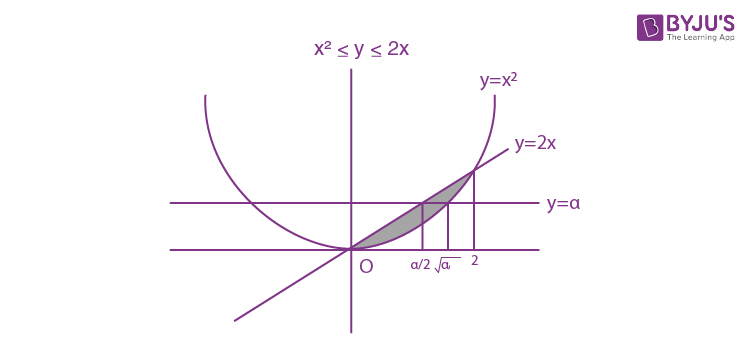
Area =
\(\begin{array}{l}\int_{0}^{2}(2x-x^{2})dx\end{array} \)
= x2-(x3/3)
= 4/3 [Applying limits]
So
\(\begin{array}{l}\int_{0}^{\alpha }(\sqrt{y}-\frac{y}{2})dy= \frac{2}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}[\frac{2}{3}y^{\frac{3}{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{4}]_{0}^{\infty }=\frac{2}{3}\end{array} \)
8.α3/2-3α2 = 8
3α2-8α3/2+8 = 0
Answer: (b)
Question 11.Let f: (-1, ∞)→R be defined by f(0) = 1 and f(x) = (1/x)loge(1+x), x ≠ 0. Then the function f:
a) increases in (-1, ∞)
b) decreases in (-1,0) and increases in (0, ∞)
c) increases in (-1,0) and decreases in (0, ∞)
d) decreases in (-1, ∞)
f(x) = (1/x)ln(1+x)
f’(x) = [x/(1+x) – ln(1 + x)]/x2 = [x – (1+x)ln (1+x)]/x2(1+x)
f’<0 ∀ x ∈(-1,∞)
Answer: (d)
Question 12.Which of the following is a tautology?
a) (p→q) ˄( q→p)
b) (~p) ˄(p ˅q)→q
c) (q→p) ˅~(p→q)
d) (~q)˅( p˄q)→q
| p |
q |
~p |
(p ˅q) |
~p ˄(p˅q) |
~p ˄(p˅q)->q |
| T |
T |
F |
T |
F |
T |
| T |
F |
F |
T |
F |
T |
| F |
T |
T |
T |
T |
T |
| F |
F |
T |
F |
F |
T |
Answer: (b)
Question 13. Let f(x) be a quadratic polynomial such that f(-1)+f(2) = 0. If one of the roots of f(x) = 0 is 3, then its other roots lies in:
a) (0,1)
b) (1,3)
c) (-1,0)
d) (-3,-1)
Let f(x) = a (x-3) (x-α)
f(-1)+f(2) = 0
a[(-1-3) (-1-α)+(2-3)(2-α)] = 0
a[4+4α-2+α]=0
5α+2 = 0
α = -2/5
Answer: (c)
Question 14. Let S be the sum of the first 9 terms of the series:
{x+ka}+{x2+(k+2)a}+{x3+(k+4)a}+{x4+(k+6)a}+… where a ≠ 0 and a ≠ 1.
If S = (x10-x+45a(x-1))/(x-1), then k is equal to:
a) 3
b) -3
c) 1
d) 5
S = {x+ka} + {x2+(k+2)a} +{x3+(k+4)a} up to 9 terms
S = (x+x2+….+x9)+a{k+(k+2)+(k+4)+……up to 9 term)}
S = x(1-x9)/(1-x) + a(9k+2×36)
= (x10-x)/(x-1) +9ak+72a
S = (x10-x+45a(x-1))/(x-1)
= (x10-x+(9k+72)a(x-1))/(x-1)
45 = 9k+72
9k = -27
k = -3
Answer: (b)
Question 15. The set of all possible values of θ in the interval (0, π) for which the points (1, 2) and (sin θ, cos θ ) lie on the same side of the line x+y = 1 is:
a) (0, π/4)
b) (0, π/2)
c) (0, 3π/4)
d) (π/4, 3π/4)
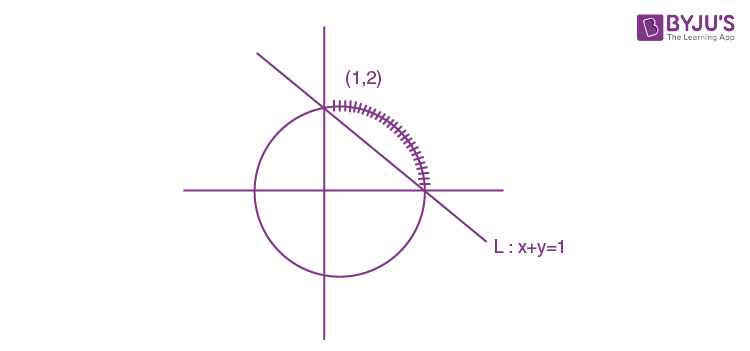
L11×L22 >0
sinθ +cosθ > 1
θ ∈(0, π/2)
Answer: (b)
Question 16. Let n>2 be an integer. Suppose that there are n metro stations in a city located along a circular path. Each pair of stations is connected by a straight track only. Further, each pair of nearest stations is connected by blue line, whereas all remaining pairs of stations are connected by red line. If the number of red lines is 99 times the number of blue lines, then the value of n is:
a) 201
b) 199
c) 101
d) 200
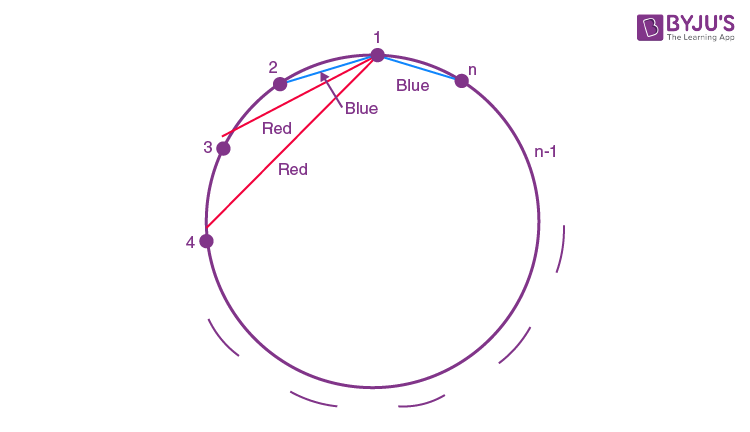
Red line = 99 blue line
nC2-n = 99n
n(n-1)/2 = 100n
n-1 = 200
n = 201
Answer: (a)
Question 17. If a curve y = f(x), passing through the point (1,2) is the solution of the differential equation, 2x2dy = (2xy+y2)dx, then f(1/2) is equal to:
a) -1/(1+loge2)
b) 1+loge 2
c) 1/(1+loge2)
d) 1/(1-loge2)
2(dy/dx) = 2(y/x)+(y/x)2 HDE
Since y = vx
2(v+x(dv/dx)) = 2v+v2
2(dv/v2) = dx/x
-(2/v) = ln x+c
-2x/y = ln x+c
c = -1
c: ln x+2x/y = 1
for f(1/2) ln(1/2) +(2/2y) = 1
y = 1/(1+ln 2)
Answer (c)
Question 18. For some θ∈(0, π/2) , if the eccentricity of the hyperbola, x2-y2sec2 θ = 10 is √5 times the eccentricity of the ellipse, x2sec2θ+y2 = 5, then the length of the latus rectum of the ellipse, is:
a) 4√5/3
b) 2√5/3
c) 2√6
d) √30
H: x2-y2sec2θ = 10
E: x2sec2θ+y2 = 5
√(1+10cos2θ/10)= √5√(1-5cos2θ/5)
1+cos2θ = 5-5cos2θ
6 cos2θ = 4
cosθ = √(2/3)
LR of ellipse = 2×5×cos2θ/√5
= 2√5×2/3
= 4√5/3
Answer (c)
Question 19.\(\begin{array}{l}\lim_{x\to0}\left ( \tan (\frac{\pi }{4}+x) \right )^{\frac{1}{x}}\end{array} \)
is equal to:
a) e
b) e2
c) 2
d) 1
\(\begin{array}{l}\lim_{x\to0}\left ( \tan (\frac{\pi }{4}+x) \right )^{\frac{1}{x}}\end{array} \)
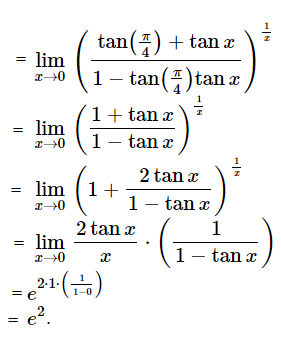
Answer: (b)
Question 20. Let a, b, c ∈ R be all non-zero and satisfy a3+b3+c3 = 2. If the matrix A = \(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} a & b & c\\ b &c &a \\ c& a & b \end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
satisfies ATA = I, then a value of abc can be:
a) 2/3
b) 3
c) -1/3
d) 1/3
a3+b3+c3 = 2
ATA = I
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} a & b & c\\ b &c &a \\ c& a & b \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} a & b & c\\ b &c &a \\ c& a & b \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 &1 &0 \\ 0& 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
a2+b2+c2 = 1
ab+bc+ca = 0
Now (a+b+c)2 = Ʃa2+2Ʃab
(Ʃa)2 = 1+0 = 1
Ʃa = 1
Now Ʃa3-3abc = (Ʃa)(Ʃa2– Ʃab)
2-3abc = ± 1(1-0)
2-3abc = ± 1
abc = 1/3 or abc = 1
Answer: (d)
Question 21. Let the position vectors of points ‘A’ and ‘B’ be \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k}\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\end{array} \)
respectively. A point ‘P’ divides the line segment AB internally in the ratio λ:1 (λ>0) . If O is the origin and \(\begin{array}{l}\vec{OB}.\vec{OP} -3\left | \vec{OA} \times \vec{OP}\right |^{2}=6\end{array} \)
, then λ is equal to:
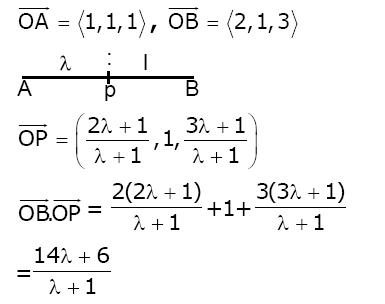

Now (14λ+6)/(λ+1) -3(6λ2)/(λ+1)2 = 6
(14λ+6) (λ+1)—18λ2 = 6(λ+1)2
-4λ2 + 20λ + 6 = 6λ2 + 12λ + 6
10λ2-8λ = 0
λ(10λ-8) = 0
Since λ >0
λ = 0.8
Answer: (0.8)
Question 22.Let [t] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then the value of \(\begin{array}{l}\int_{1}^{2}\left | 2x-[3x] \right |dx\end{array} \)
is:
Solution:
To find
\(\begin{array}{l}\int_{1}^{2}\left | 2x-[3x] \right |dx\end{array} \)
Put 3x = t
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{3}\int_{3}^{6}\left | \frac{2t}{3}-[t] \right |dt\end{array} \)
=
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{3}\int_{3}^{6}\left | \frac{2t}{3}-[t] \right |dt\end{array} \)
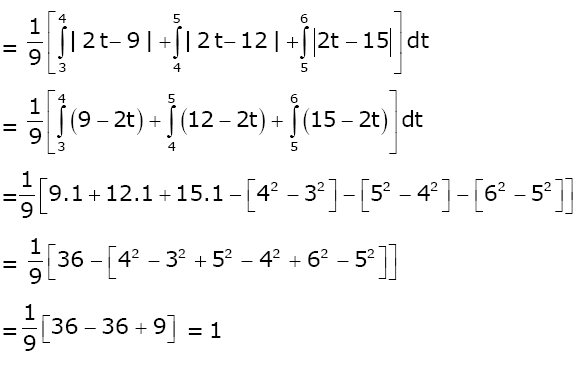
Answer: (1)
Question 23. If y = \(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{k=1}^{6}k\cos ^{-1}\left \{ \frac{3}{5}\cos kx-\frac{4}{5} \sin kx\right \}\end{array} \)
, then (dy/dx) at x = 0 is:
y =
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{k=1}^{6}k\cos ^{-1}\left \{ \cos kx+\theta \right \}\end{array} \)
where tanθ = 4/3
cos-1[cos(kx+a)] = kx+a as kx+a∈[0, π]
y = cos-1(cos (x+θ)+2 cos-1(2x+θ))….+6cos-1(cos (6x+θ))
y = x+θ+2(2x+θ)+…6(6x+θ)
dy/dx = 1×1+2×2+3×3+….+6×6
dy/dx at x = 0
= 1×1+2×2+3×3+….+6×6
= Ʃ62
= 6×7×13/6
= 91
Answer: (91)
Question 24.If the variance of the terms in an increasing A.P., b1, b2, b3, …., b11 is 90, then the common difference of this A.P. is
Var(x) = (Ʃbi2/11)- (Ʃbi/11)2
90 = [(11a2+385d2+110ad)/11]-[(11a+55d)/11]2
90 = a2+35d2+10ad- (a+5d)2
90 = a2+35d2+10ad- a2-25d2-10ad
90 = 10d2
9 = d2
d = 3
Answer: (3)
Question 25. For a positive integer n, (1+1/x)n is expanded in increasing powers of x. If three consecutive coefficients in this expansion are in the ratio, 2:5:12, then n is equal to
Let 3 consecutive coefficients are nCr-1 : nCr : nCr+1::2:5:12
nCr-1/ nCr = 2/5
and nCr/ nCr+1 = 5/12
r/(n-r+1) = 2/5
and (r+1)/(n-r) = 5/12
7r = 2n+2 and 17r = 5n-12
(2n+2)/7 = (5n-12)/17
34n+34 = 35n-84
n = 118
Answer (118)
Video Lessons – Maths
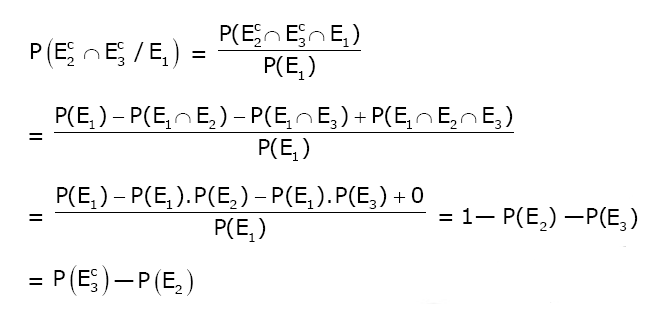




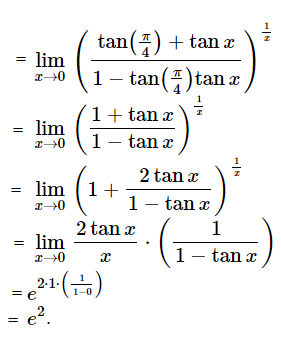
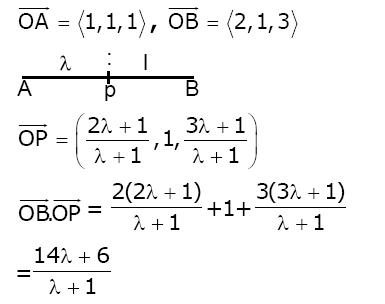

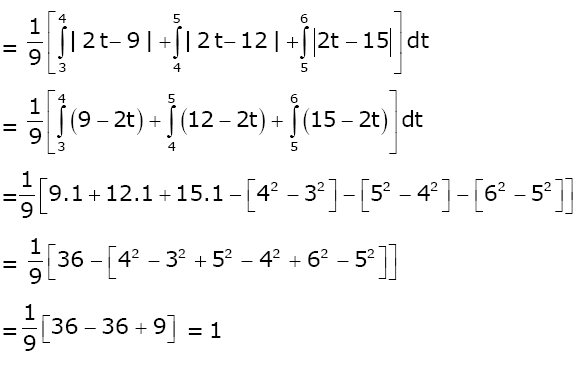

Comments