SECTION A
Question 1: Match List I with List II.
|
List I |
List II |
|
(a) Rectifier |
i) Used either for stepping up or stepping down the A.C.voltage |
|
(b) Stabilizer |
(ii) Used to convert A.C. voltage into D.C. voltage |
|
(c) Transformer |
(iii) Used to remove any ripple in the rectified output voltage |
|
(d) Filter |
(iv) Used for constant output voltage even when the input voltage or load current change |
Choose the correct answer form the options given below:
a. (a)-(ii), (b)- (i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
b. (a)-(ii), (b)- (iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
c. (a)-(ii), (b)- (i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
d. (a)-(iii), (b)- (iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(ii)
Answer: (b)
(a) Rectifier:- used to convert A.C voltage into D.C. Voltage.
(b) Stabilizer:- used for constant output voltage even when the input voltage or load current change
(c) Transformer:- used either for stepping up or stepping down the A.C. voltage.
(d) Filter:- used to remove any ripple in the rectified output voltage.
Question 2: Y = A sin(ωt + ϕ0) is the time – displacement equation of an SHM, At t = 0, the displacement of the particle is Y = A/2 and it is moving along negative x-direction. Then, the initial phase angle ϕ0 will be.
a. π/6
b. π/3
c. 2π/3
d. 5π/6
Answer: (d)

y = A sin (ωt + ϕ)
t = 0, x = A/2
1/2 = sin ϕ
ϕ = π/6, 5π/6
v = dy/dt = A ωcos(ωt + ϕ)
t = 0, v = A ωcosϕ
ϕ = π/6, for v (positive)
ϕ = 5π/6, for v (negative)
∴ϕ = 5π/6
Question 3: Two identical springs of spring constant ‘2K’ are attached to a block of mass m and to fixed support (see figure). When the mass is displaced from equilibrium position on either side, it executes simple harmonic motion. Then, time period of oscillations of this system is:

a. π√(m/k)
b. π√(m/2k)
c. 2π√(m/k)
d. 2π√(m/2k)
Answer: (a)

Springs are in parallel combination.
Hence, Keff = 2k + 2k = 4k
∵ T = 2π √(m/keff)
= 2π√(m/4k)
T = π √(m/k)
Question 4: The wavelength of the photon emitted by a hydrogen atom when an electron makes a transition from n = 2 to n = 1 state is:
a. 194.8 nm
b. 490.7 nm
c. 913.3 nm
d. 121.8 nm
Answer: (d)
∆E = 10.2 eV is the energy difference between the state n = 2 & n = 1
∆E = –3.4 – (–13.6) = 10.2 eV
hc/λ = 10.2 ev
λ = hc/(10.2)e (in meters) where ‘e’ = 1.6 × 10–19 J/V
= 12400/10.2 Å (because hc = 12400 eV nm)
= 121.56 nm
≃ 121.8 nm
Question 5: In a ferromagnetic material below the Curie temperature, a domain is defined as:
a. a macroscopic region with consecutive magnetic diploes oriented in opposite direction.
b. a macroscopic region with zero magnetization.
c. a macroscopic region with saturation magnetization.
d. a macroscopic region with randomly oriented magnetic dipoles.
Answer: (c)
In a ferromagnetic material below the Curie temperature, domain is defined as a macroscopic region with saturation magnetization.
Question 6: The point A moves with a uniform speed along the circumference of a circle of radius 0.36m and cover 30o in 0.1s. The perpendicular projection ‘P’ form ‘A’ on the diameter MN represents the simple harmonic motion of ‘P’. The restoring force per unit mass when P touches M will be:

a. 100 N
b. 50 N
c. 9.87 N
d. 0.49 N
Answer: (c)

The point a covers 30o in 0.1 sec.
Means
π/6 → 0.1sec.
1 → 0.1/(π/6)
2π = → 0.1×6×2π/π
T = 1.2 sec.
We know that ω = 2π/T
ω = 2π/1.2
Restoring force (F) = mω2A
Then, Restoring force per unit mass (F/m) = ω2A
F/m = (2π/1.2)2×0.36
≃ 9.87 N
Question 7: The stopping potential for electrons emitted from a photosensitive surface illuminated by light of wavelength 491 nm is 0.710 V. When the incident wavelength is changed to a new value, the stopping potential is 1.43 V. The new wavelength is:
a. 400 nm
b. 382 nm
c. 309 nm
d. 329 nm
Answer: (b)
From the photoelectric effect equation
hc/λ = ϕ + evs
where Vs is the stopping potential and ϕ is work function of the metal.
So, evs1 = hc/λ1 – ϕ ……(i)
evs2 = hc/λ2 – ϕ …..(ii)
Subtract equation (i) from equation (ii)
evs1 – evs2 = hc/λ1– hc/λ2
vs1 – vs2 = (hc/e) (1/λ1 – 1/λ2)
(0.710 – 1.43) = 1240 (1/491 – 1/λ2)
(because hc = 1240 eV nm)
-0.72/1240 = 1/491 – 1/λ2
1/λ2 = 1/491 + 0.72/1240
1/λ2 = 0.00203 + 0.00058
1/λ2 = 0.00261
λ2 = 383.14
λ2 ≃ 382 nm
Question 8: A charge ‘q’ is placed at one corner of a cube as shown in figure. The flux of electrostatic field

a. q/48ε0
b. q/8ε0
c. q/24ε0
d. q/4ε0
Answer: (c)
Total flux through the cube = (q/ε0)× ⅛ = q/8ε0
Total flux through one “outer” face of the cube = (q/8ε0)×1/3 = q/24ε0
[Because there is flux only through 3 faces]Hence, total flux through shaded area
ϕT = (q/24ε0 + q/24ε0)×1/2 [half of each face is shaded]
ϕT = q/24ε0
Question 9: A sphere of radius ‘a’ and mass ‘m’ rolls along horizontal plane with constant speed v0. It encounters an inclined plane at angle θ and climbs upward. Assuming that it rolls without slipping how far up the sphere will travel (along the incline)?

a. (⅖) v02/gsin θ
b. 10v02/7gsin θ
c. v02/5gsin θ
d. 7v02/10gsin θ
Answer: (d)

From energy conservation
mgh = ½ mv2 + ½ Iω2
mgh = ½ mv2 + ½×(⅖)ma2× v02/a2
gh = ½ v02+ ⅕ v02
gh = (7/10)v02
h = (7/10)v02/g
From triangle, sinθ = h/l
Then, h = lsinθ
l sinθ = (7/10) (v02/g)
l = (7/10) (v02/gsin θ)
Question 10: Consider the diffraction pattern obtained from the sunlight incident on a pinhole of diameter 0.1 μm. If the diameter of the pinhole is slightly increased, it will affect the diffraction pattern such that:
a. its size decreases, but intensity increases
b. its size increases, but intensity decreases
c. its size increases, and intensity increases
d. its size decreases, and intensity decreases
Answer: (a)
For diffraction through a single slit, for first minimum.
sin θ = 1.22λ/D
If D is increased, then sinθ will decrease i.e θ will decrease
∴ size of circular fringe will decrease but intensity increases.
Question 11: An electron of mass me and a proton of mass mp = 1836 me are moving with the same speed. The ratio of their de Broglie wavelength λelectron/λProton will be:
a. 918
b. 1836
c. 1/1836
d. 1
Answer: (b)
Given mass of electron = me
Mass of proton = mp
∴ given mp = 1836 me
From de-Broglie wavelength
λ = h/p = h/mv
λe/λp = mp/me [v is same]
= 1836me/me
λe/λp= 1836
Question 12: Thermodynamic process is shown below on a P-V diagram for one mole of an ideal gas. If V2 = 2V1 then the ratio of temperature T2/T1 is:

a. 1/√2
b. 1/2
c. 2
d. √2
Answer: (d)

From P-V diagram,
Given PV1/2 = constant …..(i)
We know that
PV = nRT
P ∝ (T/V) [for 1 mole]
Put in equation (i)
(T/V) (V)1/2 = constant
T ∝V1/2
T2/T1 = √(V2/V1)
T2/T1 = √(2V1/V1)
T2/T1 = √2
Question 13: A stone is dropped from the top of a building. When it crosses a point 5m below the top, another stone starts to fall from a point 25m below the top, both stones reach the bottom of building simultaneously. The height of the building is: [Take g = 10 m/s2]
a. 45 m
b. 35 m
c. 25 m
d. 50 m
Answer: (a)

Velocity of particle (1) at 5m below top u1 = √2gh = √(2×10×5) =10 m/s
For particle (1), using 2nd equation of motion
20+h = 10t + ½ gt2 …..(i)
For particle (2), using 2nd equation of motion
h = ½ gt2 …..(ii)
Put equation (ii) in equation (i)
20 + ½ gt2 = 10t + ½ gt2
t = 2 sec.
Put in equation (ii)
h = ½ gt2
= ½ ×10 × 22
h = 20m
The height of the building = 25 + 20 = 45m
Question 14: If a message signal of frequency ‘fm‘ is amplitude modulated with a carrier signal of frequency ‘fc‘ and radiated through an antenna, the wavelength of the corresponding signal in air is:
[Given, C is the speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum/air]
a. c/(fc+fm)
b. c/(fc-fm)
c. c/fm
d. c/fc
Answer: (d)
Equation of amplitude modulated wave y = (Ac + Am sin ωmt) sin ωct
Here angular frequency of modulated signal = ωc
Thus frequency of modulated signal = fc
Thus wavelength = c/fc
Question 15: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature obeys Maxwell’s distribution.
Statement II: In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a. Both statement I and statement II are false.
b. Both statement I and statement II are true.
c. Statement I is false but statement II is true.
d. Statement I is true but statement II is false.
Answer: (d)
The translational kinetic energy & rotational kinetic energy both obey Maxwell’s distribution independent of each other.
T.K.E. of diatomic molecules = (3/2) kT [3 translational D.O.F.]
R.K.E. of diatomic molecules = (2/2) kT = [2 rotational D.O.F.]
So statement I is true but statement II is false.
Question 16: An electron with kinetic energy K1 enters between parallel plates of a capacitor at an angle ‘α’ with the plates. It leaves the plates at angle ‘β’ with kinetic energy K2. Then the ratio of kinetic energies K1 : K2 will be:
a. sin2β/cos2α
b. cos2β/cos2α
c. cosβ/sinα
d. cosβ/cosα
Answer: (b)

∵v1cosα = v2cosβ [electric field inside a parallel plate capacitor is perpendicular to the plates, hence, there will be no change in parallel component of velocity]
v1/v2 = cosβ/cosα
Then the ratio of kinetic energies
k1/k2 = ½ mv12/ ½ mv22 = (v1/v2)2 = (cosβ/cosα)2
k1/k2 = cos2β/cos2α
Question 17: An LCR circuit contains resistance of 110 Ω and a supply of 220 V at 300 rad/s angular frequency. If only capacitance is removed from the circuit, current lags behind the voltage by 450. If on the other hand, only inductor is removed the current leads by 450 with the applied voltage. The rms current flowing in the circuit will be:
a. 2.5 A
b. 2 A
c. 1 A
d. 1.5 A
Answer: (b)
When L and C are connected with R in series the circuit will come in resonance So, current in the circuit will be:
Irms = Vrms/R
= 220/110
= 2 A
Question 18: For extrinsic semiconductors: when doping level is increased;
a. Fermi–level of p and n-type semiconductors will not be affected.
b. Fermi–level of p-type semiconductors will go downward and Fermi–level of n-type semiconductor will go upward.
c. Fermi–level of both p–type and n–type semiconductors will go upward for T >TFK and downward for T<TFK, where TF is Fermi temperature.
d. Fermi–level of p-type semiconductor will go upward and Fermi–level of n–type semiconductors will go downward.
Answer: (b)
In n-type semiconductor, pentavalent impurity is added. Each pentavalent impurity donates a free electron. So the Fermi-level of n-type semiconductor will go upward and in p-type semiconductor, trivalent impurity is added. Each trivalent impurity creates a hole in the valence band. So the Fermi-level of p-type semiconductor will go downward.
Question 19: The truth table for the following logic circuit is:


Answer: (4)

If A = B = 0 then output y = 1
If A = B = 1 then output y = 1
Question 20: If e is the electronic charged, c is the speed of light in free space and h is planck’s constant, the quantity (1/4πε0) |e|2/hc has dimensions of:
a.[ LC-1]
b. [M0 L0 T0]
c. [ M L T0]
d. [M L T-1]
Answer: (b)
Given
e = electronic charge
c = speed of light in free space
h = planck’s constant
(1/4πε0) e2/hc = (ke2/hc)× λ2/λ2 [multiply and divide by lambda = wavelength]
= F×λ/E [ke2/λ2 has dimensions of force and hc/λ = E]
= E/E [F× λ has dimension of E]
= dimensionless
= [ M0 L0 T0]
Section B
Question 1: The percentage increase in the speed of transverse waves produced in a stretched string if the tension is increased by 4% will be ___%.
Answer: 2
Speed of transverse wave is
V = √(T/μ)
Taking log on both sides
ln v = ½ lnT – ½ ln μ
Δv/v = ½ ΔT/T ⇒ (Δv/v)×100 = 1/2 ( ΔT/T)×100
= ½ ×4 [ μ is constant for a string]
(Δv/v)×100 = 2%
Question 2: Two small spheres each of mass 10 mg are suspended from a point by threads 0.5 m long. They are equally charged and repel each other to a distance of 0.20 m. Then charge on each of the sphere is (a/21)×10-8C. The value of ‘a’ will be________. [Take g = 10 m/s2]
Answer: 20

From FBD, T sinθ = kq2/d2 and T cosθ = mg
Dividing them,
mg tanθ = kq2/d2
q = √(mg tanθ)/25k
= √(10×10-6×10×1/√24(25)9×109)
= √(10-4×4/√24×25×4×9×109)
= (⅔)√(10-4/√24×1011)
Thus (a/21)×10-8 = ⅔ √(10-15/√24)
= ⅔ √(10-16/0.49)
a = 2×21/3×0.7
= 20
Question 3: The peak electric field produced by the radiation coming from the 8 W bulb at a distance of 10 m is (x/10) √(µ0c/π) V/m. The efficiency of the bulb is 10% and it is a point source. The value of x is ___.
Answer: 2
Intensity I = ½ c∈0E02
Intensity = Power / Area = 8 /(4π × 102)
(8/4π×102) ×½ =¼ × c ×(1/µ0c2) ×E02 [Multiply by ½ and ∈0 =1/μ0c2]
E0 = (2/10)√(µ0c/π)
⇒ x = 2
Question 4: Two identical conducting spheres with negligible volume have 2.1nC and -0.1nC charges, respectively. They are brought into contact and then separated by a distance of 0.5 m. The electrostatic force acting between the spheres is _______× 10-9 N. [Given : 4πε0 = 1/9×109 SI unit]
Answer: 36

When they are brought into contact & then separated by a distance = 0.5 m. Then charge distribution will be

The electrostatic force acting b/w the sphere is
Fe = kq1q2/r2
= 9×109×1×10-9×1×10-9/(0.5)2
= (900/25) × 10-9
Fe = 36 ×10-9 N
Question 5: The initial velocity v1 required to project a body vertically upward from the surface of the earth to just reach a height of 10R, where R is the radius of the earth, may be described in terms of escape velocity ve such that vi = √(x/y) ve. The value of x will be_______.
Answer: 20

Here R = radius of the earth
From energy conservation
-Gmem/R + ½ mvi2 = -Gmem/11R + 0
½ mvi2 = (10/11)Gmem/R
vi = √(20Gme/11R)
vi = √(20/11)ve {∵escape velocity ve = √(Gme/R)}
Then the value of x = 20
Question 6: A current of 6A enters one corner P of an equilateral triangle PQR having 3 wires of resistance 21Ω each and leaves by the corner R. The currents i1 in ampere is______.

Answer: 2

The current i1 = (R2/(R1 + R2))i
= (2/(4+2))×6
i1 = 2A
Question 7: The wavelength of an X-ray beam is 10 Å. The mass of a fictitious particle having the same energy as that of the X-ray photons is (x/3) h kg. The value of x is _______.
Answer: 10
Given wavelength of an X-ray beam = 10 Å
∵E = hc/λ = mc2
m = hc/λ will be the mass of a particle having the same energy
The mass of a fictitious particle having the same energy as that of the X-ray photons = (x/3)h kg
(x/3) h = h/cλ
x = 3/cλ
= 3/3×108×10×10-10
x = 10
Question 8: A reversible heat engine converts one- fourth of the heat input into work. When the temperature of the sink is reduced by 52 K, its efficiency is doubled. The temperature in Kelvin of the source will be_______.
Answer: 208
∵ n = W/Qin = 1/4
¼ = 1 – T2/T1 [for reversible heat engine]
T2/T1 = 3/4
When the temperature of the sink is reduced by 52k then its efficiency is doubled.
1/2 = 1 -(T2 – 52)/T1
(T2– 52)/T1 = 1/2
T2/T1 – 52/T1 = 1/2
¾ – 52/T1 = 1/2
52/T1 = 1/4
T1 = 208 K is the source temperature.
Question 9: Two particles having masses 4g and 16g respectively are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momentum is n:2. The value of n will be_____.
Answer: 1
Relation b/w kinetic energy & momentum is
p = √(2mKE) (∵KE = same)
p1/p2 = √(m1/m2)
n/2 = √(4/16)
n = 1
Question 10: If
Answer: 180
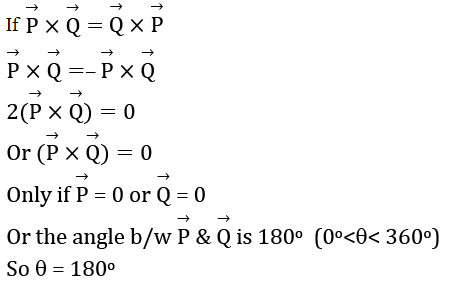









JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Physics Feb 25 Shift 2


















Comments