According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 11 Biology textbook.
Food is an important component for the sustenance and growth of any living organism. Humans have evolved specialized systems that can convert food into energy and disperse the same to all cells in the body. The human digestive system is a series of interconnected organs that span from the mouth and ends at the anus.
What are Digestion and Absorption?
Digestion is the process of breaking large, insoluble food molecules into smaller molecules for absorption into the bloodstream. Digestion begins in the mouth and continues as food travels through the small intestine.
Absorption is the process of assimilating substances into cells or across tissues and organs through the process of diffusion or osmosis. Absorption occurs in the small intestine.
Also Read: Human Digestive System
The Alimentary Canal
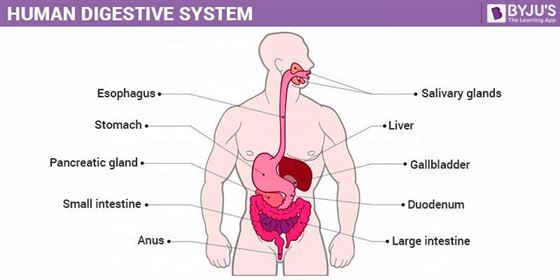
The alimentary canal is the entire passage along which the ingested food is broken down into its constituents and absorbed for use by the body. When all the components of the gastrointestinal tract are stretched out, end to end, it roughly measures 30 feet or about 9 meters. The components are as follows:
- Oral cavity (Also called the buccal cavity)
- Pharynx (plural: pharynges)
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
Also Refer: Diagram Of Digestive System
For more information on Human Digestive System, watch the below videos


Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
Besides the organs in the gastrointestinal tract, there are additional organs and glands that are not directly a part of the digestive system, but they provide crucial functions that aid digestion absorption or the breakdown of food. These are termed the accessory organs of the digestive system.
Note: They are the accessory organs of the digestive system but not the part of the digestive tract.
- Liver
- Tongue
- Pancreas
- Gallbladder
- Salivary glands
Also Read: Alimentary Canal
Important Question on Digestion and Absorption
- State the functions of the liver.
- Describe the function of the Villi.
- State the components of the digestive tract.
- What is the meaning of the term “thecodont”?
- Explain the role of pancreatic juice in the process of digestion.
Discover more related concepts regarding digestion and absorption Class 11 right here on BYJU’S.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 |
| NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 16: Digestion and Absorption
What is meant by digestion?
Digestion is the complex process of turning the food you eat into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth and cell repair needed to survive.
What are the functions of the pancreas?
The pancreas performs two main functions: Exocrine function: Produces substances (enzymes) that help with digestion. Endocrine function: Sends out hormones that control the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
What are gall bladders?
The gall bladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of the abdomen, just beneath the liver. The gall bladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that’s released into the small intestine.
Comments