According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 12.
What are Factors?
An expression can be factorised into the product of its factors. These factors can be algebraic expressions, variables and numbers also.
To know more about Factors, visit here.
Division of a monomial by another monomial
Division of a monomial by another monomial:
i) Division of 9x2 by 3:
9x2 ÷ 3 = 3(3x2) / 3 = 3x2
ii) Division of 6x2y by 2y:
6x2y÷2y = (6x2)y / 2y = 2y(3x2) / 2y = 3x2
Division of a polynomial by a monomial
A polynomial 2x3 + 4x2 + 6xis divided by monomial 2x as shown below:
(2x3+4x2+6x)2x = 2x3 / 2x + 4x22x + 6x / 2x = x2+ 2x + 3
Division of a polynomial by a polynomial
Long division method is used to divide a polynomial by a polynomial.
Example:Division of 3x2 + 3x – 5 by (x – 1) is shown below:
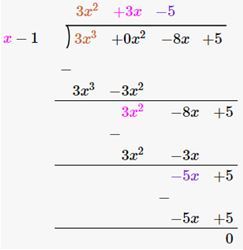
To know more about Polynomial Division, visit here.
Factors of natural numbers
Every number can be expressed in the form of product of prime factors. This is called prime factor form.
Example: Prime factor form of 42 is2 x 3 x 7, where 2, 3 and 7 are factors of 42.
Algebraic expressions
An algebraic expression is defined as a mathematical expression which consists of variables, numbers, and operations. The values of this expression are not constant, for example: x + 1, p – q, 3x, 2x+3y, 5a/6b etc.
Factors of algebraic expressions and factorisation
An irreducible factor is a factor which cannot be expressed further as a product of factors.
Algebraic expressions can be expressed in irreducible form.
To know more about Factorisation of algebraic expression, visit here.
Method of Common Factors
For more information on Common Factors, watch the below video.

Factorisation by common factors
To factorise an algebraic expression, the highest common factors are determined.
Example: Algebraic expression -2y2 + 8y can be written as 2y(-y+4), where 2y is the highest common factor in the expression.
Factorisation by regrouping terms
In some algebraic expressions, it is not possible that every term has a common factor. Therefore, to factorise those algebraic expressions, terms having common factors are grouped together.
Example:
= 12a + n – na – 12
= 12a-12+n-na
= 12(a-1)-n(a-1)
= (12-n)(a-1)
(12-n) and (a-1)are factors of the expression 12a+n-na-12
Method of Identities
Algebraic identities
The algebraic equations which are true for all values of variables in them are called algebraic identities.
Some of the identities are,
(a+b)2 = a2+ 2ab + b2
(a-b)2= a2– 2ab + b2
(a+b)(a-b)= a2 – b2
Factorisation using algebraic identities
Algebraic identities can be used for factorisation
Example: (i)9x2 + 12xy + 4y2
= ( 3x)2 + 2 x 3x x 2y+(2y)2
= (3x+4y)2
(ii)4a2 – b2 = (2a-b)(2a+b)
For more information on Algebraic Identities, watch the below videos.


Visualisation of factorisation
The algebraic expression x2 + 8x + 16 can be written as (x+4)2. This can be visualised as shown below:
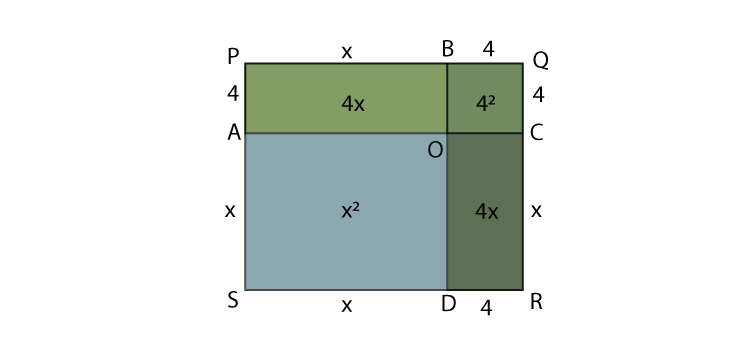
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Maths Notes Chapter 14 Factorisation
What are Factors?
A number or algebraic expression that divides another number or expression evenly—i.e., with no remainder is said to be a factor of the primary number.
What is a common multiple?
A multiple of each of two or more numbers is said to be ‘common mutiple’ of both the numbers.
What is Factorisation?
Factorisation is when a number is broken down into smaller numbers that, multiplied together, give the original number.