According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 10 Science textbook.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management Of Natural Resource Notes
The management of human and natural landscape interactions is referred to as “natural resource management” (NRM). It combines land use planning, biodiversity preservation, water management, and the long-term viability of many enterprises, including mining, tourism, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries. It also acknowledges that people and their means of subsistence depend on the productivity and health of our landscapes and that sustaining these qualities requires intensive land management.
Introduction
Natural resources are substances obtained from the planet that is used to sustain life and provide for human needs. A natural resource is something that comes from nature that humans use. Natural resources include things like stone, sand, metals, oil, coal, and natural gas. Air, sunlight, soil, and water are other natural resources.
The well-being of people depends on natural resources. We cannot survive without the freshwater we drink, the plants we consume, or the pure air we breathe. To build roofs over our heads and heat our homes, we require natural resources.
Pollution in Ganga
- The river Ganga is used as a sewage dump for more than 100 cities stretching across Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal.
- Dumping of untreated sewage, excreta and chemicals from industries increase the toxicity of the water.
- This makes it inhabitable for flora and fauna in the river system.
- In 1985 the GAP (Ganga Action Plan) project was initialised to curb the poor quality of the water of the river Ganges.
Reduce, Recycle and Reuse
The 3 Rs to save the environment can be performed by each individual in our society:
- Reduce: Reducing our usage and wasteful habits. E.g. not wasting food, turning off the switches to save electricity, repairing leaky taps, reducing the amount of water used for bathing, etc.
- Reuse: Using things again instead of discarding them. For example, reusing plastic utensils and bottles. Many things cannot be recycled or require a lot of energy; instead, we can utilize them for other purposes.
- Recycle: Collecting discarded paper, plastic, glass or metal objects to manufacture different products rather than synthesizing them from scratch. It must have a mechanism to segregate and dispose of each type of waste separately.
To know more about Saving the Environment from Pollution, visit here.
Why Do We Need to Manage Our Resources?
Need to Manage Natural Resources
- Due to the ever-increasing population and rising demands of changing lifestyles, natural resources are being depleted at an alarming rate. To ensure sustainable, equal distribution of resources and reduction of damage to the environment, management of resources must be an integral part of our society.
- We must ensure judicious use of our natural resources as it is not unlimited, and management of such requires long-term planning in order to last generations.
Increase in Demand for Natural Resources
- The increasing population is increasing the demand for more resources that are getting depleted at an exponential rate.
- Changing lifestyles and advancements in technology are compelling industries to exploit our natural reserves to meet the demands.
To know more about the Management of Natural Resources, visit here.
Forests and Wildlife
Forests and Wildlife
- Forests are termed biodiversity hotspots.
- Biodiversity is the variety and range of plant and animal life in a particular habitat.
- Loss of biodiversity may result in loss of ecological balance and damage to the ecosystem.
To know more about the Conservation of Forests and Wildlife, visit here.
Stakeholders of Forests
When we consider the conservation of forests, we must consider the following stakeholders:
- People who habituate around forests are dependent on forest produce.
- The Forest Department of Government owns the land and resources.
- Industrialists: who use the forest to produce certain products, e.g. leaves of Tendu for bidis and paper mills.
- Conservationists and wildlife enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
To know more about the Stakeholders of a forest, visit here.
Monoculture
- Monoculture is the cultivation of a single crop in a given area.
- Excessive monoculture destroys the biodiversity of the area.
- Various needs of the people local to forest areas are neglected, such as leaves for fodder, herbs and fruits for consumption.
Industrialist’s Mentality and Influence
- Industrialists consider forests as a source of raw materials.
- Industries have more political power than the locals and only bother about meeting their demands. They do not care about sustainability and will move on from one habitat to another in search of raw materials.
People’s Intervention in Forests
- Human intervention is a necessity in the management of forest resources and landscapes.
- Resources must be utilised to ensure development while preserving the environment.
- Benefits must go to the local people to ensure economic growth and conservation takes place simultaneously.
- Examples: Bishnoi community in Rajasthan for saving Khejri trees in Jodhpur Rajasthan.
Damage to Forests and Wildlife
- Excessive and lawless utilisation of forests will deplete the resources quicker than they can be restored.
- Destroys the ecological balance and may damage the habitats of various species of flora and fauna.
Sustainable Development
- Sustainable development needs all stakeholders of forest resources to be satisfied.
- In reality, industries use forests at rates far below the market rates, which causes conflict between local dwellers and industrialists.
- West Bengal’s Arabari forests are well-known for being protected areas. This forest gained notoriety as a result of the participation of locals who established a community and worked with village police and forest officials to ensure that there was no significant deforestation, land poaching, or illegal wildlife hunting there.
Chipko Movement
- The Chipko Andolan (‘Hug the Trees Movement’) is one such case of conflict between the industrialist and local dwellers in the 1970s.

Chipko Movement - Originated in Reni Garhwal, high up in the Himalayas.
- The conflict between local villagers and logging contractor → Women of the village stopped felling trees by hugging them → Contractor had to reverse the action.

Women protecting the trees by hugging them - The movement quickly gained popularity and media attention and forced the government to rethink the management of forest resources.
- The involvement of local people is equally important in the management of forest resources.
Water for All
Water
- Water is a necessity for all terrestrial forms of life.
- In India, places having water scarcity are also places experiencing acute poverty.
- Despite the monsoon, there exists a failure to retain groundwater due to the loss of vegetation and the release of effluents from industries.
- Decrease in fresh usable water due to the destruction of the water table and disruption in the water cycle.
To know more about Water, visit here.
Rains and Irrigation Practices
- Intervention of the government to pursue mega projects neglected the local irrigation methods.
- Strict regulations on the usage of stored water and building tanks, dams and canals
- Optimum cropping patterns must be followed based on water availability.
Involvement of Local People (ex: kulhs)
- Himachal Pradesh had a canal irrigation system called kulhs where flowing stream water was diverted to man-made channels, which took it to villages down the hillside.
- The water was used first by the village farthest from the origin of the kulh. This helped water percolate in the soil.
- It was made defunct after the government irrigation system took over.
Dams
- Dams can store large amounts of water and generate electricity.
- Mismanagement of dams causes exploitation, and there is no equitable distribution of this resource.
- Criticism about large dams addresses:
(i) Displacement of tribals without compensation
(ii) Corruption and consumption of money without generation of benefits
(iii) Environmental problems like deforestation.
Uses:
- For irrigation, water from dams is used.
- Dam water is purified and made available for drinking in neighbouring towns and cities.
- Hydroelectric power is produced by dams and utilised to produce electricity.
- Dams stop flooding from taking lives and property.
Coal and Petroleum
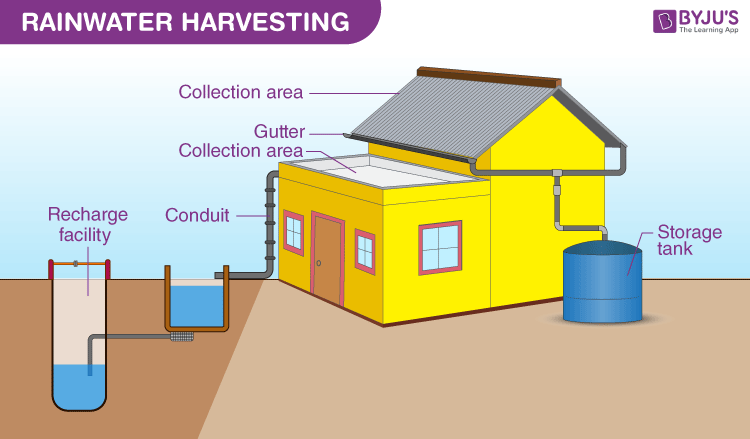
Water Harvesting
- Water harvesting encourages soil and water conservation in order to sustain and increase biomass.
- Increases income for the local community but also alleviates floods and droughts.
- Examples: Rajasthan’s tanks, Khadins, and Nadis; Maharashtra’s Tals and Bandharas; Madhya Pradesh’s and Uttar Pradesh’s Bundhis; Bihar’s Pynes and Ahars; Himachal Pradesh’s Kulhs; Kattas in Karnataka; ponds in the Kandi belt of Jammu region; Eris (tanks) in Tamil Nadu and Kerala’s Surangams.
- Water harvesting constructions are crescent-shaped earthen embankments/concrete check dams built in areas that are seasonally flooded.
- The main purpose is to recharge groundwater.
The following is a list of the advantages of a rainwater harvesting system.
- Decreases the demand for water imports.
- Encourages energy and water conservation.
- Increases groundwater availability and quality.
- Does not need a filtering system for irrigation in gardens.
- This technology is comparatively straightforward and simple to install and use.
Groundwater
Advantages:
- does not evaporate
- recharges wells
- when flowing does not allow mosquitoes to breed
- does not come in contact with human contamination
To know more about Groundwater, visit here.
Coal and Petroleum
- Coal and petroleum are derived from fossil fuels, which are non-renewable. They will get depleted in due time. Hence, proper management of the consumption of fossil fuels is important.
- Their combustion pollutes our environment due to the production of oxides of carbon, sulfur and nitrogen. Therefore, we need to use these resources judiciously.
To know more about Coal and Petroleum, visit here.
Why Should Fossil Fuels Be Used Judiciously?
- Fossil fuels are formed over millions of years of degrading biomass and have a huge amount of carbon.
- When combusted in a limited supply of oxygen, they form harmful gases that pollute the atmosphere, which leads to global warming.
- Judicious use of fossil fuels addresses the efficiency of our machines and ensures the sustainability of our resources for the future.
Choices that Can Make a Difference in Energy Consumption
- Put your computer to sleep.
- Unplug any gadgets and equipment you are not using.
- Shower for fewer minutes.
- Set the refrigerator to 37–40 degrees F.
- Reduce your plug load by using a power strip.
Read More:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 – Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 16 – Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Maths Notes For Class 10
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
What is sustainable development?
Sustainable development is defined as an approach to developing or growing by using resources in a way that allows them to renew or continue to exist for others.
What are the types of natural resources?
Natural resources include oil, coal, natural gas, metals, stone and sand. Air, sunlight, soil and water are other natural resources.
What are the main reasons for water pollution?
1. Rapid urban development 2. Improper sewage disposal 3. Oil spills 4. Chemical waste dumping 5. Radioactive waste discharge
Comments