According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 6 Science textbook.
What is Water?
Water is precious, fundamental and the essential substance required for the existence of life on earth. Water is found naturally and abundantly on our planet Earth. About two-thirds of the total earth’s surface is covered with water. It is a transparent, odourless and tasteless inorganic molecule composed of hydrogen and oxygen.
To know more about water, visit here.
Uses of Water
We all use water for different purposes, which include everyday household uses, including drinking, cooking, cleaning, washing, bathing for other domestic, irrigating, cultivating crops and industrial requirements. Thus, water is required for many activities, therefore, it is an essential element required for the continuity of life on the planet.
To know more about the Uses of Water, visit here.
Sources of Water
As mentioned above, about two-thirds of the total earth’s surface is covered with water, but unfortunately, only a small percentage (2 to 3 per cent) is suitable for human use. The other 99.7 per cent available are found in oceans, sea, groundwater, floating in the atmosphere and in icecaps. This water is not safe and is unsuitable for human consumption, as it consists of excess salt, toxins and other impurities, which can lead to illness and other health disorders.
Rivers, ponds, lakes and groundwater are the different sources of water, which can be used for drinking, cooking and other human uses only after proper treatment like boiling, filtering, etc.
Origin of water
- The origin of the water is found to be from a type of meteorite.
- The major sources of water for human use are lakes, rivers, ponds etc.
- The chemical composition of water on Earth is the same as that of some meteorites.
Availability of Water
Uses of water
Below are the different uses of water in various fields:
- Cleaning
- Drinking.
- Bathing.
- Washing.
- Irrigation.
- Gardening.
- Cooking food.
- Transportation.
- Manufacturing goods.
- For generating power.
- Production in industries.
- Recreational activities like swimming, water sports.
Freshwater
Freshwater is naturally occurring water present on the earth’s surface in ponds and rivers. The major source of rainwater is precipitation in the atmosphere.
Distribution of Freshwater
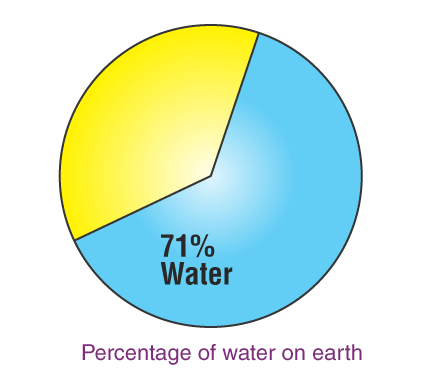
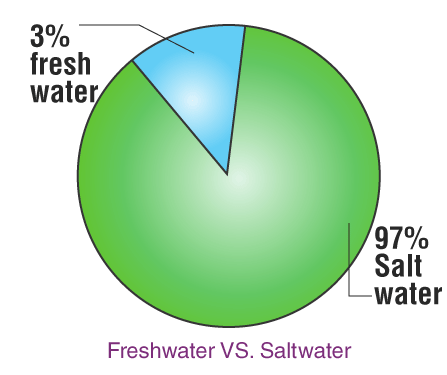
71% of Earth is filled with water; out of this 3% is fresh water, and 97% of water is in oceans and seas. Out of this 3% of freshwater, 30% is groundwater(not accessible), and 69% is in the form of glaciers and icebergs. ( not accessible), out of the remaining 1% of water, only 0.006% is used by the people for several purposes like bathing and washing.
Potable Water
The pure form of water, which does not contain any impurities or salts in it and can be used for drinking purposes is called potable water.
Water from Oceans
Out of 71% of the water on earth, 97% is water from oceans and seas. Water from oceans and seas contains dissolved salts in it, hence this water is called saltwater or saline water.
To know more about the Distribution of Water, visit here.
Water Cycle
The process of circulating or the continuous movement of water between water bodies like the ocean, rivers, ponds, lakes and land is called the water cycle. It is also also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle. In this process, the water on the earth changes into three different states of matter – solid, liquid and gas. The complete process of the water cycle involves the following process.
- Evaporation.
- Condensation.
- Precipitation.
1) Evaporation
Evaporation is the process of converting liquid or water into a gaseous form or vapour state.
2) Condensation
The process of converting vapour or gaseous form into its liquid form is called condensation.

3) Precipitation
When more water gets condensed in clouds, or condensation of water vapour in the atmosphere results in precipitation. The precipitation can be in the form of rain, snow, or hail.

To know more about Water Cycle, visit here.
The flow of water towards the oceans
- Rainwater falls into rivers, lakes etc.
- The rain droplets fall into oceans, rivers, ponds, and seas.
- Water from the rivers, lakes, and ponds finally flows into the sea and ocean.
Transpiration
In plants, the process of evaporating water through leaves when water is absorbed through roots is called transpiration.
Flood
- Rainfall brings about life, but excess rainfall leads to an increase in water levels in water bodies like rivers and ponds.
- Adverse effects of floods:
- Flood causes damage to human life, crops, domestic animals and animals living in the water.
- This excess water may spread over large areas causing floods.
Drought
- Inadequate rainfall leads to a decrease in groundwater level which makes soil dry. This condition is called drought.
- At the time of drought, it is difficult to get food and water.
Ground Water
The water present underground or beneath the earth’s surface in spaces of soil and rocks is called groundwater.
Water level
Level of water or is the height reached by the water in lakes, ponds, storage tanks, and dams.
Infiltration
The process of water seeping into the soil after falling onto the surface of the ground is called infiltration.
Aquifers
An aquifer is the underground layer of permeable rock which contains water that has seeped in from the surface.
To know more about Ground Water, visit here.
Water Management
Water management is the effective utilisation of water or managing water resources carefully. Water can be managed in the following ways:
1. Drip Irrigation: The process of pouring water into the roots of plants using narrow tubes is called Drip Irrigation.
2. Rainwater Harvesting: The collection of rainwater and using it effectively for other purposes is known as rainwater harvesting.
To know more about Water Management, visit here.
Learn more about the Water from the topics given below:
| Water | Density Of Water |
| Properties of Water | Rainwater Harvesting |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 14 Water
What are the main reasons for water pollution?
1. Rapid urban development 2. Improper sewage disposal 3. Oil spills 4. Chemical waste dumping 5. Radioactive waste discharge
What is a freshwater lake?
A freshwater lake contains water that is not salty, usually in contrast to the sea.
What are the steps involved in the water cycle of nature?
1. Evaporation 2. Condensation 3. Precipitation
Comments