NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Fractions and Decimals are available here in PDF for free download. Our expert faculty has formulated these solutions to assist you with your exam preparation to attain good marks in Maths. Students who wish to score good marks in Maths are advised to practise NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Maths regularly. This is one of the top study materials when it comes to choosing a question bank to practise.
In Chapter 4 – Fractions and Decimals, a fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. This whole may be a single object or a group of objects. Fractions with denominators 10, 100, etc., can be written in a form using a decimal point, called decimal numbers or decimals. Now, let us have a look at some of the concepts discussed in this chapter.
- Multiplication and division of fractions, along with some other concepts, like types of fractions.
- Method of changing unlike fractions to like fractions.
- Method of comparing more than two fractions.
- Method of converting a decimal into a fraction.
- Converting a fraction into a decimal, addition and subtraction of decimals.
- Multiplication of decimal by 10, 100, 100, etc.
- Multiplication of decimal by a whole number, multiplication of decimal by a decimal.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Fractions and Decimals
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 Fractions and Decimals
Exercise Page: 57
In questions 1 to 20, out of the four options, only one answer is correct. Choose the correct answer.
1. The fraction which is not equal to 4/5 is
(A) 40/50 (B) 12/15 (c) 16/20 (d) 9/15
Solution:-
(D) 9/15
All the options given in the question are further simplified as,
(A) 40/50 = 4/5
(B) 12/15
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 4/5
(C) 16/20
Divide both numerator and denominator by 4.
= 4/5
(D) 9/15
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 3/5
Therefore, 3/5 ≠ 4/5
2. The two consecutive integers between which the fraction 5/7 lies are
(A) 5 and 6 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 5 and 7 (D) 6 and 7
Solution:-
(B) 0 and 1
A fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
So, 5/7 = 0.715
Therefore, 5/7 lies between 0 and 1.
3. When ¼ is written with denominator as 12, its numerator is
(A) 3 (B) 8 (C) 24 (D) 12
Solution:-
(A) 3
(1 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 3/12
Consider, 3/12
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 1/4
4. Which of the following is not in the lowest form?
(A) 7/5 (B) 15/20 (C) 13/33 (D) 27/28
Solution:-
(B) 15/20
Divide both numerator and denominator by 5.
= ¾
5. If (5/8) = (20/p), then value of p is
(A) 23 (B) 2 (C) 32 (D) 16
Solution:-
(C) 32
Consider the given fraction, (5/8) = (20/P)
P = 20 × (8/5)
P= 4 × 8
P = 32
6. Which of the following is not equal to the others?
(A) 6/8 (B) 12/16 (C) 15/25 (D) 18/24
Solution:-
(C) 15/25
All the options given in the question are further simplified as,
(A) 6/8
Divide both numerator and denominator by 2.
= 3/4
(B) 12/16
Divide both numerator and denominator by 4.
= 3/4
(C) 15/25
Divide both numerator and denominator by 5.
= 3/5
(D) 18/24
Divide both numerator and denominator by 6.
= ¾
Comparing all results, (¾ = ¾ = ¾) ≠ 3/5
Therefore, (6/8 = 12/16 = 18/24) ≠ 15/25
7. Which of the following fractions is the greatest?
(A) 5/7 (B) 5/6 (C) 5/9 (D) 5/8
Solution:-
(B) 5/6
We know that, among all fractions with same numerator, the one having smaller denominator will be the highest fraction.
5/9 < 5/8 < 5/7 < 5/6
Therefore, among four options, (B) 5/6 has small denominator. So, it is the greatest fraction.
8. Which of the following fractions is the smallest?
(A) 7/8 (B) 9/8 (C) 3/8 (D) 5/8
Solution:-
(C) 3/8
We know that, among all fractions with same denominator, the one having smaller numerator will be the smallest fraction.
3/8 < 5/8 < 7/8 < 9/8
Therefore, among four options, (C) 3/8 has small numerator. So, it is the smallest fraction.
9. Sum of 4/17 and 15/17 is
(A) 19/17 (B) 11/17 (C) 19/34 (D) 2/17
Solution:-
(A) 19/17
If denominators of the given fractions are same, we can add both fractions.
So, (4/17) + (15/17)
= (4 + 15)/17
= 19/17
10. On subtracting 5/9 from 19/9, the result is
(A) 24/9 (B) 14/9 (C) 14/18 (D) 14/0
Solution:-
(B) 14/9
If denominators of the given fractions are same, we can subtract both fractions.
So, (19/9) – (5/9)
= (19 – 5)/9
= 14/9
11. 0.7499 lies between
(A) 0.7 and 0.74 (B) 0.75 and 0.79
(C) 0.749 and 0.75 (D) 0.74992 and 0.75
Solution:-
(C) 0.749 and 0.75
0.7499 lies between 0.749 and 0.75
12. 0. 023 lies between
(A) 0.2 and 0.3 (B) 0.02 and 0.03
(C) 0.03 and 0.029 (D) 0.026 and 0.024
Solution: –
(B) 0.02 and 0.03
0. 023 lies between 0.02 and 0.03
13. 11/7 can be expressed in the form

14. The mixed fraction  can be expressed as
can be expressed as
(A) 33/7 (B)39/7 (C) 33/4 (D) 39/4
Solution:-
(B)39/7
 can be expressed as = 5 + (4/7)
can be expressed as = 5 + (4/7)
= (35 + 4)/7
= 39/7
15. 0.07 + 0.008 is equal to
(A) 0.15 (B) 0.015 (C) 0.078 (D) 0.78
Solution:-
(C) 0.078
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.070 + 0.008
So, sum of 0.070 and 0.008 = 0.070 + 0.008
= 0.078
16. Which of the following decimals is the greatest?
(A) 0.182 (B) 0.0925 (C) 0.29 (D) 0.038
Solution:-
(C) 0.29
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.1820, 0.0925, 0.2900, 0.0380
Now, by comparing 4 decimal numbers, 0.2900 is the greatest.
17. Which of the following decimals is the smallest?
(A) 0.27 (B) 1.5 (C) 0.082 (D) 0.103
Solution:-
(C) 0.082
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.270, 1.500, 0.082, 0.103
Now, by comparing 4 decimal numbers, 0.082 is the smallest.
18. 13.572 correct to the tenths place is
(A) 10 (B) 13.57 (C) 14.5 (D) 13.6
Solution:-
(D) 13.6
Place value of the place immediately after the decimal point (i.e. tenth place) is 1/10, that of next place (i.e. hundredths place) is 1/100 and so on.
13.572 correct to the tenths place is 13.6
19. 15.8 – 6.73 is equal to
(A) 8.07 (B) 9.07 (C) 9.13 (D) 9.25
Solution:-
(B) 9.07
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 15.80
Now, 15.80 – 6.73 = 9.07
20. The decimal 0.238 is equal to the fraction
(A) 119/500 (B) 238/25 (C) 119/25 (D) 119/50
Solution:-
(A) 119/500
Decimals can be converted into fractions by removing their decimal points and writing 10,100, etc in the denominators, depending upon the number of decimal places in the decimals.
So, 0.238 = 238/1000
Divide both numerator and denominator by 2
= 119/500
In questions 21 to 44, fill in the blanks to make the statements true:
21. A number representing a part of a _________ is called a fraction.
Solution:-
A number representing a part of a whole is called a fraction.
Example: ¼, ¾, 1/5, 3/6 etc.
22. A fraction with denominator greater than the numerator is called a _________ fraction.
Solution:-
A fraction with denominator greater than the numerator is called a proper fraction.
Example: 2/5, 3/8, 10/11 etc. are proper fractions.
23. Fractions with the same denominator are called _________ fractions.
Solution:-
Fractions with the same denominator are called like fractions.
Example: ½, 3/2, 5/2, 7/2 etc.

Solution:-
Mixed fraction.
25. 18/5 is an fraction.
Solution:-
18/5 is an improper fraction.
A fraction whose numerator is greater than the denominator is called an improper fraction.
26. 7/19 is a fraction.
Solution:-
7/19 is a proper fraction.
A fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
27. 5/8 and 3/8 are proper fraction.
Solution:-
5/8 and 3/8 are like proper fraction.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
28. 6/11 and 6/13 are proper fractions.
Solution:-
6/11 and 6/13 are unlike proper fractions.
If the denominators are different, then they are called unlike fractions.
29. The fraction 6/15 in simplest form is .
Solution:-
The fraction 6/15 in simplest form is 2/5.
The given fraction 6/15, is further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 2/5
30. The fraction 17/34 in simplest form is .
Solution:-
The fraction 17/34 in simplest form is ½.
The given fraction 17/34, is further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 17.
= ½
31. 18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and fractions.
Solution:-
18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and equivalent fractions.
Consider the two given fractions, 18/135 and 90/675
So, (18/135) = (90/675)
By cross multiplication, we get
(18 × 675) = (90 × 135)
12,150 = 12,150
Therefore, 18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and equivalent fractions.
32.
 is equal to the improper fraction .
is equal to the improper fraction .
Solution:-
 is equal to the improper fraction 58/7.
is equal to the improper fraction 58/7.
Given mixed fraction is converted into improper fraction as = ((7 × 8) + 2)/7
= (56 + 2)/7
= 58/7
33. 87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction ______.
Solution:-
87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction
 .
.
We know that, mixed fraction = Quotient Remainder/Divisor
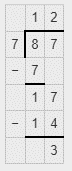
Therefore, 87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction
 .
.
34. 9 + (2/10) + (6/100) is equal to the decimal number ______.
Solution:-
9 + (2/10) + (6/100) is equal to the decimal number 9.26.
Fractions with denominators 10,100, etc. can be written in a form, using a decimal point, called decimal numbers or decimals.
9 + (2/10) + (6/100) = 9 + 0.2 + 0.06
= 9.26
35. Decimal 16.25 is equal to the fraction ______.
Solution:-
Decimal 16.25 is equal to the fraction 16¼ or 65/4.
Decimals can be converted into fractions by removing their decimal points and writing 10,100, etc in the denominators, depending upon the number of decimal places in the decimals.
16.25 = 1625/100
Divide both numerator and denominator by 25.
= 65/4
= 16¼
36. Fraction 7/25 is equal to the decimal number ______.
Solution:-
Fraction 7/25 is equal to the decimal number 0.28.
Multiply numerator and denominator by 4 to get denominator 100.
(7/25) = (7 × 4)/(25 × 4)
=28/100
We know that, fractions with denominators 10,100, etc. can be written in a form, using a decimal point, called decimal numbers or decimals.
= 0.28
37. (17/9) + (41/9) = .
Solution:-
(17/9) + (41/9) = 58/9.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Sum of two like fractions = (17 + 41)/9
= 58/9
38. (67/14) – (24/14) = .
Solution:-
(67/14) – (24/14) = 43/14.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Difference of two fractions = (67 – 24)/14
= 43/14
39. 17/2 + 3½ = .
Solution:-
17/2 + 3½ = 12.
First we have to convert mixed fraction into improper fraction = 3½ = 7/2
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Sum of two like fractions = (17/2) + (7/2)
= (17 + 7)/2
= 24/2
= 12
40. 9 ¼ – 5/4 = _________.
Solution:-
9 ¼ – 5/4 = 37/4 – 5/4 = (37 – 5)/4 = 32/4 = 8.
41. 4.55 + 9.73 = ______.
Solution:-
4.55 + 9.73 = 14.28.
42. 8.76 – 2.68 = ______.
Solution:-
8.76 – 2.68 = 6.08.
43. The value of 50 coins of 50 paisa = ₹______.
Solution:-
The value of 50 coins of 50 paisa = ₹25.
We know that, ₹ 1 = 100 paisa
So, 50 coins of 50 paisa = 50 × 50
= 2500 paisa.
Then,
= 2500/100
= ₹ 25
44. 3 Hundredths + 3 tenths = ______.
Solution:-
3 Hundredths + 3 tenths = 0.33.
Place value of the place immediately after the decimal point (i.e. tenth place) is 1/10, that of next place (i.e. hundredths place) is 1/100 and so on.
3 Hundredths is written as = 3 × (1/100)
= 0.03
3 tenths is written as = 3 × (1/10)
= 0.3
Then sum of 3 Hundredths, 3 tenths = 0.03 + 0.3
= 0.33
In each of the questions 45 to 65, state whether the statement is true or false:
45. Fractions with same numerator are called like fractions.
Solution:-
False.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
46. Fraction 18/39 is in its lowest form.
Solution:-
False.
Lowest form of given fraction 18/39
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3,
= 6/13
47. Fractions 15/39 and 45/117 are equivalent fractions.
Solution:-
True.
Consider the two given fractions, 15/39 and 45/117
So, (15/39) = (45/117)
By cross multiplication, we get
(15 × 117) = (45 × 39)
1,755 = 1,755
48. The sum of two fractions is always a fraction.
Solution:-
True.
For example: consider two fractions 10/5 and 15/5.
Sum of two fractions = (10 + 15)/5
= 25/5
= 5
= 5/1
A fraction in which there is no common factor, except 1, in its numerator and denominator is called a fraction in the simplest or lowest form.
When 2 fractions are added, the result in most cases will be a fraction p/q form, but in some case if it does happen to be just an integer, it can always be written with denominator 1 (hence p/q form).
49. The result obtained by subtracting a fraction from another fraction is necessarily a fraction.
Solution:-
False.
Not necessarily a fraction. But can be written in fraction.
50. If a whole or an object is divided into a number of equal parts, then each part represents a fraction.
Solution:-
True.
A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. This whole may be a single object or a group of objects.
For example: consider a circle is divided into 4 equal parts. Out of four equal parts 3 of them are shaded.
So, it can be represented in the form of fraction = 3/4
51. The place value of a digit at the tenths place is 10 times the same digit at the ones place.
Solution: –
False.
Let us assume a digit be ‘y’.
The place value of a digit at the tenths place = y × (1/10)
= y/10
Then,
The tenths place is 10 times the same digit at the ones place.
y/10 = 10y is not possible.
52. The place value of a digit at the hundredths place is 1/10 times the same digit at the tenths place.
Solution:-
True
Let ‘a’ be the same digit at tens and hundreds place in a number.
Place value of digit at tens place = 10 × a = 10a
Place value of digit at hundreds place = 100 × a = 100a
Hence, the place value of a digit at the hundreds place is 10 times the same digit at the tens place.
53. The decimal 3.725 is equal to 3.72 correct to two decimal places.
Solution:-
False.
Consider the given decimal number, 3.725
The thousandths place has number 5.
Then, hundredths has number 2 it will be increased by 1 number to correct two decimal places.
Therefore, the decimal 3.725 is equal to 3.73 correct to two decimal places.
54. In the decimal form, fraction 25/8 = 3.125
Solution:-
True.
25/8 can be further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 8.
= 3.125
55. The decimal 23.2 =
Solution:-
False.
The decimal 23.2 = 232/10
Dividing both denominator and numerator by 2, we get.
= 116/5
=

56. The fraction represented by the shaded portion in the adjoining figure is 3/8.
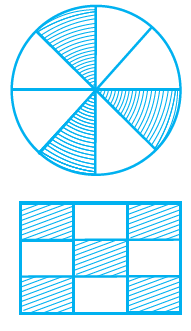
Solution:-
True.
Circle is divided into 8 equal parts. Out of 8 equal parts 3 of them are shaded.
57. The fraction represented by the unshaded portion in the adjoining figure is 5/9.
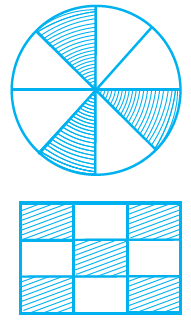
Solution:-
False.
Rectangle is divided into 9 equal parts. Out of 9 equal parts 4 of them are unshaded.
So, fraction represented by the unshaded portion in the adjoining figure = 4/9.
58. (25/19) + (6/19) = 31/38
Solution:-
False.
So, (25/19) + (6/19)
= (25 + 6)/19
= 31/19
Hence, 31/19 ≠ 31/38
59. (8/18) – (8/15) = 8/3
Solution:-
False.
Consider Left Hand Side (LHS),
LCM of 18 and 15 = 90
Then,
(8/18) = (8 × 5)/(18 × 5) = 40/90
(8/15) = (8 × 6)/(15 × 6) = 48/90
Difference of two fractions (40/90) – (48/90)
= -8/90
Right Hand Side (RHS) = 8/3
By comparing LHS and RHS,
LHS ≠ RHS
-8/90 ≠ 8/3
60. (7/12) + (11/12) = 3/2
Solution:-
True.
Consider Left Hand Side (LHS),
Sum of like fractions = (7/12) + (11/12)
= (7 + 11)/12
= 18/12
Divide both numerator and denominator by 6, we get,
= 3/2
Right Hand Side (RHS) = 3/2
By comparing LHS and RHS,
LHS = RHS
3/2 = 3/2
61. 3.03 + 0.016 =3.019
Solution:-
False.
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 3.030 and 0.016
Sum of two decimals = 3.030 + 0.016 = 3.046
62. 42.28 – 3.19 = 39.09
Solution:-
True.
Subtracting 3.19 from 42.28,
42.28
– 3.19
39.09
63. (16/25) > (13/25)
Solution:-
True.
Given two fractions are like fractions,
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
So, 16 > 13
Therefore, (16/25) > (13/25)
64. 19.25 < 19.053
Solution:-
False.
By comparing tenths place of both fractions = 2 > 0
Therefore, 19.25 > 19.053
65. 13.730 = 13.73
Solution:-
True.
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 13.730
So, 13.730 = 13.730
Therefore, 13.730 = 13.73

















Comments