NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time should be studied thoroughly to have a solid fundamental of the topic of Motion and Time. It is very important to go through this NCERT Exemplar solutions as they introduce you to a complex Physics topic, Motion and Time.
The NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science will make you understand the concept in-depth. This will help you to solve different types of questions and boost your exam preparation. It will also lay a strong foundation for this topic, which will help you in studying advanced topics.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions provided here have answers and explanations to 9 multiple-choice questions, answers to 3 very short answer questions, 5 short answer questions and 3 descriptive answer questions. Students can download the solutions in PDF for free from the link given below:
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 – Motion and Time
Importance of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time covers questions on types of motion, speed measurement, distance-time graph and the effect of speed and motion on our daily lives. This exemplar solution has questions on important derivations, numerical problems and graphs.
Topics Covered in NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
13.1 – Slow or Fast
13.2 – Speed
13.3 – Measurement of Time
13.4 – Measuring Speed
13.5 – Distance-time Graph.
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 – Motion and Time
Multiple-choice Questions
1. Which of the following cannot be used for the measurement of time?
(a) A leaking tap.
(b) Simple pendulum.
(c) Shadow of an object during the day.
(d) Blinking of eyes.
Soln:
The answer is (d) Blinking of eyes.
Explanation:
Blinking of the eye is not a periodic phenomenon. Eyes do not blink at a fixed interval of time. Hence Blinking of eyes cannot be used for measurement of time.
2. Two clocks, A and B, are shown in Figure 13.1. Clock A has an hour and a minute hand, whereas clock B has an hour hand, a minute hand as well as a second hand. Which of the following statement is correct for these clocks?

(a) A time interval of 30 seconds can be measured by clock A.
(b) A time interval of 30 seconds cannot be measured by clock B.
(c) Time interval of 5 minutes can be measured by both A and B.
(d) Time interval of 4 minutes 10 seconds can be measured by clock A.
Soln:
The answer is (c) Time interval of 5 minutes can be measured by both A and B.
Explanation:
Clock A doesn’t have a seconds hand. Hence seconds cannot be measured by clock A. 5 minutes can be measured by using both clocks.
3. Two students were asked to plot a distance-time graph for the motion described in Table A and Table B.


The graph given in Figure 13.2 is true for
(a) both A and B.
(b) A only.
(c) B only.
(d) neither A nor B.
Soln:
The answer is (a) both A and B.
Explanation:
4. A bus travels 54 km in 90 minutes. The speed of the bus is
(a) 0.6 m/s
(b) 10 m/s
(c) 5.4 m/s
(d) 3.6 m/s
Soln:
Answer is (b) 10 m/s
Explanation:
Speed = Distance / Time
Distance = 54km = 54 x1000 = 54000m
Time = 90 minutes = 90×60= 5400s
Speed = 54000/5400 = 10 m/s
5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is
(a) S = D × T
(b) T = S/D
(c) S = 1/ T x D
(c) S = T/D
Soln:
Answer is (c) S = 1/TxD
Explanation:
Option c) is the correction equation because Speed = Distance/Time
6. Observe Figure 13.3.

The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from
(a) A to B and back to A.
(b) O to A, A to B and B to A.
(c) B to A, A to B and B to O.
(d) A to B.
Soln:
The answer is (a) A to B and back to A.
7. Fig. 13.4 shows an oscillating pendulum

The time taken by the bob to move from A to C is t1, and from C to O is t2. The time period of this simple pendulum is
(a) (t1 + t2 )
(b) 2 (t1 + t 2 )
(c) 3 (t1 + t 2 )
(d) 4 (t1 + t 2 )
Soln:
Answer is (d) 4 (t1 + t 2 )
Explanation:
The total time taken by the bob to move from A to 0 is (t1+ t2), which is 1/4th time of one full cycle of the pendulum. The time period of the pendulum, i.e. time taken by the pendulum to complete one oscillation from A to B and back to A, will be 4 (t1 + t2).
8. The correct symbol to represent the speed of an object is
(a) 5 m/s
(b) 5 mp
(c) 5 m/s-1
(d) 5 s/m
Soln:
Answer is (a) 5 m/s
Explanation:
Unit of speed is meter/ second hence the answer is (a) 5 m/s.
9. Boojho walks to his school, which is at a distance of 3 km from his home in 30 minutes. On reaching, he finds that the school is closed and comes back by bicycle with his friend and reaches home in 20 minutes. His average speed in km/h is
(a) 8.3
(b) 7.2
(c) 5
(d) 3.6
Soln:
The answer is (b) 7.2
Explanation:

=7.2 km/h (⸪ 1h = 60 mins)
Very Short Answer Questions
10. A simple pendulum oscillates between two points, A and B, as shown in Figure 13.5. Is the motion of the bob uniform or non-uniform?

Soln:
The motion of the bob is non-uniform because the speed of the bob keeps changing.
12. Paheli and Boojho have to cover different distances to reach their school, but they take the same time to reach the school. What can you say about their speed?
Soln:
Because their speed will be different from one another.
12. If Boojho covers a certain distance in one hour and Paheli covers the same distance in two hours, who travels at a higher speed?
Soln:
Boojho travels at a higher speed; hence he reaches the distance early.
Short Answer Questions
13. Complete the data of the table given below with the help of the distance-time graph given in Figure 13.6.


Soln:

14. The average age of children in Class VII is 12 years and 3 months. Express this age in seconds.
Soln:
12 years 3 months
= 12 × 365 + 3 × 30 = 4470 days
= 4470 × 24 × 60 × 60 s = 386208000 s
15. A spaceship travels 36,000 km in one hour. Express its speed in km/s.
Soln:
36000 km/h=
16. Starting from A, Paheli moves along a rectangular path ABCD as shown in Figure 13.7. She takes 2 minutes to travel to each side. Plot a distance-time graph and explain whether the motion is uniform or non-uniform.

Soln:
Since the distance covered per unit of time for the entire distance covered is not the same, the motion is non-uniform.

17. Plot a distance-time graph of the tip of the second hand of a clock by selecting 4 points on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. The circumference of the circle traced by the second hand is 64 cm.
Soln:


Long Answer Questions
18. Given below as Figure 13.8 is the distance-time graph of the motion of an object.

(i) What will be the position of the object in the 20s?
(ii) What will be the distance travelled by the object in 12s?
(iii) What is the average speed of the object?
Soln:
- At 20 s, the object will be 8 m away from the starting point.
- In 12 s, the distance travelled by the object will be 6 m.
- Average speed of the object Total distance=Total distance/Time taken=8m/20s=0.4m/s
19. Distance between Bholu’s and Golu’s houses is 9 km. Bholu has to attend Golu’s birthday party at 7 o’clock. He started from his home at 6 o’clock on his bicycle and covered a distance of 6 km in 40 minutes. At that point, he met Chintu, and he spoke to him for 5 minutes and reached Golu’s birthday party at 7 o’clock. With what speed did he cover the second part of the journey? Calculate his average speed for the entire journey.
The speed with which Bholu covered the second part of the journey
Soln:

20. Boojho goes to the football ground to play football. The distance-time graph of his journey from his home to the ground is given as Figure 13.9.
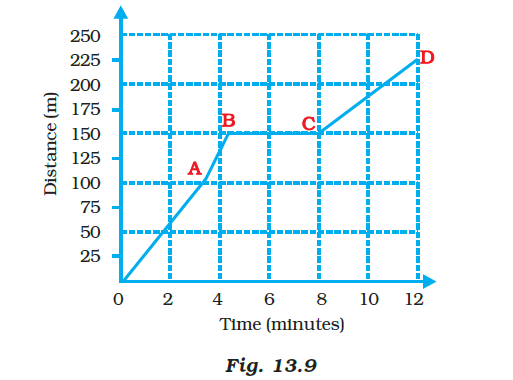
(a) What does the graph between points B and C indicate about the motion of Boojho?
(b) Is the motion between 0 to 4 minutes uniform or nonuniform?
(c) What is his speed between 8 and 12 minutes of his journey?
Soln:
(a) Boojho’s speed is zero hence he will be in rest
(b) motion between 0 to 4 minutes will be nonuniform
(c) 75/4 = 18.75 m/minute
BYJU’S innovative approach to teaching and presenting the concepts change the way students gain knowledge. BYJU’S uses effective videos, animations and study material that help the students learn the topic clearly.
To get the benefits provided by BYJU’S, log on to BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
Paheli and Boojho have to cover different distances to reach their school, but they take the same time to reach the school. What can you say about their speed?
Because their speed will be different from one another.
If Boojho covers a certain distance in one hour and Paheli covers the same distance in two hours, who travels at a higher speed?
Boojho travels at a higher speed, and hence he reaches the distance early.
The average age of children in Class 7 is 12 years and 3 months. Express this age in seconds.
12 years 3 months
= 12 × 365 + 3 × 30 = 4470 days
= 4470 × 24 × 60 × 60 s = 386208000 s












Comments