According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 8 Science textbook.
Early Days of Cells
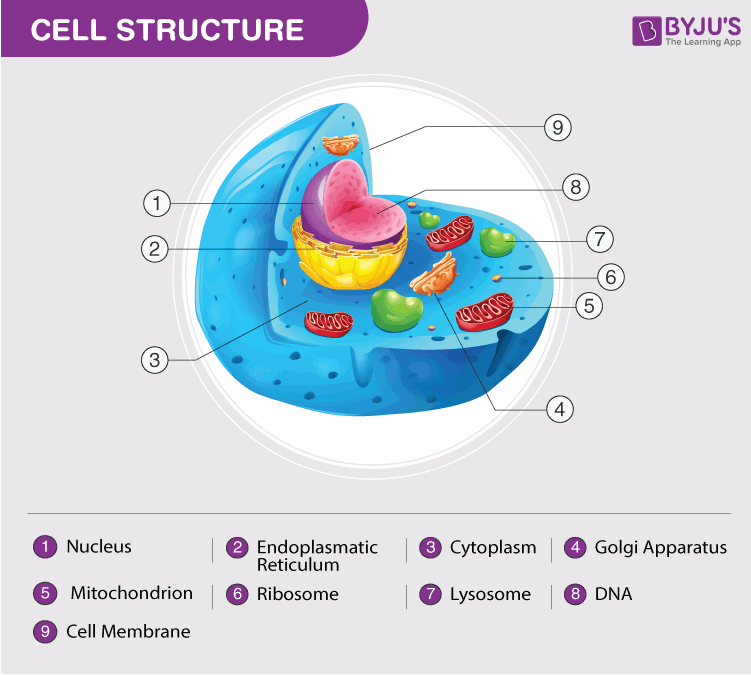
Cells
Cells are the fundamental structural units of living organisms and the basic units of life.
Robert Hooke discovered the cell in the year 1665 from a thin section of cork under a self-made microscope.
For more information on Cell Structure and Its Function, watch the below video
World of Cells
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic – Size: generally small ( 1-10 µm), Where 1 µm = 10 −6m.
- The nucleus is not well defined and known as a nucleoid.
- Single, circular chromosome.
- Membrane-bound organelles are absent. For example, Bacterial cell
Eukaryotic – Size: generally large ( 5-100 µm).
- The nucleus is well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
- Possess more than one linear chromosome.
- Membrane-bound cell organelles are present. For example, Human cells.
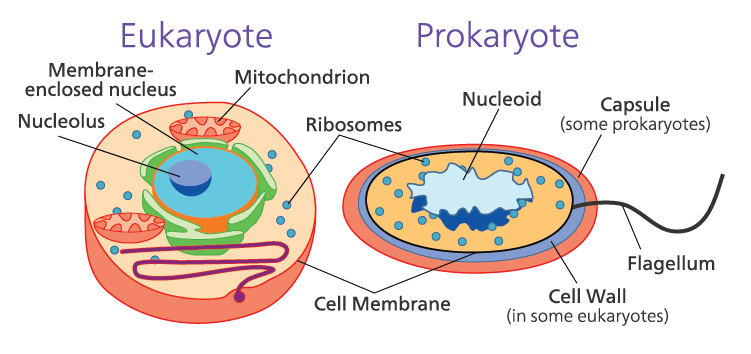
Cell structure in Eukaryotic cells
- Most eukaryotes are multicellular.
- The nucleolus is present in the nucleus.
- It contains cell organelles such as plastids, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, etc.
- Fungi, plant, and animal cells are eukaryotic.
Cell membrane
- The cell membrane separates cells from one another and also the internal contents from the surrounding medium.
- It is porous and allows the movement of substances or materials both inward and outward.
Cytoplasm
- It is the jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus.
- Various other components, or organelles of cells, are present in the cytoplasm.

Cell walls in plants
- A cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells.
- It gives shape and rigidity to these cells.
- It gives a rigid structure to plant cells, and that is why they can withstand the stress of high-velocity wind, rain, high temperature etc.
Cell Factory
Organelles
- The various components present within the cell are known as cell organelles.
- All these components are special and specific to their functions.
- For example, mitochondria, lysosomes etc.
Nucleus
- It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell.
- The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane.
- It uses information in the chromosomes to decide what each organelle should do and the functions of the cell.
- The nucleus contains an even smaller concentrated material called nucleolus.

Chromosomes
- The nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes.
- These carry genes and help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
- Chromosomes are composed of DNA in the form of Chromatin and protein.
- Chromosomes contain information for the inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA molecules.
DNA
- DNA molecules contain the information necessary for constructing and organising cells.
Functional segments of DNA are called genes.

Vacuoles, Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus
Vacuoles
- Vacuoles are storage bubbles of irregular shapes which are found in cells.
- The vacuole stores the food, a variety of nutrients that a cell might need to survive or waste.
- In plant cells, vacuoles are much larger than in animal cells, and they provide rigidity to the plant cells.

Golgi Apparatus
- Golgi Apparatus, also termed as Golgi Complex, is a membrane-bound nucleus.
- Its main function is to modify proteins.
- These modified proteins are placed in Golgi so that they can transport elsewhere in the cell when required.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- It is a membranous organelle.
- It is found in all eukaryotic cells.
- The ER is divided into two types based on their physical and functional properties viz. Smooth and Rough ER.

Rough ER
- It synthesizes and secretes proteins in the cells.
Smooth ER
- The SER is involved in the synthesis of phospholipids, the main lipids in cell membranes and are very important in the process of metabolism.
- They also transport the products of the rough endoplasmic reticulum to other cell parts like the Golgi apparatus.
Lysosomes
- Lysosomes are small membrane-bound sac-like structures which release digestive enzymes that break down food.
- They also remove the old and damaged or dead organelles from the cell and, thus protect the cell from further damage.
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria is a double membrane-bound sausage-shaped organelle.
- Also known as ‘powerhouse of the cell’.
- Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration in the cell, and it produces energy in the form of ATP.

For more information on Mitochondria, watch the below video

Plastids
- Plant cells have tiny, coloured structures called plastids.
- Plastids carry pigments of various colours like orange, red, green and even colourless.
- The plastids, which carry green-coloured pigments, i.e., chlorophyll are called chloroplasts.
For more information on Plastid and Its Functions, watch the below video

Plants vs Animals
Comparison of plant and animals cells
| Cell Organelle | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Cell wall | Yes | No |
| Cell membrane | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoplasm | Yes | Yes |
| Nucleus | Yes | Yes |
| Chloroplast | Yes | No |
| Vacuole | Yes | Yes |
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for class 8 Science Chapter 8 |
| NCERT Exemplar for class 8 Science Chapter 8 |
Learn more about the cell and its various parts and other related topics, including NCERT class 8 Science notes, at BYJU’S.
Also Read:-
| Cell Organelles | Animal Cell |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Function
What is a cell?
A cell is a basic unit of life, and it mainly comprises the nucleus, cytoplasm and cell membrane. There are several other organelles inside the cell.
What are the other important organelles of the cell?
The important organelles of the cell are Ribosomes, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Choloplasts, and Mitochondria.
What is the study/research of cells called?
The study of cells or cell biology is called Cytology.
it was very great experience learning from byju’s
This keypoints helped me in completing my notes