According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 10.
CBSE Class 9 Work and Energy Notes
Introduction to Work and Energy
Class 9 Chapter 11, ‘Work and Energy’, discusses the concept of work, energy and power in detail. In day-to-day life, we consider any useful physical or mental labour as work, but work is defined differently in science. Work done by a force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work has only magnitude and no direction. Similarly, we often use the term energy in our daily life; this also has a different definition in science. In physics, energy is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light.

Chapter Summary Video

Work
Work done on an object is defined as the product of the magnitude of the force acting on the body and the displacement in the direction of the force. W = F.s. The SI unit of force is Newton.
If a force acting on a body causes no displacement, the work done is 0. For example, pushing a wall.
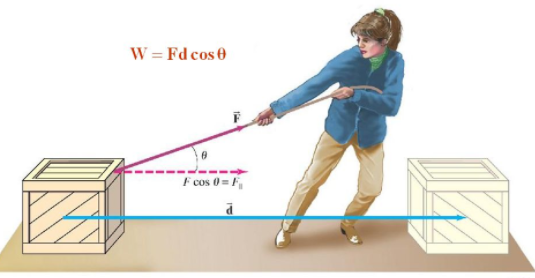
The force component F cos θ gives the component of force along the direction in that the body is displaced. Cos θ is the angle between the force vector and displacement vector.
To know more about Work, visit here.
Energy
Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Its unit is the same as that of work. Energy is a scalar quantity.
SI unit of energy or work = Joule (Nm) or Kgm2s−2.
Forms of Energy
Energy has different forms: Light, heat, chemical, electrical or mechanical.
Mechanical energy is the sum of
(i) Kinetic energy (K.E)
(ii) Potential energy (P.E)
To know more about Energy and Its Types, visit here.
Kinetic Energy
Objects in motion possess energy and can do work. This energy is called Kinetic Energy.
When two identical bodies are in motion, the body with a higher velocity has more KE.

To know more about Kinetic Energy, visit here.
Work-Energy Theorem
The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by a moving body can be calculated by finding the change in KE.
⇒ W net = KE final − KE initial
⇒ Wnet=
To know more about Work-Energy Theorem, visit here.
Factors Affecting Kinetic Energy
- Mass
- Velocity
- Momentum
Potential Energy
Energy can get stored in an object when work is done on it.
For example, stretching a rubber string. The energy that is possessed by a body by virtue of its configuration or change in position is known as Potential Energy.

The potential energy of an object at a height
When an object is raised to a certain height, work is done against gravity to change its position. This energy is stored as Potential Energy.
⇒W = F.s
⇒F = ma
In the case of increasing the height, F = mg
Therefore, W (P.E) = mgh
⇒ ΔPE=mg(h final−h initial)
For more information on Kinetic and Potential Energy, watch the below video

To know more about Potential Energy, visit here.
Law of Conservation of Energy
Law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be transferred from one form to another. The total energy before and after the transformation remains constant.
Total energy = KE + PE
where, 1/2 mv2 + mgh = constant
For example: consider a ball falling freely from a height. At height h, it has only PE = mgh.
By the time it is about to hit the ground, it has a velocity and therefore has KE=
To know more about the Law of Conservation of Energy, visit here.
Power
The rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of energy is called power. It is denoted by P
⇒ P =
SI unit is Watt (Js−1).
Average power = Total energy consumed/Total time taken
Commercial Unit of Power
The commercial unit of power is kWh, i.e. energy used in 1 hour at 1000 Joules/second.
1kWh=3.6×106J
For more information on Work Energy and Power, watch the below videos


To know more about Power, visit here.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 9 Physics Notes Chapter 11 Work and Energy
What is the definition of ‘kinetic energy’?
Kinetic energy is a form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion.
What is the definition of ‘potential energy’?
Potential energy is the stored energy that depends upon the relative position of various parts of a system.
What is ‘power’?
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time.

Comments