According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 13.
Biodiversity refers to a variety of plant and animal life on Earth. Explore in detail biodiversity and its types along with biodiversity and conservation notes at BYJU’S.
The term ‘biodiversity’ was popularized by the sociobiologist Edward Wilson. Biodiversity is of three types:

- Genetic diversity – It refers to the total number of genes in the genetic makeup of a species. For e.g., the genetic variation shown by Rauwolfia vomitoria (medicinal plant).
- Species diversity – It represents the number of species found in an ecological community. For example – The Western ghat has a greater number of amphibian species compared to the Eastern ghats.
- Ecological diversity – Greater diversity observed at the ecosystem level in a particular area with its deserts, mangroves, rain forests, etc.
Patterns of Biodiversity
Following are the different patterns of biodiversity
Latitudinal Gradients
Species diversity decreases towards the poles. There are a number of species in the tropics as compared to the temperate and polar regions. This is due to the following reasons:
- The tropical regions have remained undisturbed for several years. This resulted in the diversification of species in the tropics.
- The environment in the tropics is more predictable and constant. This is yet another reason for increased species diversity.
- Solar energy adds to higher productivity and helps in increasing biodiversity in the tropics.
Species-Area Relationship
The graph between species richness and area for a variety of taxa is a rectangular hyperbola. The diagram depicts the same.
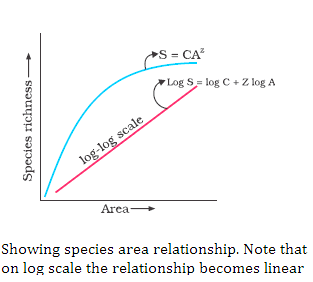
On a logarithmic scale, the relationship is a straight line described by the equation
log S = log C + Z log A
where,
S= Species richness
A= Area
Z = slope of the line (regression coefficient)
C = Y-intercept
Also Read: Important Questions on Biodiversity Conservation
Loss of Biodiversity
Loss of biodiversity in a region can lead to
- Deterioration in plant production,
- Decreased resistance to environmental issues such as drought, global warming, etc., and
- High variability in certain ecosystem processes such as plant productivity, water use and pest and disease cycles.
Causes of Biodiversity Loss
The following are the causes of the loss of biodiversity.
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Over-exploitation
- Alien species invasions
- Co-extinctions
Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity conservation is the protection, upliftment and management of biodiversity to derive sustainable benefits for present and future generations.
Biodiversity can be conserved by the following two methods:
- In situ conservation – It involves the protection and conservation of a variety of animals and plant species in its natural habitat. It includes biosphere reserves, hot spots, national parks and sanctuaries, wild forests etc.
- Ex-situ conservation – It involves the protection and conservation of rare species of animals and plants outside their natural habitats. These include zoos, aquariums, botanical gardens, gene banks, etc.
Reasons for Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity should be conserved for the following reasons:
- Humans derive a number of economic benefits from nature, such as firewood, food, construction material, fibre, and medicines.
- The Amazon forests provide 20% of the total atmospheric oxygen on Earth.
- These are our biological legacies and should be passed on to future generations.
- Birds, bees and birds are some of the pollinating agents in the ecosystem.
To learn more about biodiversity and conservation, keep visiting BYJU’S.
Further Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation
What is global warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels.
What is the meaning of extinction?
Extinction refers to the dying out or extermination of a species.
What is evolution?
Evolution is the change in the characteristics of a species over several generations and relies on the process of natural selection.
Comments