*According to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Exercise 10.5 Chapter 10 Practical Geometry in simple PDF are given here. Constructing a Right-Angled Triangle When the Length of One Leg and Its Hypotenuse are given (RHS Criterion) is the only topic covered in this exercise of the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10. To help students with their exam preparation to achieve good marks in Maths, students are advised to try solving the problems from the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths, Chapter 10 Practical Geometry. Then refer to these solutions to know the best way of approaching the different questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry – Exercise 10.5
Access Other Exercises of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 – Practical Geometry
Access Answers to NCERT Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 – Practical Geometry Exercise 10.5
1. Construct the right-angled ΔPQR, where m∠Q = 90°, QR = 8cm and PR = 10 cm.
Solution:-

Steps of construction
1. Draw a line segment QR = 8 cm.
2. At point Q, draw a ray QY to make an angle of 90o, i.e., ∠YQR = 90o.
3. With R as a centre and radius of 10 cm, draw an arc that cuts the ray QY at P.
4. Join PR.
Then, ΔPQR is the required right-angled triangle.
2. Construct a right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is 6 cm long, and one of the legs is 4 cm long.
Solution:-
Let us consider ΔABC is a right-angled triangle at ∠B = 90o
Then,
AC is hypotenuse = 6 cm … [given in the question]
BC = 4 cm
Now, we have to construct the right-angled triangle by the above values.
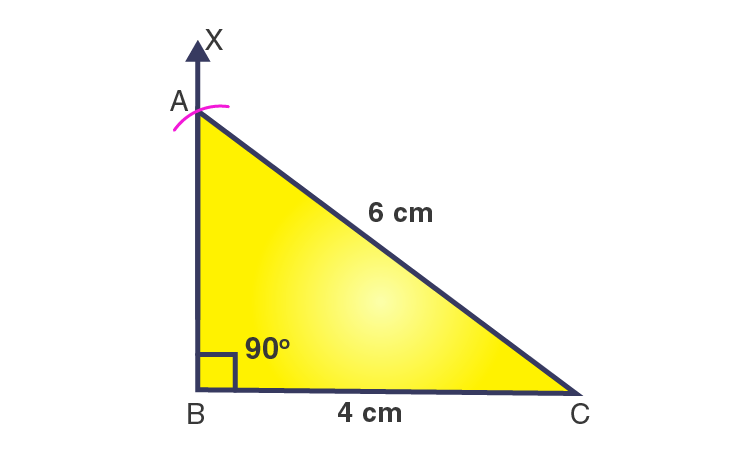
Steps of construction
1. Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm.
2. At point B, draw a ray BX to make an angle of 90o, i.e., ∠XBC = 90o.
3. With C as a centre and radius of 6 cm, draw an arc that cuts the ray BX at A.
4. Join AC.
Then, ΔABC is the required right-angled triangle.
3. Construct an isosceles right-angled triangle ABC, where m∠ACB = 90° and AC = 6 cm.
Solution:-
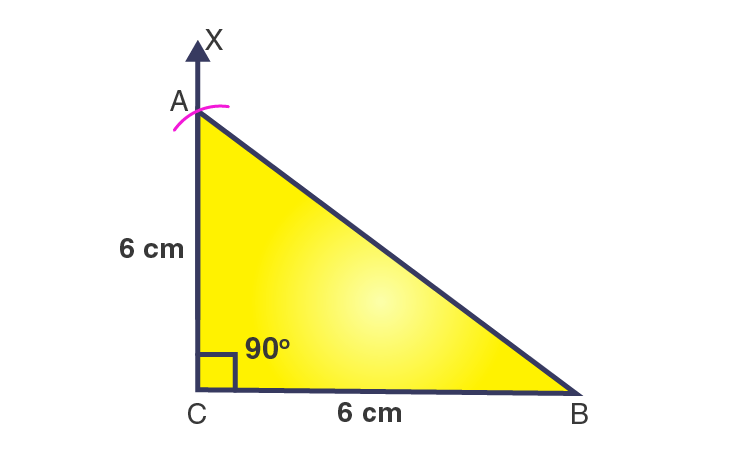
Steps of construction
1. Draw a line segment BC = 6 cm.
2. At point C, draw a ray CX to make an angle of 90o, i.e., ∠XCB = 90o.
3. With C as a centre and radius of 6 cm, draw an arc that cuts the ray CX at A.
4. Join AB.
Then, ΔABC is the required right-angled triangle.
Also, explore –
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths



Wonderful
nicely answered better than most of the sites
nicely answered better than other sites
very easy to understand
Easily understandable with ad free facility
(Better than other sites)
👍Nicely explained the answers👍