According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 7.
An Introduction to Motion
Motion
- A body is in a state of rest when it does not change its position with respect to time.
- A body is said to be in motion when it changes its position with respect to time.
For more information on Motion, watch the below video
To know more about Motion, visit the link below;
Means of Transport
- Ever since ancient times, humans have devised different means of transport to traverse from one place to another.
- They designed boats that resemble the shapes of animals living in water to travel across water bodies. They invented the wheel, which led to inventions like carts and other animal-driven modes of transport.
- During the beginning of the 19th century, humans designed the steam engine, which was followed by automobiles and motorised vehicles.
Measuring Length: A History
Length and Distance
- Distance is the measure of how far or long something is. For example, the length of a table or a soccer field or, how far is Mumbai from Delhi?
- Length can be measured in terms of a unit. A unit is a comparison of an unknown quantity with that of a known quantity. It is required to establish a common standard or convention in order to make calculations and analysis easier worldwide.
Traditional Ways of Measuring Lengths
Traditional methods of measuring length were the use of the length of one’s foot or other body parts. But, it was inconsistent since this varies from person to person and lacks uniformity.
For more information on Measuring Motion, watch the below video
Standard Units
Standardising Length Measurement
- Scientists from all over the world have accepted common standard units of measurement.
- The International System of Units (S.I unit) was set up as the convention for measurement worldwide.
- A metre is the SI unit of length. It has 100 equal divisions called centimetres.
- To measure large distances, we use kilometres. 1 Km = 1000 metres.
Zero error and the Correct way to measure the length
- The scale must be in contact with the object being measured.
- If scales are broken, or the zero mark is not visible, it can lead to a zero error. Then measuring from a different mark must be carried out.
- The correct reading will be obtained by subtracting the value from the full mark considered as zero.
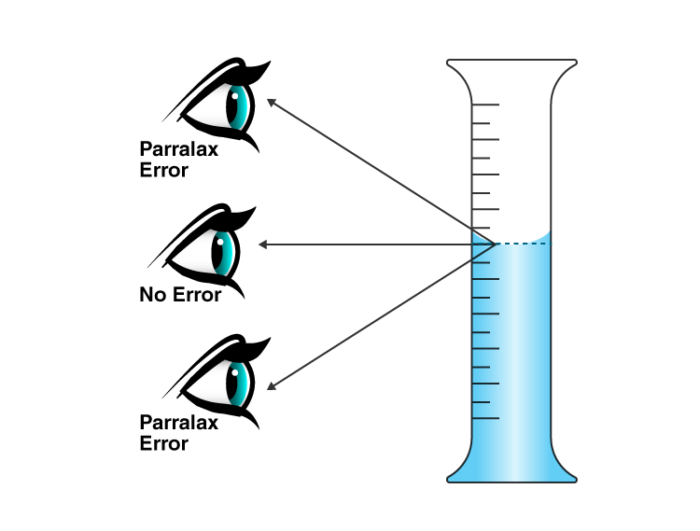
- While measuring, the eye must be exactly above the point where the measurement is to be taken in order to avoid parallax errors.
Errors in Measurements: The Basics
Parallax
Parallax is the displacement or the change in the apparent position of the object when viewed from two different points of view. This type of error while measuring is called a parallax error.
How to Measure a Curved Line
Length of a curved line
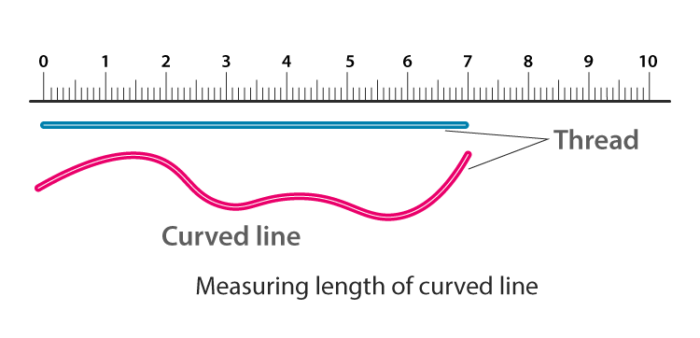
- Curved lengths cannot be measured using metre scales.
- A string or a thread can be used to measure curved lines by creating a knot at one end, and keeping that at the beginning, one can trace the curved line.
- Then this length can be stretched out and measured with the help of a metre scale.
- A measuring tape can be used to find the lengths of curved objects. E.g. girth of a tree trunk or the length of a snake.
Motion and Its Types
Types of motion
- When a body is moving in a straight line path, it is called rectilinear motion. For example, a coin falling from a building or a sprinter running a 100-metre race.
- When an object follows a circular path of motion, it is called as circular motion. For example, the moon revolves around the Earth.
- When an object moves to and fro from a mean or constant position or repeats the motion, it is called periodic motion. For example, a pendulum or a race car taking laps of a circuit.
To know more about “Types of Motion”, visit the link below;
Time
Time is the unit that measures how long it takes to do anything. Distance is measured with respect to time.
If an object is moving with some speed ‘s’ for a time interval ‘t’, then the distance covered in that time will be = s x t
Learn more about the Motion and Measurement of Distances from the topics given below:
| The SI Units | Measurement Of Length – Distance |
| Measuring The Rate Of Change Of Motion | Fundamental and Derived Units of Measurement |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
What is a parallax error?
Parallax error is the displacement or difference in the position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight.
How can parallax errors be reduced?
1. Proper orientation of the eye in a straight line 2. A fine-edged device must be used 3. Average of readings taken 4. Read lower meniscus for colourless liquids
What is zero error?
It is a condition where the measuring instrument registers a reading when there should actually be no reading.
Excellent