According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
The Electric Cell
Current
- Current is the flow of particles in a particular direction. For example, air currents that cause winds or water currents.
- When particles flow in an electric circuit to produce electricity, it is called an electric current.
Electric Current
The flow of electric charges in a circuit is called an electric current. The direction is taken from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery in an external circuit.
For more information on the Flow of Current, watch the below video
To know more about Electric Current, visit the link below;
Electric Cell
- A cell is a source of electric power created inside by internal chemical reactions.
- When the chemicals inside the cell are exhausted, the cell needs to be replaced by a new one.
- Cells have two terminals: a positive and a negative terminal. In order for current to flow, the positive terminal must be connected to the negative terminal, and this polarity must be maintained.

To know more about Electric Cell, visit the link below;
Bulb Connected to an Electric Cell
Wire
- An electric wire is a conducting path in an electric circuit through which current flows.
- It is usually made out of a metal that is a good conductor of electricity.

Electric Bulb, and its Working
- It consists of a thin wire that glows due to the passage of current. This is known as the filament.
- An electric circuit provides a closed path for the current to flow. The terminals of the bulb are connected by wires to the electric cell.
- Sometimes the bulb does not glow as the filament gets fused (breaks) due to overheating.

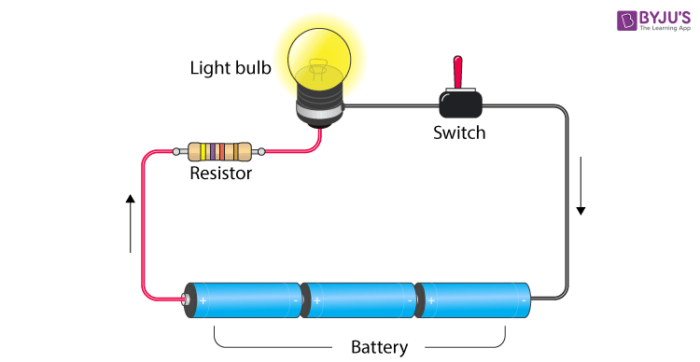
An Electric Circuit
Electric circuit
- A closed-loop path, which the current takes, is known as an electric circuit.
- When the path of the circuit is closed, current flows through it.
- When there is a break in the path (the switch is open), then the circuit is open and not conducting, so the current does not flow.
To know more about Circuit Component, visit the link below;
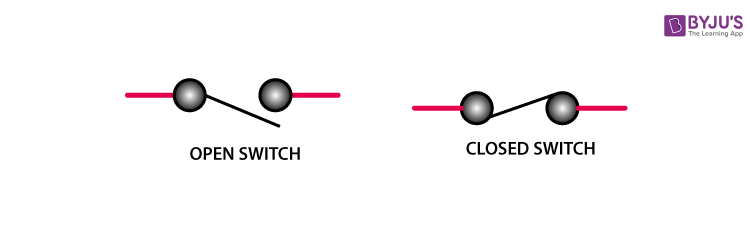
An Electric Switch
Electric switches
- Devices that are used to connect the circuit or break it.
- When the switch is connected, we call it ON, and when it’s not in contact (or open) with the circuit, the switch is OFF.
To know more about Electricity and Circuit, visit the link below;
Electricity and Circuit – Conductors and Insulators
Conductors and insulators
- Any material that allows the electric current to pass through it is called the conductor. For example, metals like copper
- Materials that do not allow the free flow of current through them are known as bad conductors or insulators. For example, rubber and plastic
For more information on Electricity, watch the below video
Learn more about Electricity and Circuits from the topics given below:
| Electric Current | Types of Circuits |
| Current Electricity | Electricity and Resistance |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
What is the flow of current?
Current flow basically means the flow of electric charges with respect to time.
What is an electric cell?
An electric cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Who invented electricity?
Benjamin Franklin had one of the greatest scientific minds of his time. He was interested in many areas of science, and made many discoveries. In the mid-1700s, he became interested in electricity.
Comments