CBSE Class 9 Science Notes on Tissues
Introduction to Tissues
Tissues
Tissues are a group of cells that combine together to perform a particular function.
To know more about Tissues, visit here.

Plant Tissues
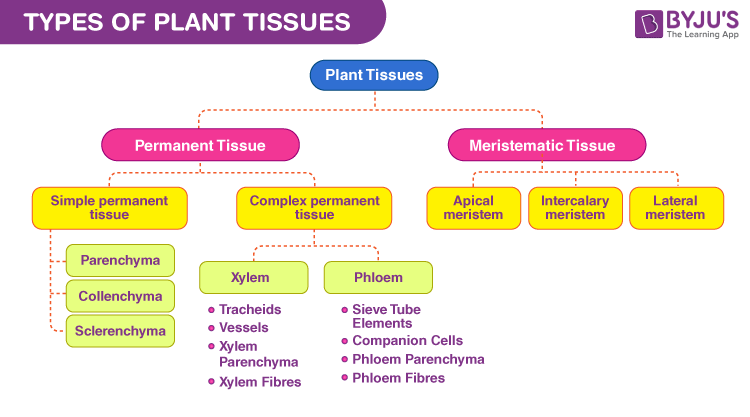
Plant tissues are of various types, and they are made up of similar types of cells. They are different from animal tissues since there are several differences between animal and plant cells. Meristematic tissues and permanent tissues are the two types of plant tissues.
Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are made up of animal cells. These tissues are usually not rigid since the cells do not have cell walls.
Watch the below videos to know the basics of Tissues


Plant Tissues
Meristematic tissues
Meristematic tissues are seen in plants. They are primarily made up of rapidly dividing cells. They are the growing tissues of the plant.
Permanent tissues
Permanent tissues arise from the meristematic tissue and have structural and functional properties. Permanent tissue can be made up of either living or dead cells. They are specialised to perform a specific function, e.g. parenchyma, collenchyma, xylem, phloem, etc. Permanent tissues are of two types simple and complex permanent tissue.
Differentiation
Differentiation is the process by which the meristematic tissues develop into different types of permanent tissues based on the location and requirements of the plant.
Apical meristem
Apical meristem is present on the apex of the plant shoot and root. They are rapidly growing tissues and aid in increasing the height of the plant.
Lateral meristem
Lateral meristem is present on the lateral walls of the stem. They help in the horizontal growth of the plant and increase the stem girth.
Intercalary meristem
Intercalary meristem can be found between the nodes of the stem and the base of the leaf. They help in branching.
Simple permanent tissues
These are tissues that are made up of only one type of cell. They usually have a structural role.
Complex permanent tissues
Complex permanent tissues are made by the combination of different types of cells. These cells work together to perform a specific task.
Parenchyma
Parenchyma tissues are made up of loosely packed cells with thin cell walls and large intercellular spaces. They are live cells and help in support and storage. Two types; Chlorenchyma and Aerenchyma.
Read more: Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Collenchyma tissues are made up of live cells which have irregularly thickened corners and thus, have decreased intercellular spaces. They help in bending various parts of the plant without breaking.
Know more: Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma tissues make up the hard and stiff parts of the plant. They are made up of dead, long and narrow cells. They almost have no intercellular space as the walls are thickened due to the presence of lignin.
Know more: Sclerenchyma
Phloem
Phloem is made up of the following components – sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres. Phloem conducts food in both directions. Among all the components, phloem fibres are the only dead cells.
Xylem
Xylem is made up of the following components. The vessels and tracheids – help in the conduction of water and minerals from the soil. Xylem parenchyma helps in food storage, and the xylem fibres provide mechanical support.
For more information on Plant Tissues, watch the below video

To know more about Plant Tissue System, visit here.
Animal Tissues
Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial tissues are seen on the outer layer of a body or organ surface. They form the outermost protective layer of most animals.
For more information on Epithelial Tissue, watch the below video

Squamous Epithelium
Squamous epithelium forms an extremely thin and flat layer of tissues. They are semi-permeable and, thus, perfect for gaseous exchange. They are present in the lining of the oesophagus and the mouth.
Cuboidal Epithelium
As the name suggests, they are cuboidal in shape and form the lining of salivary glands and kidney tubules. They provide mechanical support. They also form glandular epithelium when they form glands.
Columnar Epithelium
These tissues line the organs which help in absorption and secretion, such as the lining of the intestines. They are made up of elongated cells. When cilia are present in these cells, they form ciliated columnar epithelium like those present in the respiratory tract.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
This kind of tissue is formed when multiple layers of squamous epithelium are arranged in a pattern. Our skin is made up of this kind of tissue.
Read more: Epithelial Tissue
Muscular Tissue
These tissues make up our muscles which are responsible for almost all the movements that take place in the body.
For more information on Muscular Tissues, watch the below video

Striated/Skeletal Muscles
All the voluntary movements in our body are carried out by the striated or skeletal muscles. They are called skeletal because these tissues are mostly attached to the bones. They are long, cylindrical, unbranched with striations and multinucleated.
Unstriated/Smooth Muscles
Almost all involuntary movements in the body are carried out by the smooth or striated muscles. They are long, smooth, spindle-shaped and uninucleate. We can find them in places like the alimentary canal and blood vessels.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles make up our entire heart. These muscles are involuntary in nature and show rhythmic contractions and relaxations. Structurally they may look quite similar to striated muscles, but they are branched, uninucleated and have intercalated discs.
Know more: Muscular Tissue
Connective Tissues
These tissues help in connecting different parts of the body. Examples include blood, bones, cartilages, tendons, ligaments, areolar tissues and adipose tissues.
Read more: Connective Tissues
For more information on Connective Tissues, watch the below video

Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue makes up the entire brain, spinal cord and nerves of the body. They are responsible for all sensations, consciousness, memory and emotion.
Further reading: Nervous Tissue
Neurons
These are the cells that form the entire nervous system. Neurons consist of a cell body, axon and axon terminals.
For more information on Animal Tissues, watch the below video

To get the Summary on Tissues, watch the below video

To know more about Animal Tissues, visit here.
Also Check:
- The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 CBSE Notes – Chapter 5
- CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organism
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 6 Tissues
What are the main types of tissues?
1. Connective tissue 2. Epithelial tissue 3. Muscle tissue 4. Nervous tissue
What are the benefits of tissue in the human body?
Tissues have several functions in our human body. They are responsible for carrying oxygen, blood and other necessary materials to various organs.
How to score high grades in this chapter?
Practise diagrams and keep revising till before the exam. Remember important points and mention those in the exam.

it was very helpful
thanks a lot