According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 8.
Fear of the Dark
Light as a form of energy
- Light is the energy that enables us to see.
- Light is emitted from a source such as the Sun.
To know more about Light Energy, visit the link below;
Is Light a Traveler?
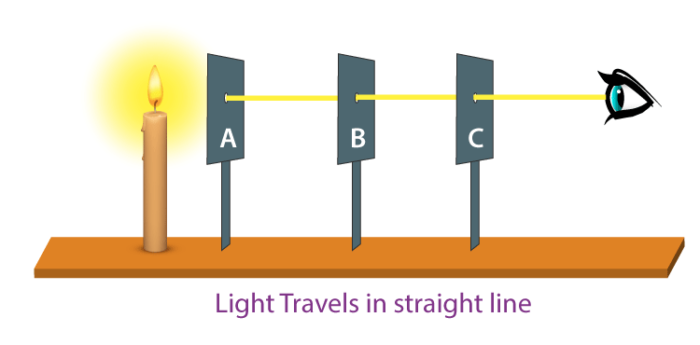
Rectilinear Propagation of Light
Light takes the quickest path between any two points. Therefore, light travels in a straight line. This is known as a rectilinear propagation of light.
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
Luminous and Non-luminous Objects
- Objects that emit light and heat are known as luminous objects. For example, Sun and other stars
- Objects that do not produce their own light but reflect the light emitted by luminous objects are known as non-luminous objects. For example, the Earth and the trees
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
Objects can be classified based on their interaction with light.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them without getting scattered. For example, glass
- Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially. For example, Butter paper
- Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them. For example, a table, a book, etc
To know more about “Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects”, visit the link below;
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque
What are Shadows?
Shadow Formation
- A shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light.
- A shadow needs a screen where it is formed, for example, the ground, walls of a room or even the surfaces of buildings.
- Shadows give us an idea about the shapes of different objects. Also, it can even mislead us about the shape of different objects. E.g. the shadow of a cone appears to be a triangle on the screen.

For more information on Shadow Formation, watch the below video

To know more about Shadow Formation, visit the link below;
The Pinhole Camera
Formation of Image by Pinhole Camera
- A pinhole camera is a simple camera that consists of a light-proof box, a thin film for a screen and a small aperture or hole to allow the passage of light rays.
- The light from outside enters through the small hole and forms an image on the screen that is inverted.
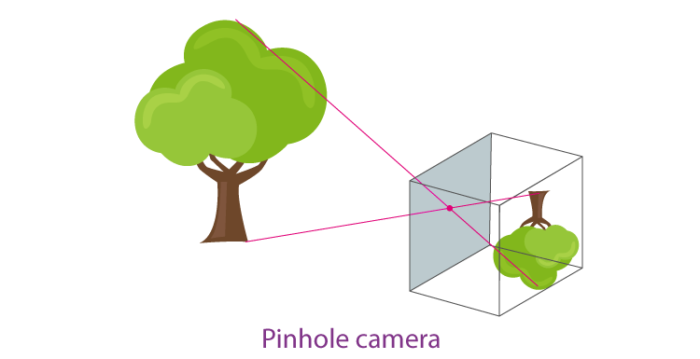
To know more about Pinhole Camera, visit the link below;
Mirrors and Reflection
Mirrors
A mirror is a surface usually consisting of glass that reflects light incident on it to form clear erect images.
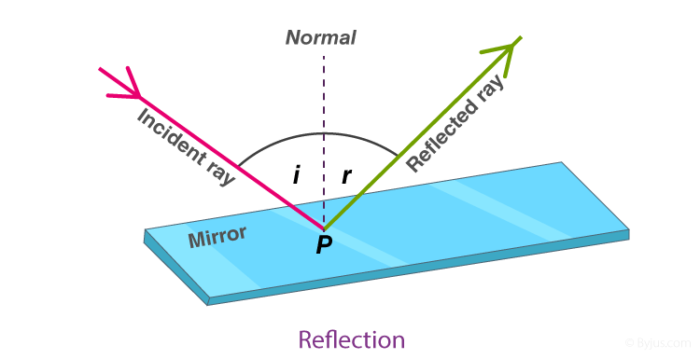
Reflection
When light is incident on a surface, it gets reflected or bounces back. Any surface that is really well-polished or shiny acts like a mirror. The phenomenon of light bouncing off surfaces is called reflection.
Characteristics of Images
- Images have colour, unlike shadows. They are formed due to the converging rays of light that come after reflecting from objects.
- A real image is formed by the actual convergence of light rays. Real images always form on a screen.
- A virtual image is the apparent convergence of diverging light rays. Virtual images cannot be obtained on a screen.
Plane Mirrors and Images Formed by Them
A plane mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it.
This enables us to see images. Take the example of a comb placed in front of a mirror over a dark-coloured paper. Let a beam of light pass through the comb on the mirror using a torch. Then an image is observed similar to the one given :
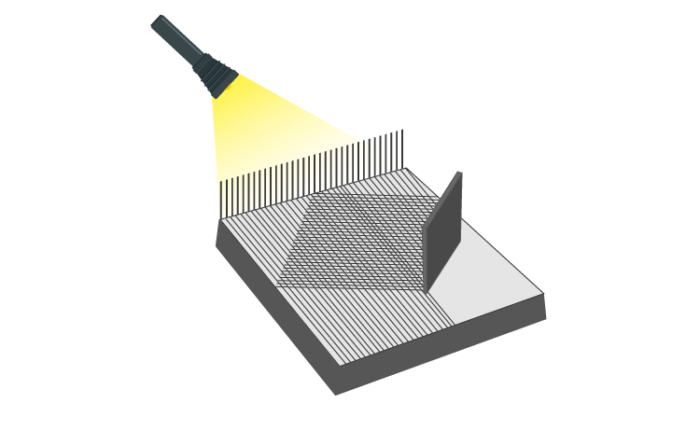
We observe that the light gets reflected from this mirror, and it travels in straight lines.
To know more about Reflection on a Plan Mirror, visit the link below;
Learn more about the Light, Shadows, and Reflections from the topics given below:
| Light Sources | Nature of Light |
| Shadow Formation | Reflection of Light |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflections
What is the definition of light?
The energy derived from the sun, a lamp, etc., that allows you to see things is called light.
What is a range of visibility?
The horizontal distance (in kilometres or miles) at which a large dark object can just be seen against the horizon sky in daylight.
What are the uses of spherical mirrors?
1. Used as a rear mirror 2. Security mirrors 3. Surveillance mirror
Comments