NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Exemplar Solutions for Chapter 7 The p Block Elements are essential study materials to ace the Class 12 board exam, as well as graduate entrance examinations. The NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Exemplar for Chapter 7 PDF will benefit students in solving the exercises given in the book and mastering the techniques of problem-solving. The NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Exemplar for Chapter 7 has exemplar questions given in the NCERT textbook, together with extra questions framed by the Chemistry experts at BYJU’S. This exemplar page also comprises problems on p block elements, important questions from previous years’ papers and sample papers.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7
Access Solutions to the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
1. On addition of conc. H2SO4 to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of an iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because
(i) H2SO4 reduces HI to I2
(ii) HI is of violet colour
(iii) HI gets oxidised to I2
(iv) HI changes to HIO3
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
2. In qualitative analysis when H2S is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. HCl, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. HNO3, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives _________.
(i) a deep blue precipitate of Cu (OH)2
(ii) a deep blue solution of [Cu (NH3)4]2+
(iii) a deep blue solution of Cu(NO3)2
(iv) a deep blue solution of Cu(OH)2.Cu(NO3)2
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
3. In a cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid molecule, how many single and double
bonds are present?
(i) 3 double bonds; 9 single bonds
(ii) 6 double bonds; 6 single bonds
(iii) 3 double bonds; 12 single bonds
(iv) Zero double bonds; 12 single bonds
Solution;
Option (iii) is the answer.
4. Which of the following elements can be involved in pπ–dπ bonding?
(i) Carbon
(ii) Nitrogen
(iii) Phosphorus
(iv) Boron
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
5. Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
(i) CO32-, NO3-
(ii) ClO3- , CO32-
(iii) SO32-, NO3-
(iv) ClO3- , SO32–Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
6. Affinity for hydrogen decreases in the group from fluorine to iodine. Which of
the halogen acids should have the highest bond dissociation enthalpy?
(i) HF
(ii) HCl
(iii) HBr
(iv) HI
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
7. Bond dissociation enthalpy of E—H (E = element) bonds are given below. Which
of the compounds will act as the strongest reducing agent?
| Compound
∆diss (E—H)/kJ mol–1 |
NH3
389 |
PH3
322 |
AsH3
297 |
SbH3
255 |
(i) NH3
(ii) PH3
(iii) AsH3
(iv) SbH3
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
8. On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
(i) It is highly poisonous and has smelled like rotten fish.
(ii) It’s a solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(iii) It is more basic than NH3
(iv) It is less basic than NH3
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
9. Which of the following acids forms three series of salts?
(i) H3PO2
(ii) H3BO3
(iii) H3PO4
(iv) H3PO3
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
10. Strong reducing behaviour of H3PO2 is due to
(i) The low oxidation state of phosphorus
(ii) Presence of two –OH groups and one P–H bond
(iii) Presence of one –OH group and two P–H bonds
(iv) High electron gain enthalpy of phosphorusSolution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
11. On heating lead, nitrate forms oxides of nitrogen and lead. The oxides formed
are ______.
(i) N2O, PbO
(ii) NO2, PbO
(iii) NO, PbO
(iv) NO, PbO2
Solution;
Option (ii) is the answer.
12. Which of the following elements does not show allotropy?
(i) Nitrogen
(ii) Bismuth
(iii) Antimony
(iv) Arsenic
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
13. Maximum covalency of nitrogen is ______________.
(i) 3
(ii) 5
(iii) 4
(iv) 6
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
14. Which of the following statements is wrong?
(i) Single N–N bond is stronger than the single P–P bond.
(ii) PH3 can act as a ligand in the formation of a coordination compound
with transition elements.
(iii) NO2 is paramagnetic.
(iv) Covalency of nitrogen in N2O5 is four
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
15. A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3
–
ion. It is due to the formation of
(i) [Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
(ii) FeSO4.NO2
(iii) [Fe(H2O)4 (NO)]2+
(iv) FeSO4.HNO3
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
16. Elements of group-15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state. However,
bismuth forms only one well-characterised compound in +5 oxidation state.
The compound is
(i) Bi2O5
(ii) BiF5
(iii) BiCl5
(iv) Bi2S5
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
17. On heating ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately we get
(i) N2 in both cases
(ii) N2 with ammonium dichromate and NO with barium azide
(iii) N2O with ammonium dichromate and N2 with barium azide
(iv) N2O with ammonium dichromate and NO2 with barium azide
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
18. In the preparation of HNO3, we get NO gas by catalytic oxidation of ammonia.
The moles of NO produced by the oxidation of two moles of NH3
will be ______.
(i) 2
(ii) 3
(iii) 4
(iv) 6
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
19. The oxidation state of a central atom in the anion of compound NaH2PO2 will
be ______.
(i) +3
(ii) +5
(iii) +1
(iv) –3
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
20. Which of the following is not tetrahedral in shape?
(i) NH4+
(ii) SiCl4
(iii) SF4
(iv) SO42–Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
21. Which of the following are peroxoacids of sulphur?
(i) H2SO5 and H2S2O8
(ii) H2SO5 and H2S2O7
(iii) H2S2O7 and H2S2O8
(iv) H2S2O6 and H2S2O7
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
22. Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as a moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
(i) Cu
(ii) S
(iii) C
(iv) Zn
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
23. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish yellow gas. When an excess of this gas reacts with NH3 an unstable trihalide is formed. In this process the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from _________.
(i) – 3 to +3
(ii) – 3 to 0
(iii) – 3 to +5
(iv) 0 to – 3
Solution:
Option (i) is the answer.
24. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O2+Pt F6– as a base compound. This is because
(i) both O2 and Xe has the same size.
(ii) both O2 and Xe has the same electron gain enthalpy.
(iii) both O2 and Xe has almost same ionisation enthalpy.
(iv) both Xe and O2 are gases.Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
25. In solid state PCl5 is a _________.
(i) covalent solid
(ii) octahedral structure
(iii) ionic solid with [PCl6]+ octahedral and [PCl4]– tetrahedra
(iv) ionic solid with [PCl4]+tetrahedral and [PCl6]– octahedral
Solution:
Option (iv) is the answer.
26. Reduction potentials of some ions are given below. Arrange them in decreasing
order of oxidising power.
| Ion
Reduction potential Eᶱ/V |
ClO4–
Eᶱ = 1.19V |
IO4–
Eᶱ = 1.65V |
BrO4 –
Eᶱ = 1.74V |
(i) ClO4–> IO4–> BrO4–
(ii) IO4–> BrO4–> ClO4–
(iii) BrO4–> IO4–> ClO4–
(iv) BrO4–> ClO4–> IO4–
Solution:
Option (iii) is the answer.
27. Which of the following is isoelectronic pair?
(i) ICl2, ClO2
(ii) BrO2–, BrF2+
(iii) ClO2, BrF
(iv) CN–, O3
Solution:
Option (ii) is the answer.
II. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
28. If chlorine gas is passed through a hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed
in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are ________
and _________.
(i) 0 to +5
(ii) 0 to +3
(iii) 0 to –1
(iv) 0 to +1
Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
29. Which of the following options are not in accordance with the property
mentioned against them?
(i) F2> Cl2> Br2> I2 Oxidising power.
(ii) MI > MBr > MCl > MF Ionic character of metal halide.
(iii) F2> Cl2> Br2> I2 Bond dissociation enthalpy.
(iv) HI < HBr < HCl < HF Hydrogen-halogen bond strength.
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers
30. Which of the following is correct for P4 the molecule of white phosphorus?
(i) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons.
(ii) It has six P–P single bonds.
(iii) It has three P–P single bonds.
(iv) It has four lone pairs of electrons.
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iv) are the answers.
31. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(ii) Leaving F—F bond, all halogens have weaker X—X bond than X—X’
bond in interhalogens.
(iii) Among interhalogen compounds, the maximum number of atoms are present
in iodine fluoride.
(iv) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Solution:
Option (i), (iii) and (iv) are the answers.
32. Which of the following statements are correct for SO2 gas?
(i) It acts as a bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(ii) Its molecule has linear geometry.
(iii) It’s dilute solution is used as a disinfectant.
(iv) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute H2SO4
with metal sulphide.
Solution:
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
33. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) All three N—O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(ii) All P—Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in the gaseous state are equal.
(iii) P4 molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white
phosphorus is very reactive.
(iv) PCl is ionic in the solid-state in which cation is tetrahedral and the anion is
octahedral.
Solution:
Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers.
34. Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against
each?
(i) As2O3< SiO2< P2O3< SO2 Acid strength.
(ii) AsH3< PH3< NH3 Enthalpy of vaporization.
(iii) S < O < Cl < F More negative electron gain enthalpy.
(iv) H2O > H2S > H2Se > H2Te Thermal stability.
Solution:
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers.
35. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) S–S bond is present in H2S2O6
(ii) In peroxosulphuric acid (H2SO5) sulphur is in +6 oxidation state.
(iii) Iron powder along with Al2O3 and K2O is used as a catalyst in the preparation of NH3
by Haber’s process.
(iv) Change in enthalpy is positive for the preparation of SO3
by catalytic oxidation of SO2
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
36. In which of the following reactions conc. H2SO4 is used as an oxidising reagent?
(i) CaF2+ H2SO4 → CaSO4+ 2HF
(ii) 2HI + H2SO4 → I2 + SO2+ 2H2O
(iii) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
(iv) NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
Solution:
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers.
37. Which of the following statements are true?
(i) The only type of interactions between particles of noble gases is due to
weak dispersion forces.
(ii) Ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(iii) Hydrolysis of XeF6
is a redox reaction.
(iv) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Solution:
Option (i) and (ii) are the answers.
III. Short Answer Type
38. In the preparation of H2SO4 by Contact Process, why is SO3 not absorbed directly in water to form H2SO4?
Solution:
Dissolution of SO3 in water is highly exothermic. This leads to the formation of a mist of tiny droplets which are highly corrosive and they can even attack the lead pipelines (lead pipelines are used to cover the tower in contact process).
39. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing catalytic oxidation of NH3 by atmospheric oxygen.
Solution:
NH3 + O2 →(Pt gauze) 4NO + 6H2O
Pt gauze reacts as a catalyst, which is added to increase the rate of reaction.
40. Write the structure of pyrophosphoric acid.
Solution:

41. PH3 forms bubbles when passed slowly in water but NH3 dissolves. Explain why?
Solution:
PH3 does not form hydrogen bonding with water. Therefore it is not soluble in water and it escapes as a gas and forms bubbles whereas ammonia forms hydrogen bonding and soluble in water.
42. In PCl5, phosphorus is in sp3d hybridised state but all its five bonds are not equivalent. Justify your answer with reason.
Solution:
The size of axial bonds is greater than the size of equatorial bonds to overcome repulsion because the three equatorial bonds cause more repulsion. Therefore two axial P-Cl bonds are longer and different from equatorial bonds.
43. Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on cooling it is diamagnetic?
Solution:
Nitric acid in the gaseous state exists in monomer form. It consists of only one unpaired electron therefore it is paramagnetic. In solid-state, it exists as a dimer (N2O2). There is no unpaired electron in its dimer form, therefore it is diamagnetic.
44. Give the reason to explain why ClF3 exists but FCl3 does not exist.
Solution:
Chlorine has vacant d orbitals hence it can show an oxidation state of +3. Fluorine has no d orbitals, it cannot show a positive oxidation state. Fluorine shows only -1 oxidation state. Therefore FCl3 does not exists.
45. Out of H2O and H2S, which one has a higher bond angle and why?
Solution:
H2O has higher bond angle than H2S because as we move from oxygen to sulphur the size of the central atom increases and electronegativity decreases due to which bond pair goes away from the central atom which results in a decrease in bond pair repulsion and hence bond angle decreases.
46. SF6 is known but SCl6 is not. Why?
Solution:
Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing agent and it can oxidize sulphur to its maximum oxidation state +6 to form SF6. Chlorine is not a good oxidizing agent, it cannot oxidize sulphur to its maximum oxidation state. Chlorine can oxidize sulphur to only +4 oxidation state. Hence it can form SCl4 but not SCl6.
47. On reaction with Cl2, phosphorus forms two types of halides ‘A’ and ‘B’. Halide A is a yellowish-white powder but halide ‘B’ is a colourless oily liquid. Identify A and B and write the formulas of their hydrolysis products.
Solution:
Halide A is PCl5 because it is a yellowish-white powder
Halide B is PCl3 because it is a colourless oily liquid.
PCl3 + 3H2O H3PO3 + 3HCl
PCl5 undergoes a violent hydrolysis
PCl5 + H2O POCl3 + 2HCl
PCl5 + 4H2O H3PO4 + 5HCl
48. In the ring test of NO3– ion, Fe2+ ion reduces nitrate ion to nitric oxide, which combines with Fe2+ (aq) ion to form the brown complex. Write the reactions involved in the formation of a brown ring.
Solution:
NO3– + 3Fe2+ + 4H+ → NO + 3Fe2+ 2H2O
[Fe(H2O)6]SO4 + NO → [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4Thus the complex formed is brown.
49. Explain why the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increases in the order given below:
HClO< HClO2< HClO3< HClO4
Solution:
As the electronegativity of halogen decreases, the tendency of XO3 group ( X = halogens) to withdraw electrons of the O-H bond towards itself decreases and hence the acid strength of the perhalic acid decreases.
50. Explain why ozone is thermodynamically less stable than oxygen.
Solution:
Ozone is thermodynamically less stable because it decomposes into oxygen and this decomposition leads result in the liberation of heat, so its entropy is positive and free energy is negative.
51. P4O6 reacts with water according to equation P4O6 + 6H2O → 4H3PO3.
Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralise the acid formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P4O6 in H2O.
Solution:
P4O6 + 6H2O 4H3PO3
4H3PO3 + 8NaOH Na2HPO3 + 8H20
Overall reaction :
P4O6 + 8NaOH 4Na2HPO3 + 2H2O
Moles of P4O6 = 1.1/220 = 0.5
Acid formed by one mole of P4o6 requires = 8 mol
Acid formed by 0.005 mol of NaOH is present in 100mL solution
0.04 of NaOH is present in solution = 1000/0.1 *0.04 = 400mL
52. White phosphorus reacts with chlorine and the product hydrolyses in the presence of water. Calculate the mass of HCl obtained by the hydrolysis of the product formed by the reaction of 62 g of white phosphorus with chlorine in the presence of water.
Solution:
When white phosphorous reacts with chlorine:
P4 + 6Cl2 4PCl3
PCl3 + 3H2O H3PO3 + 4HCl ]*4
P4 +6Cl2 +12H2O 4H3PO3 +12HCl
Moles of white P= 62/124 = 0.5mol
1mol of white P4 produces HCl = 12mol
0.5 mol of white P4 will produce HCl = 12*0.8 = 6mol
Mass of HCl = 6*36.5 = 219.0g
53. Name three oxoacids of nitrogen. Write the disproportionation reaction of that oxoacid of nitrogen in which nitrogen is in +3 oxidation state.
Solution:
There are three oxoacids of nitrogen.
Nitric acid(HNO3), Nitrous acid (HNO2), Hyponitrous acid (H2N2O1)
+ 3 oxidation is shown by HNO2, Therefore it undergoes disproportion reaction,
To calculate the oxidation state, consider the oxidation state of N is x.
3HNO2 HNO3 + 2NO +H2O
The oxidation state of nitrogen in HNO2 is +3
X + (+1) +2*(-2) = 0, x= +3
The oxidation state of nitrogen in HNO3 is +5
X + (+1) + 3*(-2) = 0, x= 5
The oxidation state of nitrogen in NO is +2
X + (-2) = 0, x =2
Therefore +3 oxidation state changes to +5 and +2 oxidation states.
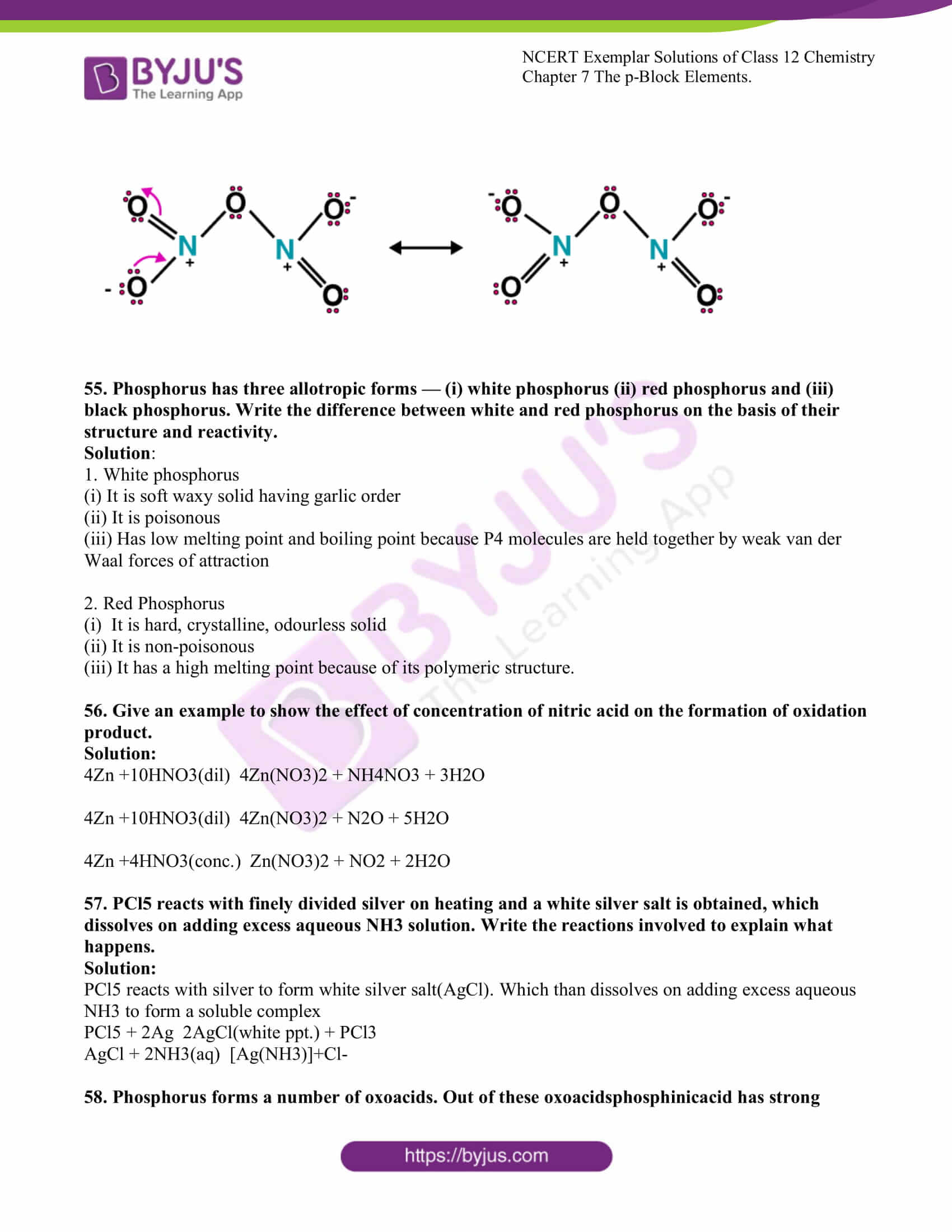
54. Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P4O10. Write the reaction involved. Also, write the resonating structures of the oxide of nitrogen formed.
Solution:
P4O10 + 4HNO3 4HPO3 + 2N2O5
White phosphorous is very reactive as compared to red phosphorous due to angular strain in white phosphorous.

55. Phosphorus has three allotropic forms — (i) white phosphorus (ii) red phosphorus and (iii) black phosphorus. Write the difference between white and red phosphorus on the basis of their structure and reactivity.
Solution:
1. White phosphorus
(i) It is soft waxy solid having garlic order
(ii) It is poisonous
(iii) Has low melting point and boiling point because P4 molecules are held together by weak van der Waal forces of attraction
2. Red Phosphorus
(i) It is hard, crystalline, odourless solid
(ii) It is non-poisonous
(iii) It has a high melting point because of its polymeric structure.
56. Give an example to show the effect of concentration of nitric acid on the formation of oxidation product.
Solution:
4Zn +10HNO3(dil) 4Zn(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3H2O
4Zn +10HNO3(dil) 4Zn(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
4Zn +4HNO3(conc.) Zn(NO3)2 + NO2 + 2H2O
57. PCl5 reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH3 solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happens.
Solution:
PCl5 reacts with silver to form white silver salt(AgCl). Which than dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH3 to form a soluble complex
PCl5 + 2Ag 2AgCl(white ppt.) + PCl3
AgCl + 2NH3(aq) [Ag(NH3)]+Cl-
58. Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids. Out of these oxoacidsphosphinicacid has strong reducing property. Write its structure and also write a reaction showing its reducing behaviour.
Solution:
4AgNO3 + H3PO2 + 2H2O 4Ag + H3PO4 + 4HNO3
2HgCl2 + H3PO2 + 2H2O 2Hg + H3PO4 + 4HCl
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Exemplar for The p Block Elements
This chapter is one of the most important chapters for the CBSE Class 12 board examination. Every year, approximately 4 questions are asked from this chapter. To answer all questions related to the chapter, students are advised to solve the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chapter 7 The P Block Elements. The important topics discussed in the chapter are
- Group 15 Elements
- Dinitrogen
- Ammonia
- Oxides of Nitrogen
- Nitric Acid
- Phosphorus — Allotropic Forms
- Phosphine
- Phosphorus Halides
- Oxoacids of Phosphorus
- Group 16 Elements
- Dioxygen
- Simple Oxides
- Ozone
- Sulphur — Allotropic Forms
- Sulphur Dioxide
- Oxoacids of Sulphur
- Sulphuric Acid
- Group 17 Elements
- Chlorine
- Hydrogen Chloride
- Oxoacids of Halogens
- Interhalogen Compounds
- Group 18 Elements
To download the PDF, click the below link.
Links Here
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 |
Why Opt for BYJU’S
NCERT Exemplar solutions, provided at BYJU’S, are the result of comprehensive research. These solutions will help students understand the important topics from the exam point of view and help them crack the board exam with a good score. For NCERT Class 12 notes, study materials, NCERT solutions, exemplar questions, textbooks, previous years’ question papers and sample papers, visit BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.













Comments