In our day-to-day lives, we come across various plane surfaces, such as the top of our study table, blackboard, etc. In Chapter 15 of Class 8, we shall discuss concepts based on polygons (A polygon is a closed curve formed by the line segment where (i) no two line segments intersect except at their end-points and (ii) no two line segments with a common endpoint are coincident). These concepts are explained by our subject experts in simple language for students to understand the concepts clearly. Students can refer to RD Sharma Class 8 as reference material to attain good command over the subject. Students can easily download the PDFs for free from the links provided below.
Chapter 15 – Understanding Shapes-I (Polygons) contains one exercise, and the RD Sharma Solutions present in this page provide solutions to the questions given in this exercise. Now, let us have a look at the concepts discussed in this chapter.
- Definitions of the curve, open curve, closed curve and simple closed curve
- Polygons and their sides
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Understanding Shapes-I (Polygons)
Access answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Chapter 15 Understanding Shapes- I (Polygons)
EXERCISE 15.1 PAGE NO: 15.5
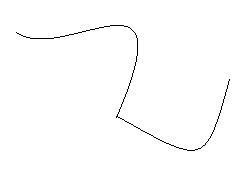
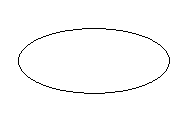
1. Draw rough diagrams to illustrate the following:
(i) Open curve
(ii) Closed curve
Solution:
Here is the illustration of
(i) Open curve
(ii) Closed curve
2. Classify the following curves as open or closed:
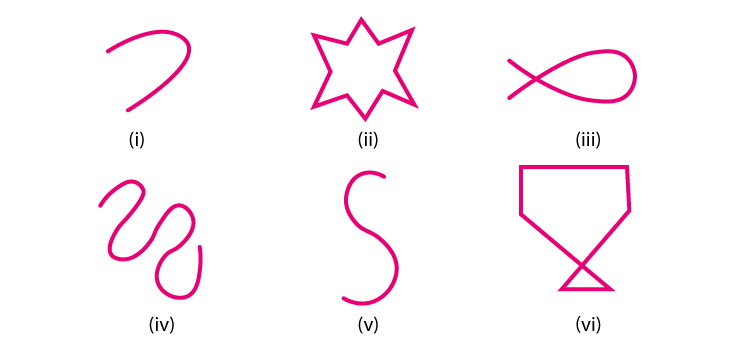
Solution:
(i) Open curve
(ii) Closed curve
(iii) Closed curve
(iv) Open curve
(v) Open curve
(vi) Closed curve
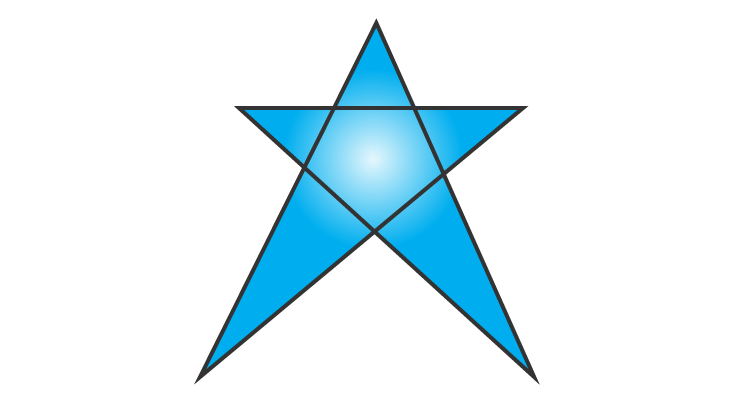
3. Draw a polygon and shade its interior. Also, draw its diagonals, if any.
Solution:
Here is the polygon with diagonals and with its interior shaded.
4. Illustrate, if possible, each one of the following with a rough diagram.
(i) A closed curve that is not a polygon.
(ii) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
(iii) A polygon with two sides.
Solution:
(i) A closed curve that is not a polygon.

(ii) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
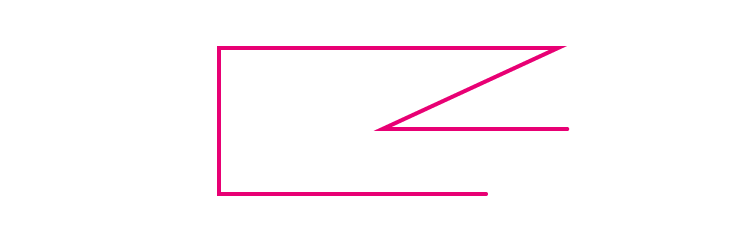
(iii) A polygon with two sides.
A polygon with two sides is not possible because, a polygon should have minimum three sides.
5. Following are some figures: Classify each of these figures on the basis of the following:
(i) Simple curve (ii) Simple closed curve (iii) Polygon
(iv) Convex polygon (v) Concave polygon (vi) Not a curve
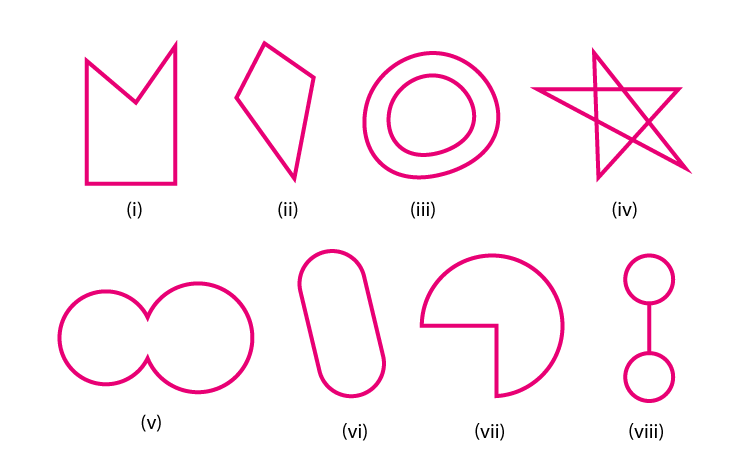
Solution:
(i) It is a Simple Closed curve and a concave polygon. This is a simple closed curve and as a concave polygon all the vertices are not pointing outwards.
(ii) It is a Simple closed curve and a convex polygon. This is a simple closed curve and as a convex polygon all the vertices are pointing outwards.
(iii) It is Not a curve and hence it is not a polygon.
(iv) It is Not a curve and hence it is not a polygon.
(v) It is a Simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(vi) It is a Simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(vii) It is a Simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(viii) It is a Simple closed curve but not a polygon.
6. How many diagonals does each of the following have?
(i) A convex quadrilateral
(ii) A regular hexagon
(iii) A triangle
Solution:
(i) A convex quadrilateral
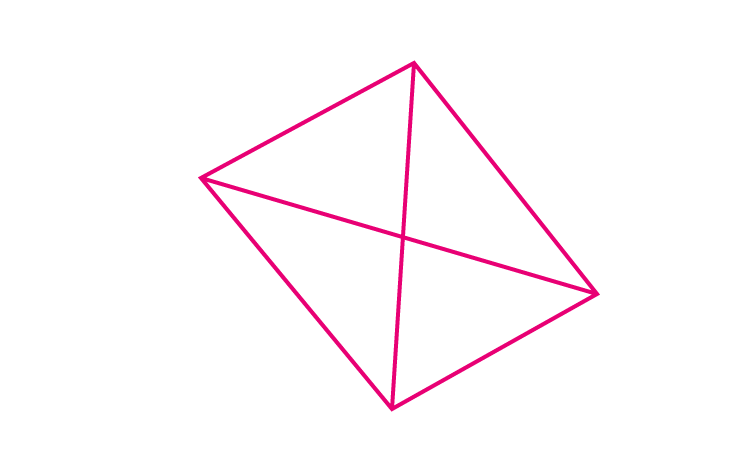
For a convex quadrilateral we shall use the formula n(n-3)/2
So, number of diagonals = 4(4-3)/2 = 4/2 = 2
A convex quadrilateral has 2 diagonals.
(ii) A regular hexagon
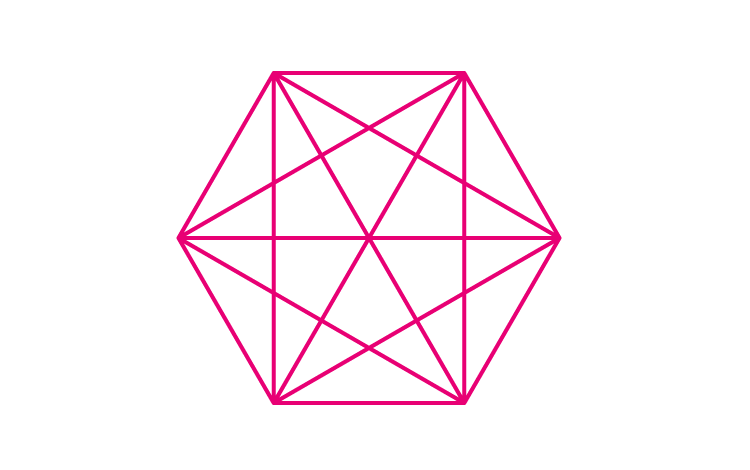
For a regular hexagon we shall use the formula n(n-3)/2
So, number of diagonals = 6(6-3)/2 = 18/2 = 9
A regular hexagon has 9 diagonals.
(iii) A triangle
For a triangle we shall use the formula n(n-3)/2
So, number of diagonals = 3(3-3)/2 = 0/2 = 0
A triangle has no diagonals.
7. What is a regular polygon? State the name of a regular polygon of
(i) 3 sides
(ii) 4 sides
(iii) 6 sides
Solution:
Regular Polygon: A regular polygon is an enclosed figure. In a regular polygon minimum sides are three.
(i) 3 sides
A regular polygon with 3 sides is known as Equilateral triangle.
(ii) 4 sides
A regular polygon with 4 sides is known as Rhombus.
(iii) 6 sides
A regular polygon with 6 sides is known as Regular hexagon.





Comments