In Exercise 20.3, we shall discuss problems based on the area of a polygon. The subject experts at BYJU’S have solved the problems from the textbook to ensure that the students are thorough with their basic concepts and help clear their doubts. RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions are the best study materials, where our experts have designed the solutions in a simple manner by using shortcut methods to solve problems. Students can refer to the RD Sharma textbook and download the PDF easily from the links provided below.
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Maths Exercise 20.3 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
Access answers to RD Sharma Maths Solutions for Class 8 Exercise 20.3 Chapter 20 Mensuration – I (Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon)
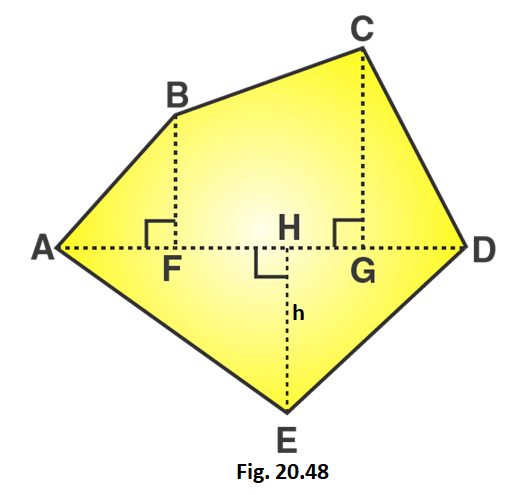
1. Find the area of the pentagon shown in fig. 20.48, if AD = 10 cm, AG = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AF = 5 cm, BF = 5 cm, CG = 7 cm and EH = 3 cm.
Solution:
GH = AG – AH = 8 – 6 = 2 cm
HF = AH – AF = 6 – 5 = 1 cm
GD = AD – AG = 10 – 8 = 2 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of given figure = Area of triangle AFB + Area of trapezium BCGF + Area of triangle CGD + Area of triangle AHE + Area of triangle EGD
We know that,
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × AF × BF + 1/2 (CG + BF) × FG + 1/2 × GD × CG + 1/2 × AH × EH + 1/2 × HD × EH
Area of given pentagon = 1/2 × 5 × 5 + 1/2 (7 + 5) × 3 + 1/2 × 2 × 7 + 1/2 × 6 × 3 + 1/2 × 4 × 3
Area of given pentagon = 12.5 + 18 + 7 + 9 + 6 = 52.5
∴ Area of given pentagon = 52.5 cm2
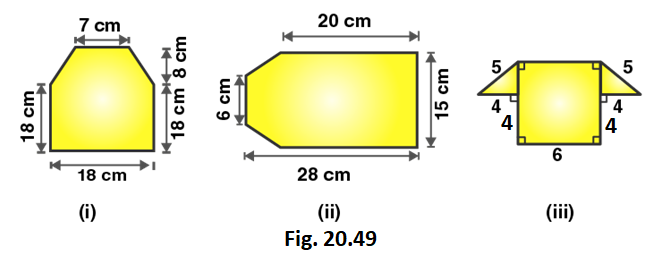
2. Find the area enclosed by each of the following figures [fig. 20.49 (i)-(ii)] as the sum of the areas of a rectangle and a trapezium.
Solution:
Figure (i)
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of figure = 1/2 (18 + 7) × 8 + 18 × 18
Area of figure = 1/2 (25) × 8 + 18 × 18
Area of figure =
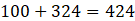
∴ Area of figure is 424 cm2
Figure (ii)
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of given figure = 1/2 (15 + 6) × 8 + 15 × 20
Area of given figure = 84 + 300 = 384
∴ Area of figure is 384 cm2
Figure (iii)
Using Pythagoras theorem in the right angled triangle,
52 = 42 + x2
x2 = 25 – 16
x2 = 9
x = 3 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of figure = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of given figure = 1/2 (14 + 6) × 3 + 4 × 6
Area of given figure = 30 + 24 = 54
∴ Area of figure is 54 cm2
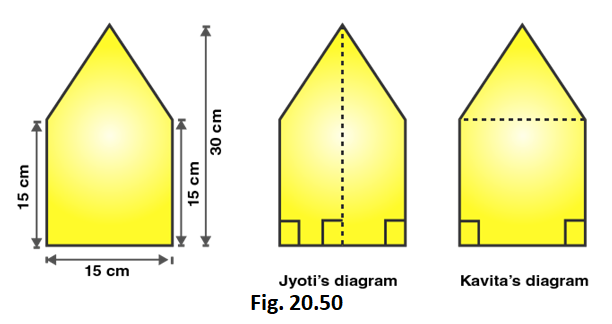
3. There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in Fig. 20.50. Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways.
Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some another way of finding its area?
Solution:
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of trapezium + Area of rectangle
Area of Jyoti’s diagram = 2 × 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of figure = 2 × 1/2 × (15 + 30) × 7.5
Area of figure = 45 × 7.5 = 337.5
Therefore, Area of figure = 337.5 cm2
We also know that,
Area of Pentagon = Area of triangle + area of rectangle
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × Base × Altitude + Length × Breadth
Area of Pentagon = 1/2 × 15 × 15 + 15 × 15
Area of Pentagon = 112.5 + 225 = 337.5
∴ Area of pentagon is 337.5 m2
4. Find the area of the following polygon, if AL = 10 cm, AM = 20 cm, AN = 50 cm. AO = 60 cm and AD = 90 cm.
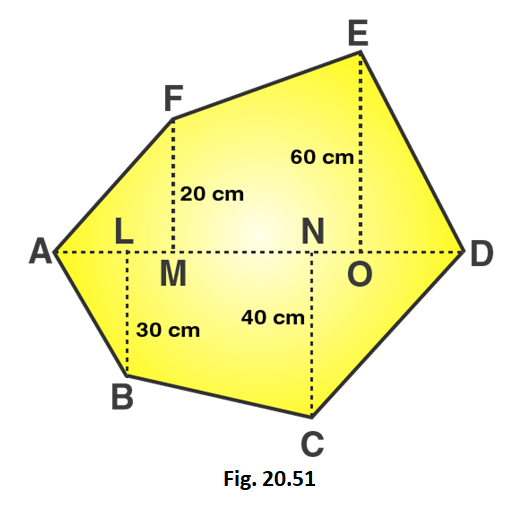
Solution:
Given that,
AL = 10 cm; AM = 20 cm; AN = 50 cm; AO = 60 cm; AD = 90 cm
LM = AM – AL = 20 – 10 = 10 cm
MN = AN – AM = 50 – 20 = 30 cm
OD = AD – AO = 90 – 60 = 30 cm
ON = AO – AN = 60 – 50 = 10 cm
DN = OD + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
OM = MN + ON = 30 + 10 = 40 cm
LN = LM + MN = 10 + 30 = 40 cm
From the figure we can write,
Area of figure = Area of triangle AMF + Area of trapezium FMNE + Area of triangle END + Area of triangle ALB + Area of trapezium LBCN + Area of triangle DNC
We know that,
Area of right angled triangle = 1/2 × base × altitude
Area of trapezium = 1/2 (Sum of lengths of parallel sides) × altitude
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × AM × FM + 1/2 (MF + OE) × OM + 1/2 × OD × OE + 1/2 × AL × BL + 1/2 × (BL + CN) × LN + 1/2 × DN × CN
Area of given hexagon = 1/2 × 20 × 20 + 1/2 (20 + 60) × 40 + 1/2 × 30 × 60 + 1/2 × 10 × 30 + 1/2 × (30 + 40) × 40 + 1/2 × 40 × 40
Area of given hexagon = 200 + 1600 + 900 + 150 + 1400 + 800 = 5050
∴ Area of given hexagon is 5050 cm2
5. Find the area of the following regular hexagon.
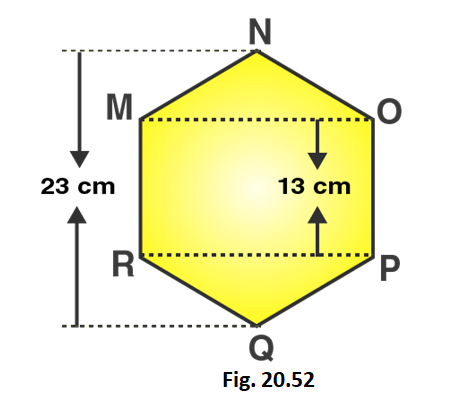
Solution:

Given that,
NQ = 23 cm
NA = BQ = 10/2 = 5 cm
MR = OP = 13 cm
In the right triangle BPQ
PQ2 = BQ2 + BP2
Substituting the values
(13)2 = (5)2 + BP2
169 = 25 + BP2
So we get
BP2 = 169 – 25 = 144
BP = 12 cm
Here
PR = MO = 2 × 12 = 24 cm
Area of rectangle RPOM = RP × PO = 24 × 13 = 321 cm2
Area of triangle PRQ = 1/2 × PR × BQ
= 1/2 × 24 × 5
= 60 cm2
Area of triangle MON = 60 cm2
Area of hexagon = 312 + 60 + 60 = 432 cm2
∴ Area of given hexagon is 432 cm2





Comments