NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism is an important study resource for students to get well-versed in the concepts as well as score good marks in Class 12 board exams and entrance exams like JEE and NEET. Solving these Exemplar problems will help you get familiar with the topics covered in Chapter 4, Moving Charges and Magnetism. Moreover, solving different kinds of questions in the exemplar book provided at BYJU’S will enhance your analytical thinking, problem-solving and memory skills.
These exemplar solutions consist of MCQs, fill in the blanks, true or false, short answer and numerical questions, worksheets, important questions from previous years’ question papers and sample papers.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4
Multiple Choice Questions I
4.1. Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in an opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field

a) they have equal z-components of momenta
b) they must have equal charges
c) they necessarily represent a particle-antiparticle pair
d) the charge to mass ratio satisfy: (e/m)1 + (e/m)2 = 0
Answer:
d) the charge to mass ratio satisfy: (e/m)1 + (e/m)2 = 0
4.2. Biot-Savart law indicates that the moving electrons produce a magnetic field B such that
a) B ┴ v
b) B ‖ v
c) it obeys the inverse cube law
d) it is along the line joining the electrons and the point of observation
Answer:
a) B ┴ v
4.3. A current circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with the centre at the origin. Half of the lop with x > 0 is now bent so that it now lies in the y-z plane.
a) the magnitude of the magnetic moment now diminishes
b) the magnetic moment does not change
c) the magnitude of B at (0,0,z),z >> R increases
d) the magnitude of B at (0,0,z),z >> R is unchanged
Answer:
a) the magnitude of the magnetic moment now diminishes
4.4. An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current-carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true?
a) the electron will be accelerated along the axis
b) the electron path will be circular about the axis
c) the electron will experience a force at 45o to the axis and hence execute a helical path
d) the electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
Answer:
d) the electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
4.5. In a cyclotron, a charged particle
a) undergoes acceleration all the time
b) speeds up between the dees because of the magnetic field
c) speeds up in a dee
d) slows down within a dee and speeds up between dees
Answer:
a) undergoes acceleration all the time
4.6. A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30o about an axis perpendicular to its plane is
a) MB
b) √3 MB/2
c) MB/2
d) zero
Answer:
d) zero
Multiple Choice Questions II
4.7. The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to the Bohr model, is
a) independent of which orbit it is in
b) negative
c) positive
d) increases with the quantum number n
Answer:
a) independent of which orbit it is in
b) negative
4.8. Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed un a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do not work. This implies that
a) motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy
b) some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B
c) if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force
d) if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire
Answer:
b) some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B
d) if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire
4.9. Two identical current-carrying coaxial loops carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple Amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C,
a)

b) the value of
 is independent of sense of C
is independent of sense of C
c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular
d) B vanishes everywhere on C
Answer:
b) the value of
 is independent of sense of C
is independent of sense of C
c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular
4.10. A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v, and a positron enters via the opposite face with velocity –v. At this instant,
a) the electric forces on both particles cause identical acceleration
b) the magnetic forces on both particles cause equal acceleration
c) both particles gain or lose energy at the same rate
d) the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone
Answer:
b) the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal acceleration
c) both particles gain or lose energy at the same rate
d) the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone
4.11. A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein,
a) E = 0, B ≠ 0
b) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
c) E ≠ 0, B = 0
d) E = 0, B = 0
Answer:
a) E = 0, B ≠ 0
b) E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0
d) E = 0, B = 0
Very Short Answers
4.12. Verify that the cyclotron frequency ꞷ = eB/m has the correct dimensions of [T]-1.
Answer:
The path traced by the particle in a cyclotron is a circular path in which magnetic force acts as a centripetal force
mv2/R = evB
eB/m = v/R = ꞷ
B = F/ev = [MLT-2]/[AT][LT-1] = [MA-1T-2] [ꞷ] = [eB/m] = [v/R] = [T]-1
4.13. Show that a force that does not work must be a velocity-dependent force.
Answer:



4.14. The magnetic force depends on v, which depends on the inertial frame of reference. Does then the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame? Is it reasonable that the net acceleration has a different value in different frames of reference?
Answer:
The net acceleration can have a different value in different frames of reference as velocity depends on the frame of reference.
4.15. Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
Answer:
When the frequency of the radio frequency field is doubled, the time period of the radio frequency is halved, which results in the half revolution of the charges.
4.16. Two long wires carrying current I1 and I2 are arranged as shown in the figure. The one carrying I1 is along in the x-axis. The other carrying current, I2, is along a line parallel to the y-axis given by x = 0 and z = d. Find the force exerted at O2 because of the wire along the x-axis.

Answer:
The magnetic field B on a current-carrying conductor is given as F = I(L×B) = ILB sinθ
O2 and I1 are parallel to the y-axis and are in the direction of –Y
I2 is parallel to the y-axis and is along Y-axis therefore, the angle between I2 and B1 is zero. The magnetic force F2 is given as F2 = B1I2L1 sin 0o = 0
Therefore, the force on O2 has current I1 zero.
Short Answers
4.17. A current-carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z, and z-x planes with their centres at the origin joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin.
Answer:
The vector sum of the magnetic field at the origin due to the quarter is given as

4.18. A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E, and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]-1.
Answer:
mv2/R = evB
eB/m = v/R = ꞷ
B = F/ev = [MA-1T-2] [ꞷ] = [eB/m]=[v/R] = [T-1]
4.19. An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in the plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
Answer:
The configuration of fields E and B are the spiral path.
4.20. Do magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law? Verify for two current elements
 located at the origin and
located at the origin and
 located at (0,R,0). Both carry current I.
located at (0,R,0). Both carry current I.
Answer:
The magnetic forces do not obey Newton’s third law if there is no current flowing in the conductor, which is placed parallel to each other.
4.21. A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit, as shown in the figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V, and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for a current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2, and R3 that have to be used.

Answer:
iG(G+R1) = 2 for 2V range
iG(G+R1+R2) = 20 for 20V range
iG(G+R1+R2+R3) = 200 for 200V range
Solving the above, we get
R1 = 1990 Ω
R2 = 18kΩ
R3 = 180 kΩ
4.22. A long straight wire carrying a current of 25 A rests on a table, as shown in the figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?

Answer:

The magnetic field produced by a long straight current-carrying wire is given as
B = μ0I/2πh
Magnetic force on the small conductor is F = BIl sin θ = BIl
F = mg = μ0I2l/2πh
h = 0.51 cm
Long Answers
4.23. A 100-turn rectangular coil ABCD is hung from one arm of a balance. A mass of 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil, and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?

Answer:
When t = 0, the external magnetic field is off.
Mgl = Wcoil l
0.5 gl = Wcoil l
Wcoil = 0.5 9.8 N
Let m be the mass which is added to regain the balance
When the magnetic field is switched is on,
Mgl + mgl = (ILC)l
m = 1 g
4.24. A rectangular conducting loop consists of two wires on two opposite sides of length l joined together by rods of length d. The wires are each of the same material but with cross-sections differing by a factor of 2. The thicker wire has a resistance R, and the rods are of low resistance, which in turn are connected to a constant voltage source Vo. The loop is placed in uniform a magnetic field B at 45o to its plane. Find τ, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop about an axis through the centres of rods.
Answer:

Force and torque on the first wire are given as
F1 = i1l B sin 90o = V0/2R lB
τ1= d/2√2
F1 = V0ldB/2√2 R
τ = 1/4√2 V0AB/R
4.25. An electron and a positron are released from (0, 0, 0) and (0, 0, 1.5R), respectively, in a uniform magnetic field
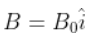 each with an equal momentum of magnitude p = eBR. Under what conditions on the direction of momentum will the orbits be non-intersecting circles?
each with an equal momentum of magnitude p = eBR. Under what conditions on the direction of momentum will the orbits be non-intersecting circles?
Answer:

When the centres are greater than 2R, then the circular orbits of the electron and positron shall not overlap.
Let d be the distance between Cp and Ce
Then d2 = 4R2 + 9/4R2 – 6R2 cosθ
As d is greater than 2R,
9/4 > 6 cos θ or cos θ < 3/8
4.26. A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current-carrying coil in the shape of i) an equilateral triangle of side a, ii) a square of sides a, and iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case.
Answer:
a) An equilateral triangle with sides a
No. of loops = 4
Area of the triangle A = √3/4 a2
Magnetic moment, m = Ia2√3

b) For a square with sides a
Area, A = a2
No.of loops = 3
Magnetic moment, m = 3Ia2

c) For a regular hexagon with sides a
Area, A = 6√3/4 a2
No.of loops = 2
Magnetic moment, m = 3√3a2I

4.27. Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with the centre at the origin. Consider the line integral
 taken along the z-axis.
taken along the z-axis.
a) show that
 monotonically increases with L
monotonically increases with L
b) use an appropriate Amperian loop to that
 where I is the current in the wire
where I is the current in the wire
c) verify directly the above result
d) suppose we replace the circular coil with a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about

Answer:

a) Magnetic field due to a circular current-carrying loop is given as

It is a monotonically increasing function of L
b) The Amperian loop is given as

c) The magnetic field at the axis of the circular coil is given as μ0I
d) When a circular coil is replaced with a square coil, it is given as

4.28. A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit shown in the figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA, and 1 A using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for a current of 1 mA. Find S1, S2, and S3 that have to be used.

Answer:

I1 is measured as = 10 mA = IGG = (I1 – IG)(S1 + S2 + S3)
I2 is measured as = 100 mA = IG(G+S1)=(I2-IG)(S2-S3)
I3 is measured as = 1 A = IG(G+S1+S2)=(I3-IG)(S3)
S1 = 1 Ω
S2 = 0.1 Ω
S3 = 0.01 Ω
4.29. Five long wires A, B, C, D, and E, each carrying I are arranged to form the edges of a pentagonal prism, as shown in the figure. Each carries current out of the plane of the paper.
a) what will be magnetic induction at a point on the axis O> Axis is at a distance R from each wire
b) what will be the field if the current in one of the wires is switched off
c) what if the current in one of the wires A is reversed

Answer:
a)

The magnetic induction at a point on the axis will be 0, which is represented by R as A, B, C, D, and E is perpendicular to the plane of paper at the given locations.
b)

When the current in one of the wires is switched off, the field μ0/2π i/R will be perpendicular to AO towards left.
c)

If the current is reversed, then the total magnetic field induction at O is μ0/4πR 2I/R
Moving charges and magnetism helps establish a relationship between magnetism and electricity. These moving charges are responsible for the effect of magnetism; however, a charged particle without acceleration can produce an electrical and magnetic field.
Some of the concepts that are introduced in this chapter are listed below:
- Ampere’s Circuital Law
- The Solenoid and the Toroid
- Moving Coil Galvanometer
- Magnetic Force
- Magnetic Field
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 |
To learn more about NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4, Moving Charges and Magnetism, download the PDFs given above.
To access the NCERT Exemplar solutions, designed according to the latest Class 12 CBSE Physics Syllabus (2023-2024), visit BYJU’S website. Also, download BYJU’S – The Learning App for a comprehensive and interactive learning experience as well as to score good marks in the board examination.














Comments