NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 – Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs are very important for students in order to develop logical and mental abilities. Exercise-wise solutions for all the questions are prepared by subject experts as per the latest CBSE Class 8 Syllabus. Class 8 Mathematics NCERT Solutions for the year 2023-24 are valuable for students in their assignments and preparation of their exams.
Class 7 NCERT Maths Solutions are given here for the students to solve regularly and practise so that they can score high marks in the exams. Maths, as a subject, deals with a lot of complex formulas and theorems. Finding the correct answers to the questions asked in the board exams can be exhausting and tricky. Despite this, any student who is extremely motivated and highly proficient in the subject will be able to crack the exams and score high very easily.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs
Access Answers to NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs
Exercise 15.1 PageNo: 236
1. The following graph shows the temperature of a patient in a hospital, recorded every hour.
(a) What was the patient’s temperature at 1 p.m.?
(b) When was the patient’s temperature 38.5° C?

(c) The patient’s temperature was the same two times during the period given. What were these two times?
(d) What was the temperature at 1.30 p.m.? How did you arrive at your answer?
(e) During which periods did the patient’s temperature show an upward trend?
Solution:
(a) The patient’s temperature was 36.5oC at 1 p.m.
(b) The patient’s temperature was 38.5oC at 12 noon.
(c) The patient’s temperature was same at 1 p.m. and 2p.m
(d) The temperature at 1.30 p.m. is 36.5oC.
The point between 1p.m.and 2 p.m., the x-axis is equidistant from the two points showing 1 p.m. and 2 p.m. So, it represents 1.30 p.m. Similarly, the point on the y-axis, between 360 C and 370 C, represents 36.50 C.
(e) The patient’s temperature showed an upward trend from 9 a.m. to 11 a.m. and from 2 p.m. to 3 p.m.
2. The following line graph shows the yearly sales figures for a manufacturing company.

(a) What were the sales in (i) 2002 (ii) 2006?
(b) What were the sales in (i) 2003 (ii) 2005?
(c) Compute the difference between the sales in 2002 and 2006.
(d) In which year was there the greatest difference between the sales as compared to the previous year?
Solution:
(a) The sales in
(i) 2002 was Rs. 4 crores and (ii) 2006 was Rs. 8 crores
(b) The sales in
(i) 2003 was Rs. 7 crores and (ii) 2005 was Rs. 10 crores.
(c) The difference of sales in 2002 and 2006 = Rs. 8 crores–Rs. 4 crores= Rs. 4 crores
(d) In the year 2005, there was the greatest difference between the sales, and compared to its previous year, which is (Rs. 10 crores –Rs. 6 crores) = Rs. 4 crores
3. For an experiment in Botany, two different plants, plant A and plant B, were grown under similar laboratory conditions. Their heights were measured at the end of each week for 3 weeks. The results are shown by the following graph.

(a) How high was Plant A after (i) 2 weeks (ii) 3 weeks?
(b) How high was Plant B after (i) 2 weeks (ii) 3 weeks?
(c) How much did Plant A grow during the 3rd week?
(d) How much did Plant B grow from the end of the 2nd week to the end of the 3rd week?
(e) During which week did Plant A grow most?
(f) During which week did Plant B grow least?
(g) Were the two plants of the same height during any week shown here? Specify.
Solution:
(a)
(i) Plant A was 7 cm high after 2 weeks.
(ii) After 3 weeks, it was 9 cm high.
(b)
(i) Plant B was also 7 cm high after 2 weeks.
(ii) After 3 weeks, it was 10 cm high.
(c) Plant A grew=9 cm–7 cm = 2 cm during 3rd week
(d) Plant B grew from end of the 2nd week to the end of the 3rdweek = 10cm–7cm= 3cm
(e) Plant A grew the highest during the second week.
(f) Plant B grew the least during first week.
(g) Yes. At the end of the second week, plants A and B were of the same height, which is 7 cm.
4. The following graph shows the temperature forecast and the actual temperature for each day of the week.
(a) On which days was the forecast temperature the same as the actual temperature?
(b) What was the maximum forecast temperature during the week?
(c) What was the minimum actual temperature during the week?
(d) On which day did the actual temperature differ the most from the forecast temperature?

Solution:
(a) On Tuesday, Friday and Sunday, the forecast temperature was same as the actual temperature.
(b) The maximum forecast temperature was 35oC.
(c) The minimum actual temperature was 15oC.
(d) The actual temperature differed the most from the forecast temperature on Thursday.
5. Use the tables below to draw linear graphs
(a) The number of days a hillside city received snow in different years.

(b) Population (in thousands) of men and women in a village in different years.

Solution:
(a) Consider “Years” along the x-axis and “Days” along the y-axis. Using the given information, the linear graph will look like this:

(b) Consider “Years” along the x-axis and “No. of Men and No. of Women” along the y-axis (2 graphs). Using the given information, the linear graph will look like this:

6. A courier person cycles from a town to a neighboring suburban area to deliver a parcel to a merchant. His distance from the town at different times is shown by the following graph.
(a) What is the scale taken for the time axis?
(b) How much time did the person take for the travel?
(c) How far is the place of the merchant from the town?
(d) Did the person stop on his way? Explain.
(e) During which period did he ride fastest?

Solution:
(a) 4 units = 1 hour
(b) The person took 3 ½ hours for the travel.
(c) It was 22 km far from the town.
(d) Yes, this has been indicated by the horizontal part of the graph. He stayed from 10 a.m. to 10.30 a.m.
(e) He rides the fastest between 8 a.m. and 9 a.m.
7. Can there be a time-temperature graph as follows? Justify your answer.

Solution:
(i) It is a time-temperature graph. It is showing the increase in temperature as time increases.
(ii) It is a time-temperature graph. It is showing the decrease in temperature as time increases.
(iii) The graph figure (iii) is not possible since the temperature is increasing very rapidly, which is not possible.
(iv) It is a time-temperature graph. It is showing constant temperature.
Exercise 15.2 PageNo: 243
1. Plot the following points on a graph sheet. Verify if they lie on a line
(a) A(4,0), B(4, 2),C(4,6), D(4, 2.5)
(b) P(1, 1), Q(2, 2), R(3,3), S(4, 4)
(c) K(2, 3), L(5, 3), M(5,5), N(2, 5)
Solution:
Plot all the points on the graph.

(a) All points, A, B, C and D, lie on a vertical line.
(b) P,Q, R and S points also make a line. It verifies that these points lie on a line.
(c) Points K, L, M and N. These points do not lie in a straight line.
2. Draw the line passing through (2,3)and(3,2). Find the coordinates of the points at which this line meets the x-axis and y-axis.
Solution:
Graph for the line passes through points (2, 3) and (3, 2) is

The coordinates of the points at which this line meets the x-axis at (5, 0) and Y axis at (0,5).
3. Write the coordinates of the vertices of each of these adjoining figures.

Solution:
We can observe three figures named as, OABC, PQRS and LMK.
Vertices of figure OABC
O (0, 0), A (2, 0), B (2, 3) and C (0, 3)
Vertices of figure PQRS
P (4, 3), Q (6, 1), R (6, 5) and S (4, 7)
Vertices of figure LMK
L (7, 7), M(10, 8) and K(10,5)
4. State whether True or False. Correct those that are False.
(i) A point whose x-coordinate is zero and y-coordinate is non-zero will lie on the y-axis.
(ii) A point whose y-coordinate is zero and x-coordinate is 5 will lie on the y-axis.
(iii) The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
Solution:
i) True.
ii) False; it will lie on the x-axis.
(iii) True.
Exercise 15.3 Page No: 247
1. Draw the graphs for the following tables of values, with suitable scales on the axes.
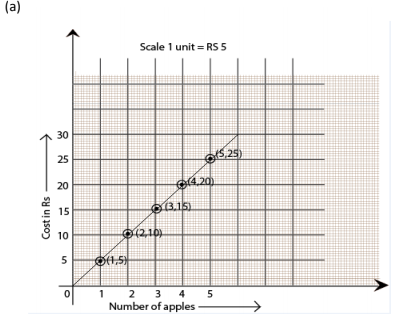
(a) Cost of apples.

(b) Distance travelled by car.

(i) How much distance did the car cover during the period 7.30 a.m. to 8 a.m.?
(ii) What was the time when the car had covered a distance of 100 km since its start?
(c) Interest on deposits for a year.
(i) Does the graph pass through the origin?
(ii) Use the graph to find the interest on Rs 2500 for a year.
(iii) To get an interest of Rs. 280 per year, how much money should be deposited?
Solution:
Mark “number of apples” on the x-axis and “cost” on the y-axis. The graph is
(b) Represent the “time” on the x-axis and “distance” on the y-axis.
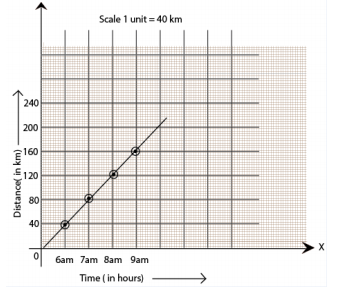
(i) The car covered a distance of 20 km.
(ii) It was 7.30 am, when it covered a distance of 100 km.
(c) Represent “Deposit” on the y-axis and “simple interest” on the x-axis.
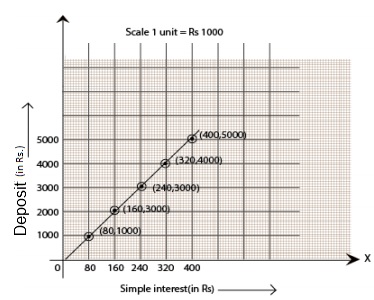
(i) Yes, the graph passes through the origin.
(ii) Interest on Rs. 2500 is Rs. 200 for a year.
(iii) Rs. 3500 should be deposited for the interest of Rs. 280.
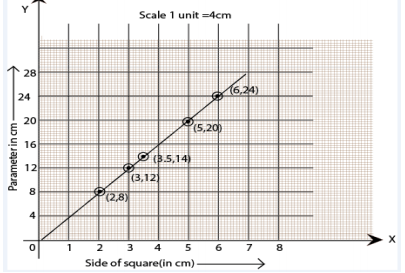
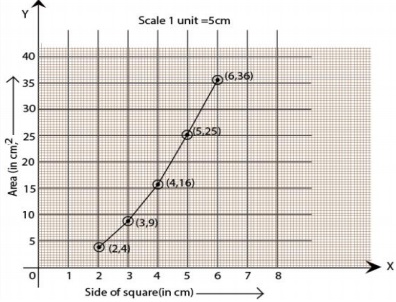
2. Draw a graph for the following.
Solution:
(i) Yes, it is a linear graph.
(ii) No, it is not a linear graph because the graph does not provide a straight line.
| Also Access |
| CBSE Notes for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs Summary
Class 8 NCERT exercise-wise questions and answers will help students get step-by-step explanations to every question specified in the textbooks. Some of the important topics introduced in Class 8 NCERT Solutions of Maths are a graphical presentation of data using a bar graph, pie graph, histogram, line graph, and students will also study about Linear Graphs and some of the basic applications of graphs.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Exercises
Get a detailed solution for all the questions from the below-given links.
Exercise 15.1 Solutions: 7 Questions (Long answer type)
Exercise 15.2 Solutions: 4 Questions (Short answer type)
Exercise 15.3 Solutions: 2 Questions (Short answer type)
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs
NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 deal primarily with the representation of data using different graph diagrams. In this section, students will learn mainly about, Introduction to Graphs, A Bar graph, A Pie graph (or a circle graph), A histogram, A line graph, Linear Graphs, Location of a point, Coordinates and Some Applications.
The main topics and subtopics of NCERT Chapter 15 Class 8 Maths are given below.
| Exercise | Topics/Subtopics |
| 15.1 | Introduction to Graphs |
| 15.1.1 | A Bar Graphs |
| 15.1.2 | A Pie Graphs or a Circle Graph |
| 15.1.3 | A Histogram |
| 15.1.4 | A Line Graphs |
| 15.2 | Linear Graphs |
| 15.2.1 | Location of a Point |
| 15.2.2 | Coordinates |
| 15.3 | Some Applications |
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 15 Introduction to Graphs
- The subject experts have solved each question of NCERT exercise meticulously with the help of diagrams.
- Precise and easy language used.
- Step-by-step explanations to every question specified in the textbooks.
- These NCERT solutions are valuable as they help students in their homework and competitive exams.
Disclaimer:
Dropped Topics – 15.1.1 A bar graph, 15.1.2 A Pie graph, 15.1.3 A histogram, 15.2 Linear Graphs, 15.2.1 Location of a point and 15.2.2 Coordinates.















Comments