The solutions to all the questions in the Class 8 Maths NCERT textbook are present in the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths. The subject experts at BYJU’S have solved each question of NCERT exercises carefully to help the students to solve any question from the NCERT textbook. NCERT Class 8 Exercise 3.4 is based on the different types of quadrilaterals. Students can download the NCERT Solutions of Class 8 Mathematics to understand the concept in an effective way.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 – Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 – Understanding Quadrilaterals
Exercise 3.1 Solutions 7 Questions (1 Long Answer Question, 6 Short Answer Questions)
Exercise 3.2 Solutions 6 Questions (6 Short Answer Questions)
Exercise 3.3 Solutions 12 Questions (6 Long Answer Questions, 6 Short Answer Questions)
Access Answers to Maths NCERT Class 8 Chapter 3 – Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4 Page Number 55
1. State whether True or False.
(a) All rectangles are squares.
(b) All rhombuses are parallelograms.
(c) All squares are rhombuses and also rectangles.
(d) All squares are not parallelograms.
(e) All kites are rhombuses.
(f) All rhombuses are kites.
(g) All parallelograms are trapeziums.
(h) All squares are trapeziums.
Solution:
(a) False
Because all squares are rectangles, but all rectangles are not squares.
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
Because all squares are parallelograms, as opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles are equal.
(e) False
Because, for example, the length of the sides of a kite is not the same length.
(f) True
(g) True
(h) True
2. Identify all the quadrilaterals that have
(a) four sides of equal length. (b) four right angles.
Solution:
(a) Rhombus and square have all four sides of equal length.
(b) Square and rectangle have four right angles.
3. Explain how a square is
(i) a quadrilateral. (ii) a parallelogram. (iii) a rhombus. (iv) a rectangle.
Solution:
(i) A square is a quadrilateral because it has four sides.
(ii) A square is a parallelogram because its opposite sides are parallel, and opposite angles are equal.
(iii) A square is a rhombus because all four sides are of equal length, and diagonals bisect at right angles.
(iv) A square is a rectangle because each interior angle of the square is 90°.
4. Name the quadrilaterals whose diagonals
(i) bisect each other. (ii) are perpendicular bisectors of each other. (iii) are equal.
Solution:
(i) Parallelogram, Rhombus, Square and Rectangle
(ii) Rhombus and Square
(iii) Rectangle and Square
5. Explain why a rectangle is a convex quadrilateral.
Solution:
A rectangle is a convex quadrilateral because both of its diagonals lie inside the rectangle.
6. ABC is a right-angled triangle, and O is the mid-point of the side opposite to the right angle. Explain why O is equidistant from A, B and C. (The dotted lines are drawn additionally to help you.)
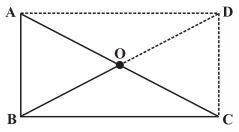
Solution:
AD and DC are drawn so that AD || BC and AB || DC.
AD = BC and AB = DC
ABCD is a rectangle, as opposite sides are equal and parallel to each other, and all the
interior angles are 90°.
In a rectangle, diagonals are of equal length and also bisect each other.
Hence, AO = OC = BO = OD
Thus, O is equidistant from A, B and C.
Exercise 3.4 of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 – Understanding Quadrilaterals is based on the following topics:
- Some special parallelograms
- Rhombus
- A rectangle
- A square
Also, explore –



Byjus explains very good.
Very nice app