According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 13.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Notes
Introduction
Environment refers to the surrounding of an organism where it thrives. It constitutes both living and non-living things, i.e. physical, chemical and biotic factors. Here, in this chapter, we will learn about various components of the environment, their interactions and how our activities affect the environment.
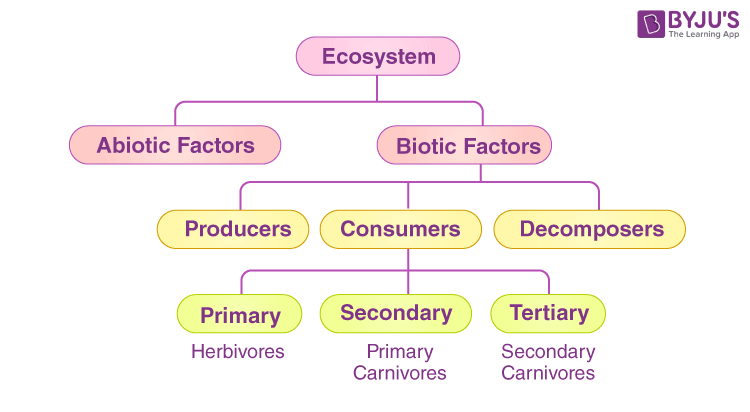
Ecosystem
The ecosystem comprises all the biotic and abiotic factors interacting with one another in a given area. Biotic components include all living organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and humans, etc., and abiotic components include sunlight, temperature, air, wind, rainfall, soil and minerals, etc. E.g. pond ecosystem, grassland ecosystem, etc.
Watch the video below to learn about our environment and its components
Mode of Nutrition in Animals and Plants
Autotrophic and Heterotrophic are the two modes of nutrition in living organisms. Plants and some bacteria are autotrophic as they make their own food. Animals, fungi and some bacteria are heterotrophic as they derive their food from other organisms.
Read more: Difference between Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Saprophytes and Decomposers
Saprophytes feed on dead and decaying material, e.g. fungi and microorganisms. They absorb nutrients from dead and decaying plants and animal parts. Decomposers break down the organic matter or waste material and release nutrients into the soil. For example, bacteria, worms, slugs, and snails. They are considered extremely important in soil biology. They break down the complex organic matter into simpler substances that are taken up by the plants for various metabolic activities.
Read more: Saprophytes
Abiotic Components
Non-living chemical and physical components of the environment like the soil, air, water, temperature, etc.
Biotic Components
Living organisms of the environment like plants, animals, microbes and fungi.
Read more: Biotic and Abiotic
Trophic Levels
It refers to the various levels in a food web as per the flow of energy. The different trophic levels are –
- Producers (T1)
- Primary consumers (herbivores-T2)
- Secondary consumers (primary carnivores -T2)
- Tertiary consumers(Sec carnivores -T3)
- Quaternary consumers (Ter. carnivores T4)
- Decomposers
Also see: What do you understand by trophic level?
Pyramid of Trophic Levels
- Is a graphical representation.
- Can be the pyramid of numbers, the pyramid of biomass or the pyramid of energy.
- Start with producers.
a) Pyramid of numbers: gives the number of organisms present at each trophic level.
It can be upright or inverted.
b) Pyramid of biomass: gives the biomass of each trophic level and could be upright or inverted.
c) Pyramid of energy: is always upright as it shows the flow of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level.
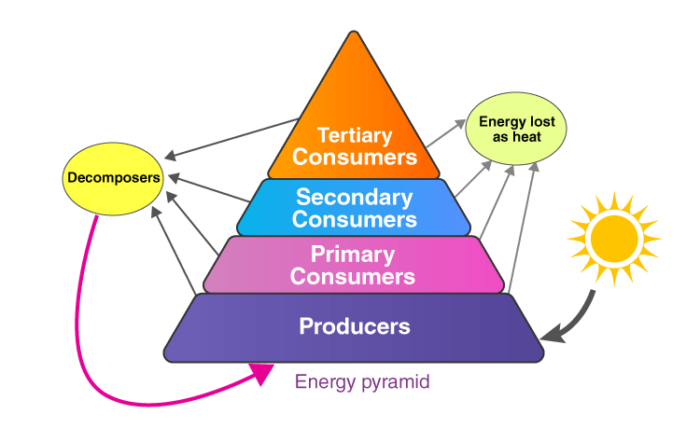
To know more about different types of ecological pyramids, visit here.
Law of Conservation of Energy
- Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it transforms from one form to another.
- In biological systems, it gets passed from one organism to another across trophic levels.
To know more about the Law of conservation of energy, visit here.
Energy Flow
- Transfer of energy from one trophic level to another depicting its direction and amount.
- Represented by the pyramid of energy.
- In any food chain, only 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to another.
To know more about Energy Flow in Ecosystem, visit here.
Food Chain
A series of organisms, each dependent on the next as a source of food.
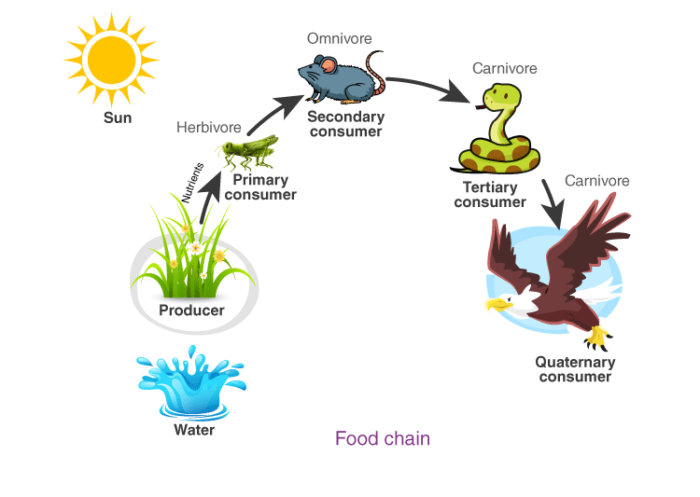
To know more about Food Chain, visit here.
Food Web
- Is formed by interconnections of different food chains.
- Is a graphical representation of ‘Who eats Whom’ in an ecosystem.
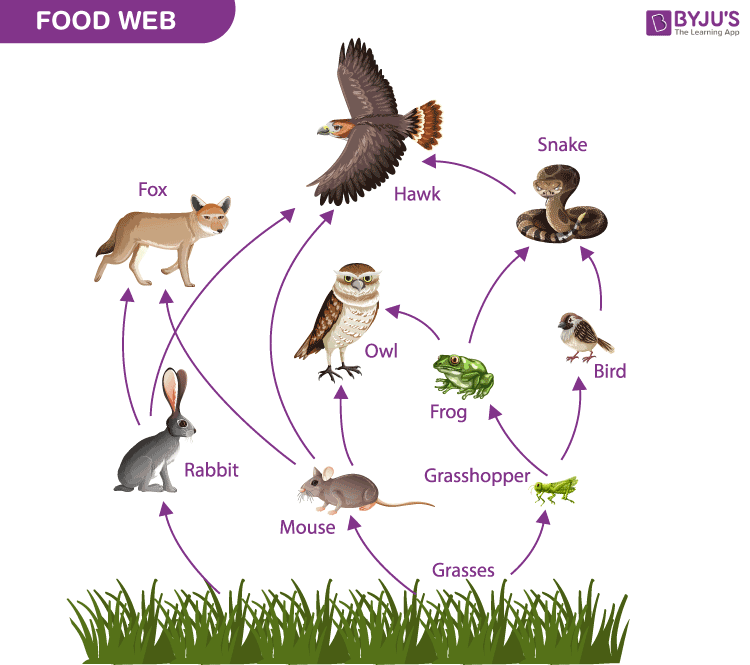
To know more about Food Web, visit here.
Characteristics of Ecosystem
- Includes the summary of trophic levels.
- Their energy flow and pyramids.
Environment
- Includes all living and nonliving things.
- Unlike ecosystems, there need not be any necessary interaction between them.
Also see: Our Environment
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials (pollutants) into the environment. Pollution can be due to natural causes, such as volcanic eruptions, forest fires, etc. or due to human activities, such as carbon emission, industrial runoff, etc.
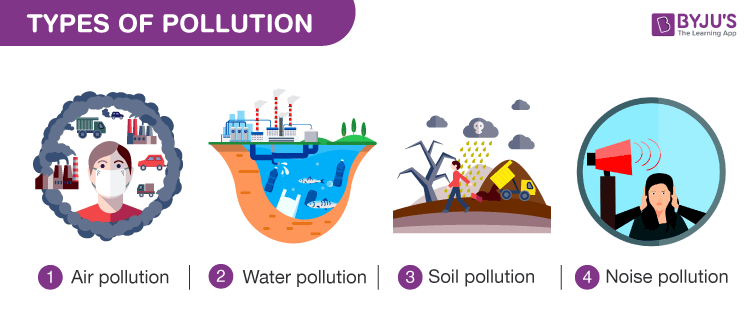
Know more: Types of Pollution
Air Pollution
Introduction of pollutants, organic molecules, or other hazardous substances into the earth’s atmosphere.
Sources:
a) Natural – forest fire, dust storms, and volcanic activity
b) Man-made – power plants, homes, industries, oil refineries, and transportation
To know more about Air Pollution, visit here.
Ozone Layer Depletion
The ozone layer protects the Earth from the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. CFCs released into the atmosphere react chemically with ozone molecules and deplete the layer.
For more information on Ozone Layer Depletion, watch the video below

Know more: Ozone Layer Depletion
Garbage Management
- Involves all the activities and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal.
- Ensures environmental best practices are followed along with proper monitoring and regulation.
Steps involved:
1. Segregation of waste
2. Collection
3. Transport
4. Treatment
5. Processing & Recycling
6. Disposal

For more information on Waste Disposal, watch the video below

Read more: Solid Waste Management
Biodegradable Waste
- Waste is derived from plants or animals.
- Decomposed into the soil by a natural agent such as weather, water, air, heat, micro-organisms, etc.
Watch the video below to know more about Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable waste

Biodegradation
Decomposition of garbage or waste material by living organisms or biological processes.
To know more about Different Types of Pollution, visit here.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 15 Our Environment
What are the different types of landforms present in our environment?
Mountains, hills, plateaus and plains are the four major types of landforms which are majorly present in our environment.
What is lithosphere’?
The lithosphere is the rocky outer part of the Earth. It is made up of the brittle crust and the top part of the upper mantle.
Where is the biosphere present?
The biosphere makes up the portion of the Earth where life exists.
Also Check:
Comments