NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 14 – Free PDF Download
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy provide students with necessary insights into the concepts covered in the chapter, Sources of Energy. Solving the solutions provided in this NCERT Exemplar is very crucial as it helps you get familiar with the types of questions that can be asked on the topic in the board exam. Having proper knowledge of the questions of varying difficulty will boost your confidence, and thus attempt the examination without fear. This chapter sheds light on important topics like the non-conventional sources of energy, their importance, the difference between conventional and non-conventional energy resources and their usage, and types of energy sources and their utilisation.
Nowadays, we hear so much about the energy crisis and the need for the conservation of sources of energy. Thus, Chapter 14 of NCERT Exemplar is an important chapter for students; here, they will study the good sources of energy and their conservation methods. They will also learn about conventional or non-conventional sources of energy, renewable and non-renewable sources of energy as well as learn about thermal power plants, hydroelectric power plants, and biogas plants. Take a closer look at NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 14 by downloading the solutions in PDF from the link below.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 – Sources of Energy
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 – Sources of Energy
Multiple-choice Questions
1. Which of the following is a non-renewable source of energy?
(a) Wood
(b) Sun
(c) Fossil fuels
(d) Wind
Soln:
The answer is (b) Sun
2. Acid rain happens because
(a) sun leads to the heating of the upper layer of the atmosphere
(b) burning of fossil fuels releases oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur in the atmosphere
(c) electrical charges are produced due to friction among clouds
(d) earth atmosphere contains acids
Soln:
The answer is (b) burning of fossil fuels releases oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur in the atmosphere
Explanation:
Acid rain happens when rainwater mixes with oxides of Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulphur in the atmosphere.
3. Fuel used in thermal power plants is
(a) water
(b) uranium
(c) biomass
(d) fossil fuels
Soln:
The answer is (d) fossil fuels
Explanation:
Coal is the major fossil fuel used in thermal power plants. Along with coal, natural gas and petroleum are also used.
4. In a hydropower plant
(a) Potential energy possessed by stored water is converted into electricity
(b) Kinetic energy possessed by stored water is converted into potential energy
(c) Electricity is extracted from water
(d) Water is converted into steam to produce electricity
Soln:
Answer is (a) Potential energy possessed by stored water is converted into electricity.
Explanation:
Water stored in dams possesses potential energy. When it is released, it possesses potential energy, which is used to turn the turbines. Turbines produce electricity.
5. Which is the ultimate source of energy?
(a) Water
(b) Sun
(c) Uranium
(d) Fossil fuels
Soln:
The answer is (b) Sun
Explanation:
Plants produce food by using solar energy. Fossil fuels are produced from dead plants. Hence Sunlight is the source of all energy, either directly or indirectly.
6. Which one of the following forms of energy leads to the least environmental pollution in the process of its harnessing and utilisation?
(a) Nuclear energy
(b) Thermal energy
(c) Solar energy
(d) Geothermal energy
Soln:
Answer is (c) Solar energy
Explanation:
In nuclear energy, metals like uranium are used, which releases harmful rays than can affect living organisms. In Thermal energy, coal is used, which releases Sulphur and Carbon-di-oxide and causes air pollution. In the case of geothermal energy, the energy is absorbed by the pressure by the heat from the core, which can sometimes be extremely hot and dangerous.
7. Ocean thermal energy is due to
(a) energy stored by waves in the ocean
(b) temperature difference at different levels in the ocean
(c) pressure difference at different levels in the ocean
(d) tides arising out in the ocean
Soln:
Answer is (b) temperature difference at different levels in the ocean
Explanation:
Energy from the surface is used to boil volatile liquid. Vapours from these are utilized to turn the turbine.
8. The major problem in harnessing nuclear energy is how to
(a) split nuclei?
(b) sustain the reaction?
(c) dispose of spent fuel safely?
(d) convert nuclear energy into electrical energy?
Soln:
The answer is (c) dispose off spent fuel safely.
Explanation:
Nuclear plants produce highly radioactive material. This is released to the environment they pose a major threat to living organisms. Hence, disposing of the spent fuel safely is a major problem in harnessing nuclear energy.
9. Which part of the solar cooker is responsible for the greenhouse effect?
(a) Coating with black colour inside the box
(b) Mirror
(c) Glass sheet
(d) Outer cover of the solar cooker
Soln:
The answer is (c) Glass sheet
Explanation:
The greenhouse effect is due to the trapping of heat by the atmosphere. Heat is produced is due to the presence of greenhouse gases like CO2, SO2. In Solar cooker, the same thing happens. Solar energy trapped is reflected by the glass sheet, which makes the food cook.
10. The main constituent of biogas is
(a) methane
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) hydrogen
(d) hydrogen sulphide
Soln:
The answer is (a) methane
Explanation:
Methane gas is the main product of biogas. Around 70% of the gas produced is methane, and the remaining will be ammonia, carbon dioxide.
11. The power generated in a windmill
(a) is more in the rainy season since damp air would mean more air mass hitting the blades
(b) depends on the height of the tower
(c) depends on wind velocity
(d) can be increased by planting tall trees close to the tower
Soln:
The answer is (c) depends on wind velocity
Explanation:
High wind velocity will turn the turbine with at higher speed. This will increase the production of electricity.
12. Choose the correct statement
(a) Sun can be taken as an inexhaustible source of energy
(b) There is infinite storage of fossil fuel inside the earth
(c) Hydro and wind energy plants are non-polluting sources of energy
(d) Waste from a nuclear power plant can be easily disposed off
Soln:
The answer is (a) Sun can be taken as an inexhaustible source of energy
Explanation:
Fossil fuel is an exhaustible source. Hydro and wind energy plants can have large environmental impacts by changing the environment and affecting land use, homes, and natural habitats in the dam area. Disposing of waste from a nuclear power plant is the major issue faced by a nuclear plant.
13. In a hydroelectric power plant, more electrical power can be generated if waterfalls from a greater height because
(a) its temperature increases
(b) larger amount of potential energy is converted into kinetic energy
(c) the electricity content of water increases with height
(d) more water molecules dissociate into ions
Soln:
The answer is (b) larger amount of potential energy is converted into kinetic energy
14. Choose the incorrect statement regarding wind power
(a) It is expected to harness wind power to minimum in open space
(b) The potential energy content of wind blowing at high altitudes is the source of wind power
(c) Wind hitting at the blades of a windmill causes them to rotate The rotation thus achieved can be utilised further
(d) One possible method of utilising the energy of rotational motion of the blades of a windmill is to run the turbine of an electric generator
Soln:
The answer is (b) The potential energy content of wind blowing at high altitudes is the source of wind power.
Explanation:
Wind power runs by kinetic energy of the wind. Hence statement b) is wrong.
15. Choose the incorrect statement
(a) We are encouraged to plant more trees so as to ensure a clean environment and also provide bio-mass fuel
(b) Gobar-gas is produced when crops, vegetable wastes etc., decompose in the absence of oxygen
(c) The main ingredient of bio-gas is ethane and it gives a lot of smoke and also produces a lot of residual ash
(d) Biomass is a renewable source of energy
Soln:
The answer is (c) The main ingredient of bio-gas is ethane and it gives a lot of smoke and also produces a lot of residual ash
Explanation:
Main product of a biogas is methane. It burns with less smoke and does not produce residual ash.
Short Answer Questions
16. Why is there a need to harness non-conventional sources of energy? Give two main reasons.
Soln:
The following are the reason for the need to harness non-conventional sources of energy.
- Conventional sources are an exhaustible source of energy and they will get exhausted in the near future.
- Non-conventional source of energy did not lead to environmental pollution.
17. Write two different ways of harnessing energy from the ocean.
Soln:
- Tidal energy
- Ocean Thermal energy
18. What steps would you suggest to minimise environmental pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels?
Soln:
Steps to minimise environmental pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels are as follows.
- Use non-conventional sources of energy such as hydrothermal and wind energy.
- Afforestation should be adopted to control air pollution
- Smokeless appliances should be used to reduce the pollution
19. What is the role of a plane mirror and a glass sheet in a solar cooker?
Soln:
Plane mirror reflects the sunlight, thereby increasing the intensity of solar energy. Glass sheet prevents heat to escape from solar cooker.
20. Mention three advantages of a solar cell?
Soln:
Advantages of a solar cell are as follows.
- Solar cells are the source of renewable energy
- Solar cells do not produce pollution
- Solar cells need minimum maintenance
21. What is biomass? What can be done to obtain bio-energy using biomass?
Soln:
Fuel obtained from organic material is called biomass. Following are the methods to obtain bio-energy using biomass.
- Using firewood as a fuel
- Preparing cow dung cake and using them as heating source
- Gobar gas can be produced
- Electricity can be produced by using a gobar.
22. What are the limitations in obtaining energy from wind?
Soln:
Limitations in obtaining energy from wind.
- There will not be continuous and consistent production
- Area required to install wind power mill is large.
- Minimum speed of the wind should be 15 km/hour.
Long Answer Questions
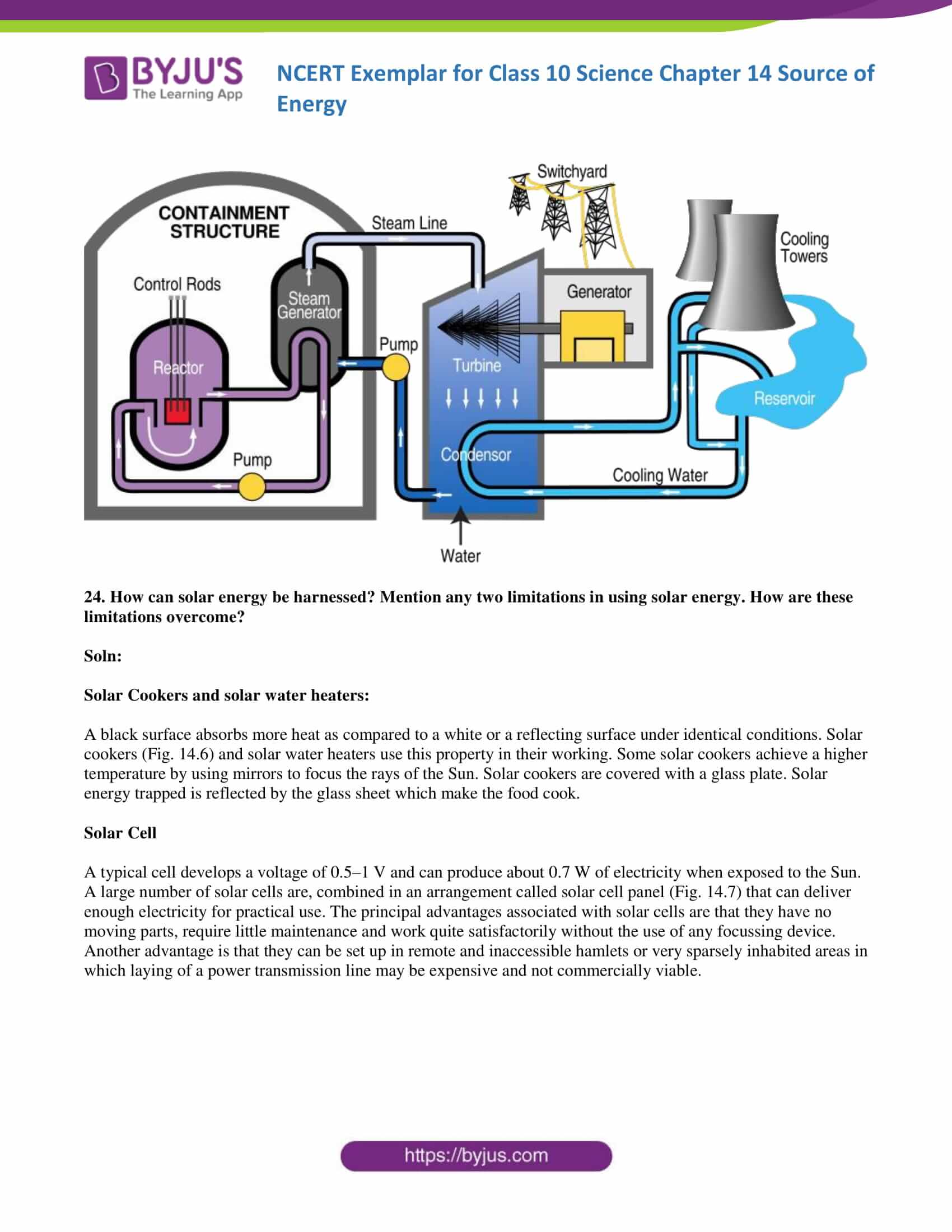
23. What is the process used to harness nuclear energy these days? Explain it briefly.
Soln:
Nuclear energy is harnessed in nuclear power plants. It has a nuclear reactor, boiler and turbine.
- The nuclear reactor is the place where nuclear fission is carded out. Nuclear fission produces a huge amount of energy.
- Energy produced during nuclear fission is utilized to boil water, so that steam can be generated.
- Steam is utilized to turn the turbines to produce electricity.

24. How can solar energy be harnessed? Mention any two limitations in using solar energy. How are these limitations overcome?
Soln:
Solar Cookers and solar water heaters:
A black surface absorbs more heat as compared to a white or reflecting surface under identical conditions. Solar cookers (Fig. 14.6) and solar water heaters use this property in their work. Some solar cookers achieve a higher temperature by using mirrors to focus the rays of the Sun. Solar cookers are covered with a glass plate. Solar energy trapped is reflected by the glass sheet, which makes the food cook.
Solar Cell
A typical cell develops a voltage of 0.5–1 V and can produce about 0.7 W of electricity when exposed to the Sun. A large number of solar cells are, combined in an arrangement called solar cell panel (Fig. 14.7) that can deliver enough electricity for practical use. The principal advantages associated with solar cells are that they have no moving parts, require little maintenance and work quite satisfactorily without the use of any focussing device. Another advantage is that they can be set up in remote and inaccessible hamlets or very sparsely inhabited areas in which laying of a power transmission line may be expensive and not commercially viable.
25. Make a list of conventional and non-conventional sources of energy. Give a brief description of harnessing one nonconventional source of energy.
Soln:
Conventional sources of energy are coal, petroleum, firewood and tidal energy.
Non-conventional sources are Solar energy, nuclear energy, Biogas, Tidal energy, Ocean thermal energy, wave energy etc.
Methods to harness Non-conventional sources of energy.
Solar Energy can be harnessed by using solar cookers, solar water heaters, solar cells and solar panels.
Nuclear power can be converted to electric energy with the help of nuclear reactors.
The water at the surface of the sea or ocean is heated by the Sun, while the water in deeper sections is relatively cold. This difference in temperature is exploited to obtain energy in ocean-thermal-energy conversion plants.
The kinetic energy possessed by huge waves near the seashore can be trapped in a similar manner to generate electricity. The waves are generated by strong winds blowing across the sea. Wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong.
26. Why is there a need for harnessing non-conventional sources of energy? How can energy be harnessed from the sea in different ways?
Soln:
The following are the reasons for the need to harness non-conventional sources of energy.
- Conventional sources are an exhaustible source of energy and they will get exhausted in the near future.
- Non-conventional source of energy did not lead to environmental pollution.
Energy can be harnessed from the sea in the following ways
Tidal energy:
Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam across a narrow opening to the sea. A turbine fixed at the opening of the dam converts tidal energy to electricity. As you can guess, the locations where such dams can be built are limited.
Wave energy:
The kinetic energy possessed by huge waves near the seashore can be trapped in a similar manner to generate electricity. The waves are generated by strong winds blowing across the sea. Wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong.
Ocean Thermal Energy
The water at the surface of the sea or ocean is heated by the Sun, while the water in deeper sections is relatively cold. This difference in temperature is exploited to obtain energy in ocean-thermal-energy conversion plants.
27. What are the environmental consequences of using fossil fuels? Suggest the steps to minimise the pollution caused by various sources of energy, including non-conventional sources of energy.
Soln:
Following are the consequences of using fossil fuels.
- Global warming will result due to the increase in the level of Carbon-di-oxide,
- Sulphur oxides cause acid rain
- Burning of fossil fuels will result in the accumulation of smog in big cities which will result in decreased visibility
- Air pollution leads to health hazards to humans and animals.
Steps to minimise the pollution caused by various sources of energy, including non-conventional sources of energy.
- Use of public transport
- Use of vehicles like electric bikes and bi-cycle that can reduce air pollution
- Adopting 3R’s policy- reduce, reuse and recycle.
- Afforestation
28. Energy from various sources is considered to have been derived from the sun. Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Soln:
Energy from various sources is considered to have been derived from the sun. The following points can justify the statement.
Energy from fossil fuels is indirectly harnessed from sunlight because. Plants trap sunlight to produce food which ultimately makes biomass. Biomass gets converted to fossil fuels.
- Biomass will be helping in obtaining wood and gobar gas.
- Water on the earth gets circulated because of kinetic energy possessed by the sun.
- Waves and oceans are formed due to the heating of water. Hence sun is indirectly responsible for harnessing Tidal, Wave and Geothermal energy.
29. What is biomass? Explain the principle and working of a biogas plant using a labelled schematic diagram.
Soln:
Sources of fuel obtained from organic material is called as biomass.
Cow dung, various plant materials like the residue after harvesting the crops, vegetable waste and sewage are decomposed in the absence of oxygen to give biogas.
The plant has a dome-like structure built with bricks. A slurry of cow dung and water is made in the mixing tank from where it is fed into the digester. The digester is a sealed chamber in which there is no oxygen. Anaerobic micro-organisms that do not require oxygen decompose or break down complex compounds of the cow-dung slurry. It takes a few days for the decomposition process to be complete and generate gases like methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide. The bio-gas is stored in the gas tank above the digester from which they are drawn through pipes for use.

Biogas is an excellent fuel as it contains up to 75% methane. It burns without smoke and leaves no residue like ash in wood, charcoal and coal burning. Its heating capacity is high. Biogas is also used for lighting. The slurry left behind is removed periodically and used as excellent manure, rich in nitrogen and phosphorous. The large-scale utilisation of bio-waste and sewage material provides a safe and efficient method of waste disposal besides supplying energy and manure.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 |
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Sources of Energy
While Chapter 14 is not so difficult compared to other chapters, we are offering free NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 here to help students understand all the topics covered in the chapter smoothly. The exemplars provide detailed answers to all the questions given at the end of the chapter, and our experts have also provided additional explanations for difficult topics. Students can use these exemplars to practise solving different types of questions and also to have a thorough revision before the examinations.
Topics Covered in NCERT Exemplar of Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- What Is a Good Source of Energy?
- Conventional Sources of Energy
- Fossil Fuels
- Thermal Power Plant
- Hydro Power Plants
- Improvements in Technology for Using Conventional Sources of Energy
- Alternative or Non-conventional Sources of Energy
- Solar Energy
- Energy From the Sea
- Geothermal Energy
- Nuclear Energy
- Environmental Consequences
- How Long Will an Energy Source Last Us?
BYJU’S provides you with CBSE notes, CBSE textbooks, sample papers and previous years’ question papers for the benefit of the students. At BYJU’S, students are provided with proper guidance, and their performance is assessed periodically through exercises, tests and assignments, which will help them excel in board exams. To get all the benefits we provide, download BYJU’S – The Learning App and experience a new way of learning.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14
What will I learn from Chapter 14 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science?
What Is a Good Source of Energy?
Conventional Sources of Energy
Fossil Fuels
Thermal Power Plant
Hydro Power Plants
Improvements in Technology for Using Conventional Sources of Energy
Alternative or Non-conventional Sources of Energy
Solar Energy
Energy From The Sea
Geothermal Energy
Nuclear Energy
Environmental Consequences
How Long Will an Energy Source Last Us?
What are the environmental consequences of using fossil fuels in Chapter 14 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science?
1. Global warming will result due to the increase in the level of carbon dioxide
2. Sulphur oxides cause acid rain
3. Burning of fossil fuels will result in the accumulation of smog in big cities, which will result in decreased visibility
4. Air pollution leads to health hazards for humans and animals
What are the limitations in obtaining energy from wind covered in Chapter 14 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science?
1. There will not be continuous and consistent production
2. Area required to install a windpower mill is large.
3 Minimum speed of the wind should be 15 km/hour.
Students of Class 10 can refer to the NCERT Solutions designed by the subject experts at BYJU’S to understand concepts easily. Simple and understandable language is used to explain complex topics to help students, irrespective of their understanding abilities.[FAQ_SCHEMA_END]










Comments