NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Free PDF Download
The NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds is an important study material for students to gain in-depth knowledge on the topics covered in CBSE Class 10 Chapter 4 syllabus. Studying this NCERT Exemplar will help you make your foundation strong, and you can easily understand the tough topics as well.
In Chapter 4 of NCERT Exemplar, students will learn everything about carbon and its significance in both the elemental form and a combined form. Furthermore, they will have to recall the versatile nature of carbon and study all its allotropes, discuss hydrocarbons and explain the nomenclature of carbon. They will also be learning about some interesting carbon compounds and their properties. While students have to cover a lot of topics, NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 4, given here, will act as the perfect study tool for them.
Students can take a closer look at the Class 10 Science Chapter 4 NCERT exemplar PDF below.
Download the PDF of the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds
Access Answers to the NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) carbon monoxide only
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) carbon dioxide only
(d) coal
Soln:
The answer is (c) carbon dioxide only
2. Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
(i) are good conductors of electricity
(ii) are poor conductors of electricity
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(iv) do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (d) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Carbon compounds form covalent bonds hence they have very weak force of attraction. Carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity.
3. A molecule of ammonia (NH3 ) has
(a) only single bonds
(b) only double bonds
(c) only triple bonds
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
Soln:
The answer is (a) only single bonds
Explanation:
Nitrogen has three electrons in its outermost shell and hydrogen has 1. 3 hydrogen atoms combine with 1 nitrogen atom to make ammonia. These bonds are single bonds.
4. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
Soln:
The answer is (c) carbon
Explanation:
Diamond, Graphite, Lonsdaleite, C60 (Buckminsterfullerene or buckyball), C540, C70, Amorphous carbon, and a single-walled carbon nanotube, or buckytube. Are the allotropes of Carbon.
5. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?

(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (c) (i) and (ii)
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Butane isC4H10, here option iii) and iv) have 8 hydrogen atoms, hence they are wrong.
6. CH3 – CH2 – OH Alkaline KMnO Heat 4 + → CH3 – COOH
In the above-given reaction, alkaline KMnO4 acts as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) dehydrating agent
Soln:
The answer is (b) oxidising agent
Explanation:
Two Hydrogen atoms are replaced by an atom of oxygen making oxidation of ethanol. Here addition of oxygen is provided by potassium.
7. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an example of
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Substitution reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Soln:
The answer is (a) Addition reaction
Explanation:
Here Hydrogen is added to oil, hence it is an addition reaction.
8. In which of the following compounds, — OH is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic acid
(d) Butanal
Soln:
The answer is (b) Butanol
Explanation:
Compound with OH Functional group will have a suffix ol in them hence answer is (b) Butanol.
9. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Soln:
Answer is (a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
Explanation:
Because of hydrophobic tail Oil and grease is trapped inside a micelle. Hydrophobic head makes the outer surface of micelle. Hence micelle is easily washed by water.
10. Which of the following is the correct representation of the electron dot structure of nitrogen?

Soln:
The answer is d)
Explanation:
In this structure Nitrogen atoms get 8 electrons whereas in other options it is different.
11. Structural formula of ethyne is

Solution:
The answer is a)
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Ethyne is C2H2, Hence answer is a)
12. Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following
(i) Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Soln:
The answer is (d) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
Propene has double bond and Propyne is having a triple bond. Hence they are unsaturated compounds.
13. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Soln:
The answer is (b) presence of sunlight
Explanation:
In the presence of sunlight, Chlorine reacts with Hydrocarbons and displaces Hydrogen atoms.
14. In the soap micelles
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
(b) ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(c) both ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster
(d) both ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster
Soln:
The answer is (a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
Explanation:
A micelle is a spherical aggregate soap molecules in soap solution. In the soap micelles, the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
15. Pentane has the molecular formula C5 H12. It has
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Soln:
The answer is (c) 16 covalent bonds
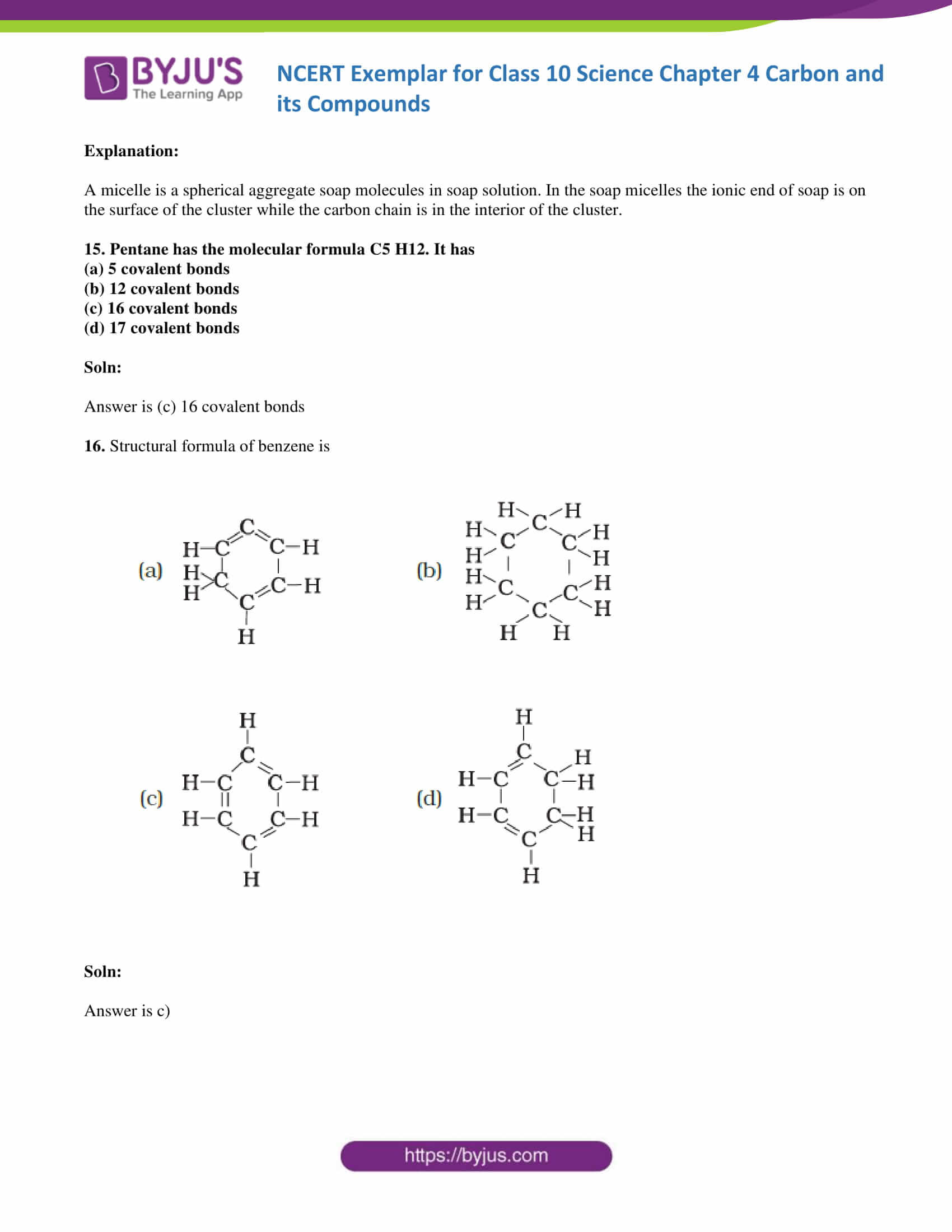
16. Structural formula of benzene is

Soln:
The answer is c)
Explanation:
Chemical formula of Benzene is C6H6. In option call the arms of carbon atoms are occupied hence it is the right answer.
17. Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Soln:
The answer is (c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
Explanation:
2Na+2CH3CH2OH →2CH3CH2ONa+H2
18. The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is

Soln:
The answer is d)
19. Vinegar is a solution of
(a) 50% – 60% acetic acid in alcohol
(b) 5% – 8% acetic acid in alcohol
(c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
(d) 50% – 60% acetic acid in water
Soln:
The answer is (c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
20. Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (a) (i) and (iv)
Explanation:
Mineral acids are completely ionized whereas carboxylic acids are partially ionized. Hence mineral acids are stronger than carboxylic acids.
21. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
(a) helium
(b) neon
(c) argon
(d) krypton
Soln:
The answer is (b) neon
Explanation:
After sharing four valence electrons with univalent atoms. Electronic configuration of Carbon becomes 2.8 which is same as the electronic configuration of Neon.
22. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is

Soln:
Answer is c)
Explanation:
Option c) represents a complete octet configuration. Hence it is the right answer.
23. Which of the following is not a straight-chain hydrocarbon?

Soln:
The answer is d)
24. Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?

(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (c) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Option (ii and (iv )having double and triple bonds, hence they are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
25. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2 H6
(c) C3 H8
(d) C4 H8
Soln:
The answer is (d) C4 H8
Explanation
General formula for C4H8 is CnH2n and for other option it is CnH2n+2
26. The name of the compound CH3 — CH2 — CHO is
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Soln:
The answer is (a) Propanal
Explanation:
This compound has 3 carbon atoms and an aldehyde which add suffix al to 3 carbon compound.
27. The heteroatoms present in CH3 — CH2 — O — CH2— CH2 Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (d) (i) and (iv)
Explanation:
Oxygen and chlorine are not among essential components of Hydrocarbon hence they are heteroatoms.
28. Which of the following represents the saponification reaction?
(a) CH3COONa + NaOH CH4 + Na2CO3
(b) CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH3 COOC2H5 +H2O
(c) 2CH3COOH + 2Na → 2CH3 COONa + H2
(d) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3 COONa + C2 H5OH
Soln:
The answer is (d) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3 COONa + C2 H5OH
Explanation:
Saponification is a reaction in which ethanol and sodium ethanoate are produced upon treatment of ester with an alkali.
29. The first member of the alkyne homologous series is
(a) ethyne
(b) ethene
(c) propyne
(d) methane
Soln:
The answer is (a) ethyne
Short Answer Questions
30. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula
Soln:
Molecular formula= C2H2
Electronic Formula

Structural formula= H-C≡C-H
31. Write the names of the following compounds

Soln:
- Pentanoic acid
- Butyne
- Heptanal
- Pentanol
32. Identify and name the functional groups present in the following compounds.

Soln:
- Alcohol
- Carboxylic acid
- Ketone
- Alkene
33. A compound X is formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid C2H4O2 and an alcohol in the presence of a few drops of H2SO4. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid as used in this reaction. Give the names and structures of (a) carboxylic acid, (b) alcohol and (c) the compound X. Also write the reaction.
Soln:
Carboxylic acid = CH3COOH ethanoic acid

Alcohol = CH3CH2OH ethanol

X = CH3COOCH2CH3 ethyl ethanoate

34. Why detergents are better cleansing agents than soaps? Explain.
Soln:
Detergents are better than soaps because detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. Charged ends of theses will not for precipitate with calcium and magnesium present in hard water. On the other hand, soaps will form a precipitate with calcium and magnesium ions present in the hard water.
35. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds
(a) CH3COCH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
(b) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(c) CH3CH2 CH2 CH2 CHO
(d) CH3CH2OH
Soln:
- Ketone
- Carboxylic acid
- Aldehyde
- Alcohol
36. How is ethene prepared from ethanol? Give the reaction involved in it.
Soln:
Ethanol is heated at 443k along with excess Sulphuric acid to obtain Ethene.
CH3-CH2OH ——->CH2=CH2 +H2O
(ethanol) (H2SO4) (ethene)
37. Intake of a small quantity of methanol can be lethal. Comment.
Soln:
Methanol gets converted to Methanal and liver and kills all the cells. Methanol also affects the optic nerves and causes blindness. Hence intake of a small quantity of methanol can be lethal.
38. A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Soln:
When ethanol reacts with sodium it gives Sodium ethoxide with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
2CH₃- CH₂-OH +2Na——>2 CH₃- CH₂- ONa + H₂
39. Ethene is formed when ethanol at 443 K is heated with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid. What is the role of sulphuric acid in this reaction? Write the balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Soln:
Sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst and a dehydrating agent in the formation of ethene.

40. Carbon, Group (14) element in the Periodic Table, is known to form compounds with many elements. Write an example of a compound formed with
(a) chlorine (Group 17 of Periodic Table)
(b) oxygen (Group 16 of Periodic Table)
Soln:
a)CCl4– Carbon Tetrachloride
b) Carbon-di-oxide- CO2
41. In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
(a) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. Write its electronic configuration
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule
Soln:
- KLM- 2,8,7

42. Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Soln:
Catenation is shown by both Silicon and Carbon. Silicon bonds are less stable and reactive whereas bonds formed by Carbon bonds are very strong hence carbon shows better catenation than Silicon.
43. Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain multiple bonds between the two C-atoms and show addition reactions. Give the test to distinguish ethane from ethene.
Soln:
Saturated Hydrocarbons burns with a clean flame and produce no soot whereas non-saturated Hydrocarbons burns with a yellow flame and produces a lot of soot. Ethane is saturated hydrocarbon and it burns with clean flame with no soot. Ethene is unsaturated hence it burns with yellow flame producing a lot of soot.
44. Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in column (B).
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) CH3OH + CH3COOH CH3COOCH3 + H2O | (i) Addition reaction |
| (b) CH2 = CH2 + H2 CH3 — CH3 | (ii) Substitution reaction |
| (c) CH4 + Cl2 Sunlight CH3Cl + HCl | (iii) Neutralisation reaction |
| (d) CH3COOH+NaOH CH3COONa+H2O | (iv) Esterification reaction |
Soln:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) CH3OH + CH3COOH CH3COOCH3 + H2O | (iv) Esterification reaction |
| (b) CH2 = CH2 + H2 CH3 — CH3 | (i) Addition reaction |
| (c) CH4 + Cl2 Sunlight CH3Cl + HCl | (ii) Substitution reaction |
| (d) CH3COOH+NaOH CH3COONa+H2O | (iii) Neutralisation reaction |
45. Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane.
Soln:

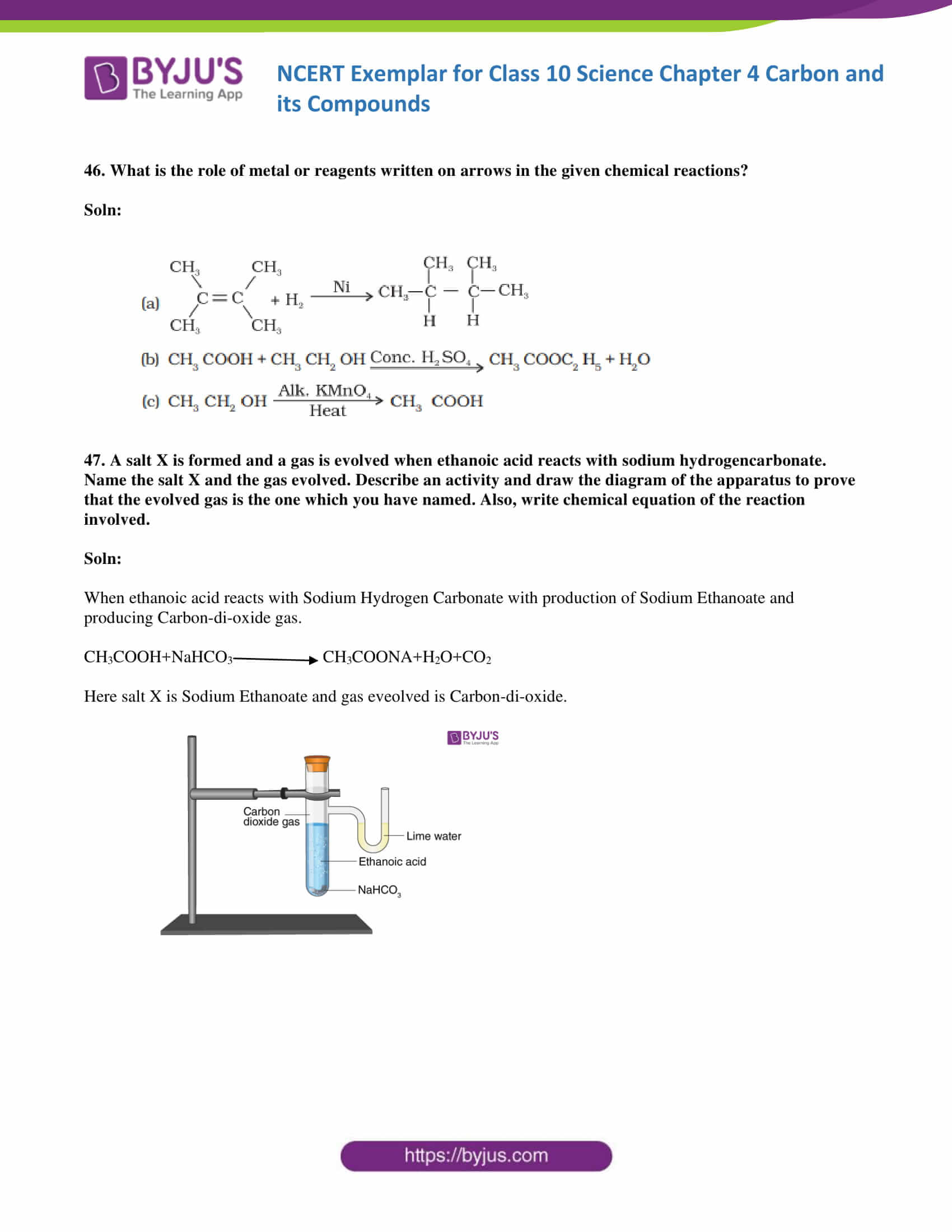
46. What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?
Soln:

47. A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also, write a chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Soln:
When ethanoic acid reacts with Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate with production of Sodium Ethanoate and producing Carbon-di-oxide gas.
CH3COOH+NaHCO3 → CH3COONA+H2O+CO2
Here salt X is Sodium Ethanoate and gas evolved is Carbon-di-oxide.

Activity
- Set up the experiment as shown in figure.
- Take a spoon full of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate in a test-tube and add 2ml of dilute ethanoic acid.
- Brisk effervescence occur in testtube.
- Pass the produced gas into lime water
- Lime water turns milky confirming the evolution of CO2
48. (a) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each. (c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Soln:
- Compounds of Carbon and hydrogen are called as Hydrocarbons. Ex: Ethane, Methane
- All the bond in saturated Hydrocarbons are single bonds whereas bonds in the unsaturated Hydrocarbons are either double or triple bonds.
Saturated Hydrocarbon Ex: Ethane, Methane
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons-Ethyne, Ethene
- Functional groups are a set of atoms joined in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristic chemical property of the compound. Ex: CHO-Aldehyde, OH-Hydroxyl, COOH- Carboxylic acid.
49. Name the reaction which is commonly used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction involved in detail.
Soln:
Addition reaction is involved in the conversion of oils into fats. This process is known as Hydrogenation. Here Unsaturated vegetable are converted to saturated fats which have saturated carbons.
Nickel is used as a catalyst in the hydrogenation process and the reaction is given below

50. (a) Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride.
(b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.
Soln:
- Carbon tetrachloride- CCl4

- The reaction of an ester in the presence of base to give sodium salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol is known as saponification and it is used in the preparation of soap.
CH3COOC2H5+NaOH CH3COONa+C2H5OH
51. Esters are sweet-smelling substances and are used in making perfumes. Suggest some activity and the reaction involved in the preparation of an ester with well-labelled diagram.
Soln:
In a test- tube take 1ml ethanol and 1 ml glacial acetic acid and add few drops of concentrated H2SO4. Warm the test tube for 5 minutes over a water bath. Transfer the content in a beaker. Sweet smell confirms the formation of Ester.

CH3COOH+ CH3CH2OH Acid CH3COCH2CH3
O
(Ester)
52. A compound C (molecular formula, C2H4O2 ) reacts with Na – metal to form a compound R and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound. Compound C on treatment with an alcohol A in presence of an acid forms a sweet-smelling compound S (molecular formula, C3H6O2 ). On addition of NaOH to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with NaOH solution gives back R and A. Identify C, R, A, S and write down the reactions involved.
Soln:
1)Compound C is Ethanoic acid[Acetic acid]
It reacts with sodium metal to form a compound called R.
R is Sodium Ethanoate.
2CH3COOH +2 Na →2CH3COONa+H2
(in the presence of Conc H2SO4)
2) CH3COOH +C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H20
so compound S is Ester or Ethyl ethanoate and compound A is Ethanol
3)CH3COOC2H5+NaoH →CH3COONa + C2H5OH.
so compound R is again Sodium Ethanoate.
So compound C is Ethanoic acid
A is Ethanol
S is Ester and R is sodium Ethanoate.
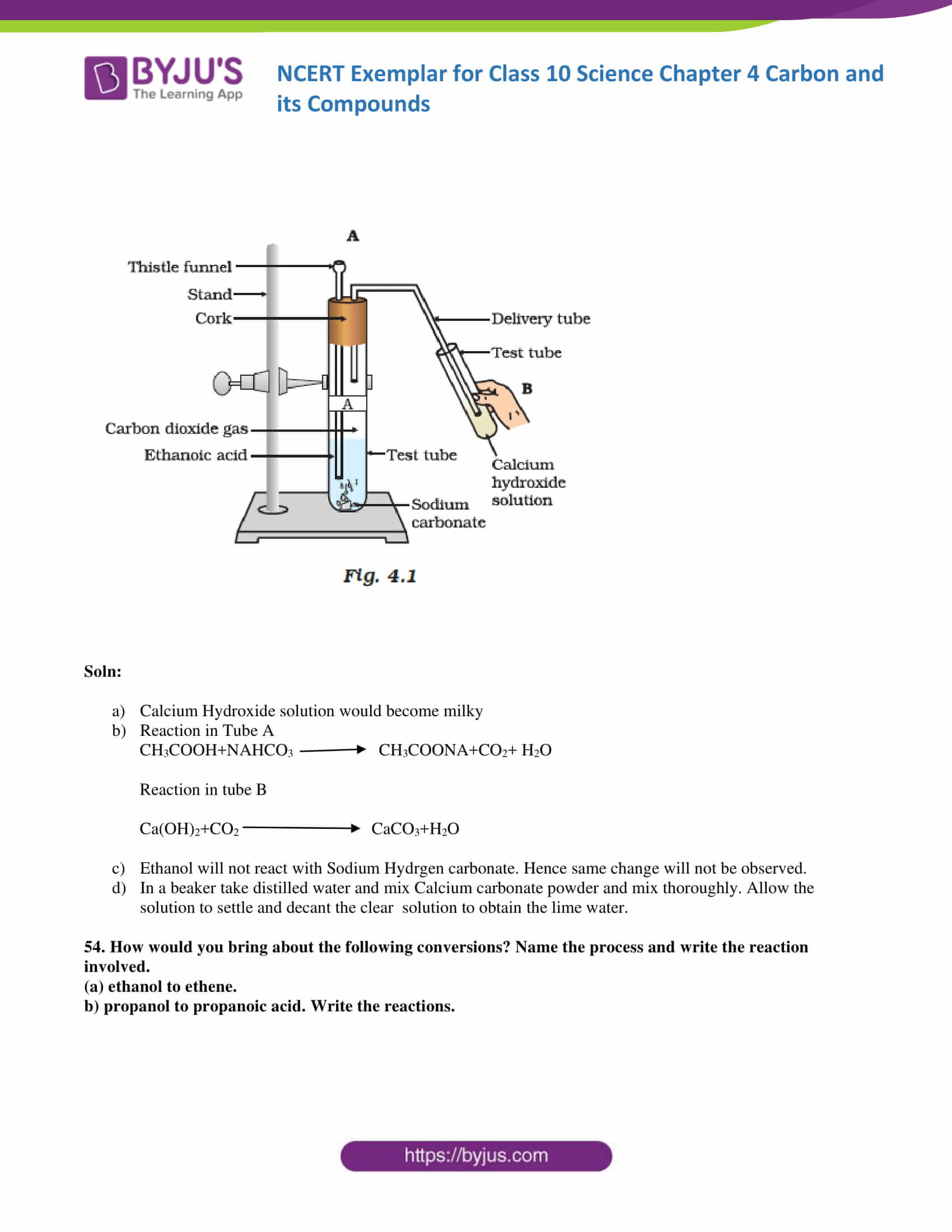
53. Look at Figure 4.1 and answer the following questions
(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B respectively.
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?

Soln:
- Calcium Hydroxide solution would become milky
- Reaction in Tube A
CH3COOH+NAHCO3 →CH3COONA+CO2+ H2O
Reaction in tube B
Ca(OH)2+CO2 CaCO3+H2O
- Ethanol will not react with Sodium Hydrogen carbonate. Hence same change will not be observed.
- In a beaker take distilled water and mix Calcium carbonate powder and mix thoroughly. Allow the solution to settle and decant the clear solution to obtain the lime water.
54. How would you bring about the following conversions? Name the process and write the reaction involved.
(a) ethanol to ethene.
b) propanol to propanoic acid. Write the reactions.
Soln:
- Ethene is formed when ethanol is heated at 443 K with an excess of concentrated sulphuric acid.
CH3CH2OH Con H2SO4 CH2=CH+H2O
- Propanol is treated with alkaline Potassium permanganate or acidified Potassium-di-chromate to obtain propanoic acid.
CH3CH2CH2OH Alk KMnO4/ acidified K2Cr2O7 CH3CH2COOH
55. Draw the possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and also give their electron dot structures.
Soln:


56. Explain the given reactions with the examples
(a) Hydrogenation reaction
(b) Oxidation reaction
(c) Substitution reaction
(d) Saponification reaction
(e) Combustion reaction
Soln:
(a) Hydrogenation reaction can be defined as an addition reaction between the hydrogen and other compounds in the presence of a catalyst.
CH2 = CH2 → CH3CH3
(b) An oxidation reaction is a reaction in which oxygen combines with an element or a compound. In other words, it can also be defined as a molecule loses its electrons.
2Mg + O2→ 2MgO
(c) Substitution reaction can be defined as the reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its aqueous salt solution.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
(d) Saponification reaction is the reaction in which the hydrolysis of an ester takes place with NaOH or KOH to give alcohol and sodium or potassium salt of the acid.
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → C2H5OH + CH3COONa
(e) Combustion reaction is the reaction in which oxygen combines with a compound to form carbon dioxide and water. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they give off heat.
CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2
57. An organic compound A on heating with concentrated H2 SO4 forms a compound B which on addition of one mole of hydrogen in presence of Ni forms a compound C. One mole of compound C on combustion forms two moles of CO2 and 3 moles of H2O. Identify the compounds A, B and C and write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Soln:
Compound A is Ethanol
Compound A = CH3CH2OH
CH3CH2OH (in the presence of conc. H2SO4) → CH2-CH2+ H2O
Compound B is Ethene
Compound B is CH2= CH2
CH2=CH2 (in the presence of Ni) →C2H6
Compound C = CH3 — CH3
2C2H6+7O2 4CO2 +6H2O
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 |
Class 10 Carbon and Its Compounds: Important Concepts to Study
These Exemplars are prepared by our subject experts, and when students go through them, they will be able to grasp topics and understand them clearly. Besides, students can even use the NCERT Exemplar to solve difficult questions while preparing effectively for the board exam.
- Bonding in Carbon- The Covalent Bond
- Versatile Nature of Carbon Ex
- Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
- Chains, Branches and Rings
- Will You Be My Friend? E
- Homologous Series
- Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Combustion
- Oxidation
- Addition Reaction
- Substitution Reaction
- Some Important Carbon Compounds – Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid
- Properties of Ethanol
- Properties of Ethanoic Acid
- Soaps and Detergents
Students studying in Class 10 are advised to follow good study materials. NCERT textbooks are one of the most preferred study materials for 10th standard students. Chemical reactions are a very important topic to study if learners are planning to take science in their undergraduate. Hence, they are advised to solve this NCERT Exemplar for a clear understanding of the topics and to clear all their doubts about chemical reactions.
Keep visiting BYJU’S website for the latest updates and notifications. At BYJU’S, we also provide NCERT notes, books, exemplar problems and chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Classes 6 to 12 for all subjects.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4
List the topics and sub-topics covered in Chapter 4 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science.
1. Bonding in Carbon – The Covalent Bond
2. Versatile Nature of Carbon Ex
a. Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
b. Chains, Branches and Rings
c. Will You Be My Friend?
d. Homologous Series
e. Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
3. Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
a. Combustion
b. Oxidation
c. Addition Reaction
d. Substitution Reaction
4. Some Important Carbon Compounds – Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid
a. Properties of Ethanol
b. Properties of Ethanoic Acid
5. Soaps and Detergents
What is the covalent bond explained in Chapter 4 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science?
Where can I find NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 online?
Also, Read





















Comments