Man has been exposed to changing surroundings ever since he came into existence. He has been quite interested in learning about his surroundings and studying and explaining the things that are happening around him. He has conducted experiments and observations to gather information as a result of his interest. Through the decades, it has also been in charge of many people’s research endeavours around the globe. Systematizing and organising the knowledge acquired in this way was absolutely necessary for the good of humanity.
Science is the name given to this knowledge. So, systematised knowledge that humans have acquired through observations and experimentation may be referred to as science. Due to its vast expansion and variety of subjects, science has been further divided into many branches.
One of the most significant fields of science is chemistry. Chemistry can be summed up as the area of science that studies matter, including its properties, composition, and the changes that occur to it as a result of various activities. Several branches of chemistry have been created based on the specialised disciplines of research.
Table of Content
IntroductionBranches of ChemistryExamples in Daily LifeFree Study MaterialCBSE Chemistry ResourcesFAQs
What is Chemistry?
Chemistry is a subdiscipline of science that deals with the study of matter and the substances that constitute it. It also deals with the properties of these substances and the reactions undergone by them to form new substances. Chemistry primarily focuses on atoms, ions, and molecules which, in turn, make up elements and compounds. These chemical species tend to interact with each other through chemical bonds. It is important to note that the interactions between matter and energy are also studied in the field of chemistry.
The study of elements and compounds’ properties, compositions, and structures, as well as how they can change and the energy that is released or absorbed during such changes, is the subject matter of the science known as chemistry.
Learn more on Interactive Periodic Table
Relationship Between Chemistry and Other Branches of Science
‘Science’ can be defined as the systematic study of the natural universe, its structure, and everything it encompasses. Due to the immensity of the natural universe, science has been divided into several disciplines that deal with certain aspects of the universe. The three primary subcategories of science under which these disciplines can be grouped are:
- The Formal Sciences: Involves the study of the language disciplines that concern formal systems. Examples of scientific disciplines that fall under this category include logic and mathematics. Can be thought of as the “language of science”.
- The Natural Sciences: Involves the study of natural phenomena through experiments and observations. Chemistry, physics, and biology fall under this category of science.
- The Social Sciences: Involves the study of human societies and the relationships between the humans that dwell in these societies. Examples of scientific disciplines that fall under this category include psychology, sociology, and economics.
When the relationships between the major branches of science are considered, chemistry is found to lie close to the centre (as illustrated below).
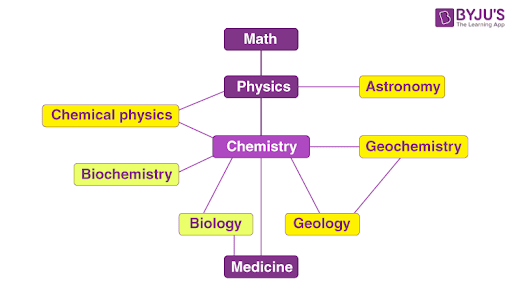
Thus, chemistry can be viewed as a central science whose roots bore into several other subdisciplines of science.
Branches of Chemistry
The five primary branches of chemistry are physical chemistry, organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and biochemistry. Follow the buttons provided below to learn more about each individual branch.
Apart from these primary branches, there exist several specialized fields of chemistry that deal with cross-disciplinary matters. Some such examples include medicinal chemistry, neurochemistry, materials chemistry, nuclear chemistry, environmental chemistry, polymer chemistry, and thermochemistry.
Examples of Chemistry in Our Daily Lives
Chemical reactions are constantly taking place around us. The human body facilitates thousands of chemical reactions every day. From the digestion of food to the movement of muscles – all bodily actions involve chemical reactions. A few other examples of chemistry in the day-to-day lives of humans are listed below.
- The process of photosynthesis that enables plants to convert water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen is a chemical reaction. This process is the foundation upon which the entire food chain is built.
- Soaps and detergents used for hygiene work use a chemical process known as emulsification. Furthermore, they are produced using a chemical process known as saponification.
- Even the sunscreen used by humans to protect themselves from the harmful UV-A and UV-B radiation of the sun is based on chemistry. These lotions and creams consist of a combination of inorganic and organic compounds that either filter or block the incoming ultraviolet radiation.
Follow the link to learn more about the importance of chemistry in everyday life.
Free Chemistry Study Material
The BYJU’S chemistry section hosts over 1500 chemistry articles for students to use as free study resources. Links to each of these articles have been sorted under their parent concepts and can be found in the collapsible tables provided below.
Chemistry Resources for CBSE Students
| Chemistry Important Questions: |
| Chemistry MCQs |
| Chemistry Practicals |
| Chemistry Worksheets |
| Chemistry NCERT Solutions: |
| Chemistry Syllabus: |
| NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry: |
| NCERT Books for Chemistry: |
| CBSE Chemistry Notes: |
| CBSE Sample Papers for Chemistry: |
Balancing a Chemical Equation

Chemical Reactions and Equations

The Modern Periodic Table

Hydrocarbons

Frequently Asked Questions on Chemistry
What Is the Periodic Table?
The periodic table of chemical elements, often called the periodic table, organizes all discovered chemical elements in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) according to increasing atomic number. In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev created the framework that became the modern periodic table, leaving gaps for elements that were yet to be discovered.
“Sulphuric acid” is called the king of acids and “Nitric acid” is called the Queen of acids.
What are the 3 laws of gas?
Boyle’s Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles’ Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases. And Avogadro’s Law tell us that the volume of gas increases as the amount of gas increases.
“Sulphuric acid” is called the king of acids and “Nitric acid” is called the Queen of acids.
What is a chemical change? Is cooking an egg a chemical change?
There are changes all around us like sugar dissolves in water, the lake freezes in winter etc. Some changes are what scientists call chemical changes and some are not. A chemical change takes place when new substances are made that are different from the substances that we started with.
Yes Cooking eggs, for instance, is an example of a chemical change; the egg white and egg yolk change from liquid to solid. The heat makes the proteins in the egg hardens.
Which acid is called “Kingly Water” and why?
Aqua Regia is the King’s Water, this is because it is strong enough to dissolve gold – the king of metals. It is prepared by mixing three parts of hydrochloric acid with one part nitric acid but in olden days it is prepared to mix and distill salts. For example, we can mix two parts niter with one part Sal. Ammoniac and distill at a high temperature to form Aqua Regia.
“Sulphuric acid” is called the king of acids and “Nitric acid” is called the Queen of acids.
What are the main branches of chemistry?
Chemistry is the science that studies atoms and molecules along with their properties. All matter is composed of atoms and molecules. There are 5 main branches of chemistry are
- Organic chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Analytical chemistry
What is the importance of organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry is simply the study of carbon compounds. Organic chemistry is important because it is life studies and all life-related chemical reactions. Organic chemistry initially involves the study of compounds that could be obtained from living organisms.
Approximately 7 million different organic compounds are known present while there are only 1.5 million known inorganic compounds. This large number of organic compounds arise from the unique property of carbon.
Which compound is known as “Blue Vitriol”?
Blue vitriol is also known as blue copperas. The word blue vitriol has a strict and definite meaning. It means sulphate of copper with the chemical formula CuSO4.5H2O. The chemical name for blue vitriol is Copper (II) Sulphate Pentahydrate. This salt occurs in the form of rhomboidal prisms of a deep blue colour, having an exceedingly harsh and styptic taste.
Similarly, “Green Vitriol” refers to Ferrous Sulphate.






